Generalizations of Fibonacci numbers
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers form a sequence defined recursively by:
That is, after two starting values, each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers.
The Fibonacci sequence has been studied extensively and generalized in many ways, for example, by starting with other numbers than 0 and 1, by adding more than two numbers to generate the next number, or by adding objects other than numbers.
Extension to negative integers
Using , one can extend the Fibonacci numbers to negative integers. So we get:
- ... −8, 5, −3, 2, −1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, ...
and . [1]
See also Negafibonacci coding.
Extension to all real or complex numbers
There are a number of possible generalizations of the Fibonacci numbers which include the real numbers (and sometimes the complex numbers) in their domain. These each involve the golden ratio φ, and are based on Binet's formula
- .
has the property that for even integers .[2] Similarly, the analytic function:
satisfies for odd integers .
Finally, putting these together, the analytic function
satisfies for all integers .[3]
Since for all complex numbers , this function also provides an extension of the Fibonacci sequence to the entire complex plane. Hence we can calculate the generalized Fibonacci function of a complex variable, for example,
However, this extension is by no means unique. For example, either
- or
for any odd integer k is an extension of the Fibonacci number sequence to the entire complex plane, as is any linear combination of them for which the coefficients sum to 1.
Vector space
The term Fibonacci sequence is also applied more generally to any function from the integers to a field for which . These functions are precisely those of the form , so the Fibonacci sequences form a vector space with the functions and as a basis.
More generally, the range of may be taken to be any abelian group (regarded as a Z-module). Then the Fibonacci sequences form a 2-dimensional Z-module in the same way.
Similar integer sequences
Fibonacci integer sequences
The 2-dimensional -module of Fibonacci integer sequences consists of all integer sequences satisfying . Expressed in terms of two initial values we have:
where is the golden ratio.
The ratio between two consecutive elements converges to the golden ratio, except in the case of the sequence which is constantly zero and the sequences where the ratio of the two first terms is .
The sequence can be written in the form
in which if and only if . In this form the simplest non-trivial example has , which is the sequence of Lucas numbers:
- .
We have and . The properties include:
Every nontrivial Fibonacci integer sequence appears (possibly after a shift by a finite number of positions) as one of the rows of the Wythoff array. The Fibonacci sequence itself is the first row, and a shift of the Lucas sequence is the second row.[4]
See also Fibonacci integer sequences modulo n.
Lucas sequences
A different generalization of the Fibonacci sequence is the Lucas sequences of the kind defined as follows:
where the normal Fibonacci sequence is the special case of and . Another kind of Lucas sequence begins with , . Such sequences have applications in number theory and primality proving.
When , this sequence is called P-Fibonacci sequence, for example, Pell sequence is also called 2-Fibonacci sequence.
The 3-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 3, 10, 33, 109, 360, 1189, 3927, 12970, 42837, 141481, 467280, 1543321, 5097243, 16835050, 55602393, 183642229, 606529080, ... (sequence A006190 in the OEIS)
The 4-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 4, 17, 72, 305, 1292, 5473, 23184, 98209, 416020, 1762289, 7465176, 31622993, 133957148, 567451585, 2403763488, ... (sequence A001076 in the OEIS)
The 5-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 5, 26, 135, 701, 3640, 18901, 98145, 509626, 2646275, 13741001, 71351280, 370497401, 1923838285, 9989688826, ... (sequence A052918 in the OEIS)
The 6-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 6, 37, 228, 1405, 8658, 53353, 328776, 2026009, 12484830, 76934989, 474094764, 2921503573, 18003116202, ... (sequence A005668 in the OEIS)
The n-Fibonacci constant is the ratio toward which adjacent -Fibonacci numbers tend; it is also called the nth metallic mean, and it is the only positive root of . For example, the case of is , or the golden ratio, and the case of is , or the silver ratio. Generally, the case of is . Generally, can be called (P,−Q)-Fibonacci sequence, and V(n) can be called (P,−Q)-Lucas sequence.
