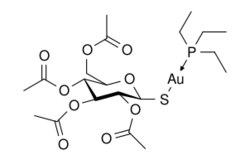
Chemistry:Auranofin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ridaura |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a685038 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40%[1][2] |
| Protein binding | 60%[1][2] |
| Metabolism | Plasma membrane of the cell removes the acetyl groups of the glucose moiety. |
| Elimination half-life | 21-31 days[1][2] |
| Excretion | Urine (60%), faeces[1][2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H34AuO9PS0 |
| Molar mass | 678.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Auranofin is a gold salt classified by the World Health Organization as an antirheumatic agent. It has the brand name Ridaura.
Use
Auranofin is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. It improves arthritis symptoms including painful or tender and swollen joints and morning stiffness.[3] Auranofin is a safer treatment compared to the more common injectable gold thiolates (gold sodium thiomalate and gold thioglucose), but meta-analysis of 66 clinical trials concluded that it is somewhat less effective.[4]
The drug was approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in 1985. No longer a first-line treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, due to its adverse effects, "most of which are associated with long-term use for chronic disease. The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal complaints such as loose stools, abdominal cramping and watery diarrhea, which can develop in the early months of treatment. The development of loose stools occurs in 40 % of patients, while watery diarrhea is reported in just 2–5 % of patients, and in most cases these symptoms were alleviated by reducing or splitting the dose".[5]
Research
HIV infection
Auranofin is under investigation as a means of reducing the viral reservoir of HIV that lies latent in the body's T-cells despite treatment with antiretroviral therapy.[6] The drug was shown to reduce the amount of latent virus in monkey trials.[7] A human study testing auranofin and other investigational treatments is ongoing in Brazil.[8] Preliminary results show that auranofin contributed to a decrease in the viral reservoir.[9]
Amebiasis
Auranofin has been identified in a high-throughput drug screen as 10 times more potent than metronidazole against Entamoeba histolytica, the protozoan agent of human amebiasis. Assays of thioredoxin reductase and transcriptional profiling suggest that the effect of auranofin on the enzyme enhances the sensitivity of the trophozoites to reactive oxygen-mediated killing in mouse and hamster models; the results are marked reductions of the number of parasites, the inflammatory reaction to the infestation, and the damage to the liver.[10][11][12]
Acanthamoeba Keratitis and Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
Auranofin may be useful in the prevention and control of Acanthamoeba infections, and in the treatment of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, caused by pathogenic free-living amoebae Acanthamoeba spp. and Naegleria fowleri, respectively.[13][14]
Tuberculosis
In a cell-based screen, auranofin showed potent activity against replicating and non-replicating M. tuberculosis as well as other gram-positive bacteria. Auranofin protected mice from an otherwise lethal infection with methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The drug acts in a similar manner in bacteria as in parasites by inhibiting thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). Studies in humans are needed to evaluate the potential of this drug to treat Gram-positive bacterial infections in humans.[15]
Ovarian cancer
Drug-screening reveals auranofin induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells in vitro.[16][17]
Lung cancer including Adenocarcinoma
When mice with Protein kinase Cι (PKCι)–dependent KP adenocarcinoma tumors that exhibited resistance to anti–PD-1 antibody therapy (α-PD-1) were treated with auranofin, the PKCι inhibitor auranofin inhibited KP tumor growth and sensitized these tumors to α-PD-1. [18] The Mayo clinic is running a clinical trial to research the effects of auranofin and sirolimus on squamous, ras mutated lung adenocarcinoma, and small cell lung cancer. [19]
COVID-19
Auranofin may inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for causing COVID-19 in cell culture. Inflammation may also be reduced.[20]
Etymology
The brand name Ridaura was coined from the phrase Remission-Inducing Drug + Auranofin. [21]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Auranofin". British Journal of Rheumatology 36 (5): 560–572. May 1997. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/36.5.560. PMID 9189058.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Ridaura (auranofin) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. http://reference.medscape.com/drug/ridaura-auranofin-343186#showall.
- ↑ MedlinePlus DrugInfo medmaster-a685038
- ↑ "The comparative efficacy and toxicity of second-line drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Results of two metaanalyses". Arthritis and Rheumatism 33 (10): 1449–1461. October 1990. doi:10.1002/art.1780331001. PMID 1977391.
- ↑ "Auranofin: repurposing an old drug for a golden new age". Drugs in R&D 15 (1): 13–20. March 2015. doi:10.1007/s40268-015-0083-y. PMID 25698589.
