Chemistry:Gold(I) cyanide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Gold monocyanide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CAuN | |
| Molar mass | 222.985 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark yellow powder[1] |
| Density | 7.12 g·cm−3[2] |
| insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| hexagonal | |
| P6mm (No. 183) | |
a = 340 pm, c = 509 pm[2]
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H300, H310, H330, H410 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Copper(I) cyanide Silver cyanide |
Related compounds
|
Gold(III) cyanide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Gold(I) cyanide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula AuCN. It is the binary cyanide of gold(I). It is an odourless, tasteless yellow solid.[4] Wet gold(I) cyanide is unstable to light and will become greenish.[4] Gold(I) cyanide itself is only of academic interest, but its derivative dicyanoaurate is an intermediate in gold cyanidation, the extraction of gold from its ores.[5]
Preparation
Solid gold(I) cyanide precipitates upon reaction of potassium dicyanoaurate with hydrochloric acid:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{K[Au(CN)_2] + HCl \longrightarrow AuCN + HCN + KCl} }[/math]
It can also be produced by the reaction of gold(III) chloride and potassium cyanide.[2]
Reactions
The solid dissolves to form water-soluble adducts with a variety of ligands: cyanides, hydroxide, ammonia, thiosulfate and hydrosulfide.[2]
Like most gold compounds, it converts to metallic gold upon heating.[citation needed]
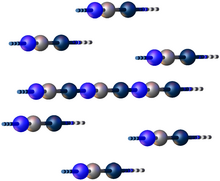
Structure
Gold(I) cyanide's is a coordination polymer consisting of linear chains of AuCN such that each Au(I) center is bonded to carbon and nitrogen. The structure is hexagonal with the lattice parameters a = 3.40 Å and c = 5.09 Å.[2] T[6]
References
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich Co., product no. 254088.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 O. Glemser; O. Glemser, H. Sauer (1963). "Gold(I) Cyanide". in G. Brauer. Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed.. 2pages=1064. NY, NY: Academic Press.
- ↑ "C&L Inventory". https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/73934.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Meyers Konversations-Lexikon, 1888: Goldcyanid
- ↑ Rubo, Andreas; Kellens, Raf; Reddy, Jay; Steier, Norbert; Hasenpusch, Wolfgang (2006). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.i01_i01.
- ↑ Bowmaker, Graham A.; Kennedy, Brendan J.; Reid, Jason C. (1998). "Crystal Structures of AuCN and AgCN and Vibrational Spectroscopic Studies of AuCN, AgCN, and CuCN". Inorganic Chemistry 37 (16): 3968–3974. doi:10.1021/ic9714697. PMID 11670511.
 |