The (1,2)-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 1, 3, 5, 11, 21, 43, 85, 171, 341, 683, 1365, 2731, 5461, 10923, 21845, 43691, 87381, 174763, 349525, 699051, 1398101, 2796203, 5592405, 11184811, 22369621, 44739243, 89478485, ... (sequence A001045 in the OEIS)
The (1,3)-Fibonacci sequence is
- 1, 1, 4, 7, 19, 40, 97, 217, 508, 1159, 2683, 6160, 14209, 32689, 75316, 173383, 399331, 919480, 2117473, 4875913, 11228332, 25856071, 59541067, ... (sequence A006130 in the OEIS)
The (2,2)-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 2, 6, 16, 44, 120, 328, 896, 2448, 6688, 18272, 49920, 136384, 372608, 1017984, 2781184, 7598336, 20759040, 56714752, ... (sequence A002605 in the OEIS)
The (3,3)-Fibonacci sequence is
- 0, 1, 3, 12, 45, 171, 648, 2457, 9315, 35316, 133893, 507627, 1924560, 7296561, 27663363, 104879772, 397629405, 1507527531, 5715470808, ... (sequence A030195 in the OEIS)
Fibonacci numbers of higher order
A Fibonacci sequence of order n is an integer sequence in which each sequence element is the sum of the previous elements (with the exception of the first elements in the sequence). The usual Fibonacci numbers are a Fibonacci sequence of order 2. The cases and have been thoroughly investigated. The number of compositions of nonnegative integers into parts that are at most is a Fibonacci sequence of order . The sequence of the number of strings of 0s and 1s of length that contain at most consecutive 0s is also a Fibonacci sequence of order .
These sequences, their limiting ratios, and the limit of these limiting ratios, were investigated by Mark Barr in 1913. [5]: 101
Tribonacci numbers
A variation of the Fibonacci number sequence is the tribonacci number sequence, where each number is the sum of the three preceding numbers. Starting with the initial values , and , the recurrence gives this sequence of numbers as
Further terms can be found under sequence number A000073 in The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS).
The tribonacci sequence has a long and interesting history.[6] The most notable historical occurrence of the sequence is connected to Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and his seminal book On the Origin of Species, where the procreation and population growth of elephants is considered as an illustrative example.[7] In 1892, the sequence of numbers appeared in the solution of a recreational problem, concerning a farmer and the raising of sheep, that was posed by the American mathematician Artemas Martin (1835–1918).[8]: 107–108 The first mathematical treatment of the tribonacci sequence and an investigation of its properties was done in 1914 and is due to Agronomof.[9] The moniker tribonacci appeared much later, not until 1963, and is due to Mark Feinberg, at the time a fourteen-year-old high-school student, who introduced the term in an article in the Fibonacci Quarterly.[10]
Agronomof's identity. Agronomof's 1914 note is a small gem that was ignored, made no impact at the time, and gathered dust for over half a century.[6]: 709-710 Although a very brief note (the modern day replica easily fits on a single page[6]: 719 ), it contains the powerful identity Note that Agronomof's identity is symmetric in and , and that, for , one recovers the original tribonacci recurrence. Agronomof made his derivation under the assumption that both parameters and are nonnegative integers. However, one can show that the identity is more general and actually holds for arbitrary integers and by extending the defining recurrence (1) to include tribonacci numbers with negative indices.[6]: 712 Agronomof ends his note by showcasing the following propriétés remarquables of the tribonacci numbers, These are easily derived from his identity by taking and . In turn, these two identities can be leveraged to derive a simple expression for the sum of squares of the tribonacci numbers.[6]: Eqn. (9)
Reflection formula. As with the Fibonacci numbers, one can run the recurrence for the tribonacci numbers backwards. From , and , one can determine . From , and , one can determine , and so on. Thus, the values for the tribonacci numbers at negative indices are well defined. Starting with , , and , and reversing the tribonacci recurrence (1), gives the sequence of negatively indexed tribonacci numbers as
Further terms can be found under sequence number A057597 in The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS). The extension to negative indices means that one can view the tribonacci sequence as a double infinite sequence:
where the value at index zero is given in bold. Traversing the sequence from left to right, one uses recurrence (1). Traversing the sequence from right to left, one uses the recurrence . The relationship between the negative and positive indexed segments of the tribonacci sequence is given by This identity holds for all integers , and is known as the reflection formula for the tribonacci numbers. It can be derived using Agronomof's identity.[6]: 714
The tribonacci constant
is the ratio toward which adjacent tribonacci numbers tend. It is the unique real root of the polynomial , approximately 1.839286755214161... (sequence A058265 in the OEIS), and also satisfies the equation . It is important in the study of the snub cube.