- ↑ Gold-based drug shows promise in clearing HIV reservoir in monkey study. Keith Alcorn. AIDSmaps.com. Accessed 23 April 2011.
- ↑ "Gold drug auranofin restricts the viral reservoir in the monkey AIDS model and induces containment of viral load following ART suspension" (in en-US). AIDS 25 (11): 1347–1356. July 2011. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328347bd77. PMID 21505294.
- ↑ "Multi Interventional Study Exploring HIV-1 Residual Replication: a Step Towards HIV-1 Eradication and Sterilizing Cure - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov" (in en). https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02961829.
- ↑ "Auranofin plus nicotinamide impact HIV reservoir among ART suppressed HIV individuals" (in en) (MS Power Point). https://programme.aids2018.org/PAGMaterial/PPT/4795_6436/AIDS2018_template%20rd%202.pptx.
- ↑ "A high-throughput drug screen for Entamoeba histolytica identifies a new lead and target". Nature Medicine 18 (6): 956–960. June 2012. doi:10.1038/nm.2758. PMID 22610278.
- ↑ "Drug Found for Parasite That Is Major Cause of Death Worldwide". Science Daily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120520133508.htm.
- ↑ "Arthritis Drug Effective Against Global Parasite, Study Suggests". Science Daily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120520133503.htm.
- ↑ "Antimicrobial effect of auranofin against Acanthamoeba spp". International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 58 (5): 106425. November 2021. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106425. PMID 34419578.
- ↑ "Antiparasitic Activity of Auranofin against Pathogenic Naegleria fowleri". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 66 (4): 684–688. July 2019. doi:10.1111/jeu.12706. PMID 30520183.
- ↑ "Auranofin exerts broad-spectrum bactericidal activities by targeting thiol-redox homeostasis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112 (14): 4453–4458. April 2015. doi:10.1073/pnas.1504022112. PMID 25831516. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..112.4453H.
- ↑ "Auranofin displays anticancer activity against ovarian cancer cells through FOXO3 activation independent of p53". International Journal of Oncology 45 (4): 1691–1698. October 2014. doi:10.3892/ijo.2014.2579. PMID 25096914.
- ↑ "BRCA1 deficiency increases the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to auranofin". Mutation Research 784-785: 8–15. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.11.002. PMID 26731315.
- ↑ "Protein kinase Cι mediates immunosuppression in lung adenocarcinoma". Science Translational Medicine 14 (671): eabq5931. November 2022. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abq5931. PMID 36383684.
- ↑ "PKCι & mTOR Inhibition With Auranofin+Sirolimus for Squamous Cell Lung Cancer". https://www.mayo.edu/research/clinical-trials/cls-20115754.
- ↑ "Georgia State Researchers Find Rheumatoid Arthritis Drug Is Effective Against Coronavirus". 15 April 2020. https://news.gsu.edu/2020/04/15/georgia-state-researchers-find-rheumatoid-arthritis-drug-is-effective-against-coronavirus/.
- ↑ (in fr) La chaîne des médicaments: Perspectives pluridisciplinaires. PUQ Presse de l'Université du Québec. 2007. ISBN 978-2760519510. https://books.google.com/books?id=-fQNfIyHi4wC&dq=Auranofine&pg=PA298.
Further reading
- "Gold compound auranofin inhibits IkappaB kinase (IKK) by modifying Cys-179 of IKKbeta subunit". Experimental & Molecular Medicine 35 (2): 61–66. April 2003. doi:10.1038/emm.2003.9. PMID 12754408.
- "Auranofin induces apoptosis and when combined with retinoic acid enhances differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells in vitro". British Journal of Pharmacology 142 (4): 749–755. June 2004. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705708. PMID 15159275.
- "Auranofin increases apoptosis and ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat isolated heart". Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 31 (5–6): 289–294. 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2004.03993.x. PMID 15191400.
- "Jessner's lymphocytic infiltrate responding to oral auranofin". The Journal of Dermatological Treatment 15 (5): 331–332. September 2004. doi:10.1080/09546630410016924. PMID 15370403.
- "Effect of auranofin on the mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role of thioredoxin reductase". Free Radical Research 39 (7): 687–695. July 2005. doi:10.1080/10715760500135391. PMID 16036347.
- "Auranofin versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000 (2): CD002048. 2000. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002048. PMID 10796461.
External links
 |