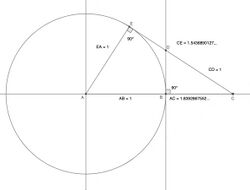
The reciprocal of the tribonacci constant, expressed by the relation , can be written as: approximately 0.543689012692076... (sequence A192918 in the OEIS).
The tribonacci numbers are also given by[11]
where denotes the nearest integer function and
Corresponding to the Lucas numbers for the Fibonacci sequence, if one instead starts with , , and and applies the tribonacci recursion then whenever (sequence A001644 in the OEIS)
Tetranacci numbers
The tetranacci numbers start with four predetermined terms, each term afterwards being the sum of the preceding four terms. The first few tetranacci numbers are:
- 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 15, 29, 56, 108, 208, 401, 773, 1490, 2872, 5536, 10671, 20569, 39648, 76424, 147312, 283953, 547337, … (sequence A000078 in the OEIS)
Feinberg also coined the term tetranacci.[10]: 73
The tetranacci constant is the ratio toward which adjacent tetranacci numbers tend. It is the unique positive real root of the polynomial , approximately 1.927561975482925... (sequence A086088 in the OEIS), and also satisfies the equation .
The tetranacci constant can be expressed in terms of radicals by the following expression: [12]
where,
and is the real root of the cubic equation .
Corresponding to the Lucas numbers for the Fibonacci sequence, if one instead starts with , , , and and applies the tetranacci recursion then whenever (sequence A073817 in the OEIS)
Higher orders
Pentanacci, hexanacci, heptanacci, octanacci and enneanacci numbers have been computed.
Pentanacci numbers:
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 31, 61, 120, 236, 464, 912, 1793, 3525, 6930, 13624, … (sequence A001591 in the OEIS)
The pentanacci constant is the ratio toward which adjacent pentanacci numbers tend. It is the unique real root of the polynomial , approximately 1.965948236645485... (sequence A103814 in the OEIS), and also satisfies the equation .
Hexanacci numbers:
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 63, 125, 248, 492, 976, 1936, 3840, 7617, 15109, … (sequence A001592 in the OEIS)
The hexanacci constant is the ratio toward which adjacent hexanacci numbers tend. It is the unique positive real root of the polynomial , approximately 1.983582843424326... (sequence A118427 in the OEIS), and also satisfies the equation .
Heptanacci numbers:
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 127, 253, 504, 1004, 2000, 3984, 7936, 15808, … (sequence A122189 in the OEIS)
The heptanacci constant is the ratio toward which adjacent heptanacci numbers tend. It is the unique real root of the polynomial , approximately 1.991964196605035... (sequence A118428 in the OEIS), and also satisfies the equation .
Octanacci numbers:
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 255, 509, 1016, 2028, 4048, 8080, 16128, ... (sequence A079262 in the OEIS)
Enneanacci numbers:
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 511, 1021, 2040, 4076, 8144, 16272, ... (sequence A104144 in the OEIS)
An "infinacci" sequence, if one could be described, would, after an infinite number of zeroes, yield the sequence
- [..., 0, 0, 1,] 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, …
which are simply the powers of two.
The limit of the ratio of successive terms of an -nacci series tends to a root of the equation (OEIS: A103814, OEIS: A118427, OEIS: A118428).
The limit of the ratio for any is the unique positive root of the characteristic equation[12]
- .
The special case is the traditional Fibonacci series yielding the golden section .
The above formulas for the ratio hold even for -nacci series generated from arbitrary starting numbers. The ratio approaches 2 in the limit that increases to infinity.
The root is in the interval . The negative root of the characteristic equation is in the interval (−1, 0) when is even. This root and each complex root of the characteristic equation has modulus .[12]
A series for the positive root for any is[12]
- .
There is no solution of the characteristic equation in terms of radicals when 5 ≤ n ≤ 11.[12]
The kth element of the n-nacci sequence is given by
where denotes the nearest integer function and is the -nacci constant, which is the root of nearest to 2.
A coin-tossing problem is related to the -nacci sequence. The probability that no consecutive tails will occur in tosses of an idealized coin is .[13]
Fibonacci word
In analogy to its numerical counterpart, the Fibonacci word is defined by:
where denotes the concatenation of two strings. The sequence of Fibonacci strings starts:
The length of each Fibonacci string is a Fibonacci number, and similarly there exists a corresponding Fibonacci string for each Fibonacci number.
Fibonacci strings appear as inputs for the worst case in some computer algorithms.
If "a" and "b" represent two different materials or atomic bond lengths, the structure corresponding to a Fibonacci string is a Fibonacci quasicrystal, an aperiodic quasicrystal structure with unusual spectral properties.
Convolved Fibonacci sequences
A convolved Fibonacci sequence is obtained applying a convolution operation to the Fibonacci sequence one or more times. Specifically, define [14]
and
The first few sequences are
- : 0, 0, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 38, 71, … (sequence A001629 in the OEIS).
- : 0, 0, 0, 1, 3, 9, 22, 51, 111, … (sequence A001628 in the OEIS).
- : 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 4, 14, 40, 105, … (sequence A001872 in the OEIS).
The sequences can be calculated using the recurrence
The generating function of the th convolution is
- .
The sequences are related to the sequence of Fibonacci polynomials by the relation
where is the th derivative of . Equivalently, is the coefficient of when is expanded in powers of .
The first convolution, can be written in terms of the Fibonacci and Lucas numbers as
and follows the recurrence
- .
Similar expressions can be found for with increasing complexity as increases. The numbers are the row sums of Hosoya's triangle.
As with Fibonacci numbers, there are several combinatorial interpretations of these sequences. For example is the number of ways can be written as an ordered sum involving only 0, 1, and 2 with 0 used exactly once. In particular and 2 can be written 0 + 1 + 1, 0 + 2, 1 + 0 + 1, 1 + 1 + 0, 2 + 0.[15]
Other generalizations
The Fibonacci polynomials are another generalization of Fibonacci numbers.
The Padovan sequence is generated by the recurrence .
The Narayana's cows sequence is generated by the recurrence .
A random Fibonacci sequence can be defined by tossing a coin for each position of the sequence and taking if it lands heads and if it lands tails. Work by Furstenberg and Kesten guarantees that this sequence almost surely grows exponentially at a constant rate: the constant is independent of the coin tosses and was computed in 1999 by Divakar Viswanath. It is now known as Viswanath's constant.
A repfigit, or Keith number, is an integer such that, when its digits start a Fibonacci sequence with that number of digits, the original number is eventually reached. An example is 47, because the Fibonacci sequence starting with 4 and 7 (4, 7, 11, 18, 29, 47) reaches 47. A repfigit can be a tribonacci sequence if there are 3 digits in the number, a tetranacci number if the number has four digits, etc. The first few repfigits are:
- 14, 19, 28, 47, 61, 75, 197, 742, 1104, 1537, 2208, 2580, 3684, 4788, 7385, 7647, 7909, … (sequence A007629 in the OEIS)
Since the set of sequences satisfying the relation is closed under termwise addition and under termwise multiplication by a constant, it can be viewed as a vector space. Any such sequence is uniquely determined by a choice of two elements, so the vector space is two-dimensional. If we abbreviate such a sequence as , the Fibonacci sequence and the shifted Fibonacci sequence are seen to form a canonical basis for this space, yielding the identity:
for all such sequences S. For example, if S is the Lucas sequence 2, 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, ..., then we obtain
- .
N-generated Fibonacci sequence
We can define the N-generated Fibonacci sequence (where N is a positive rational number): if
where pr is the rth prime, then we define
If , then , and if , then .
Sequence N OEIS sequence Fibonacci sequence 6 A000045 Pell sequence 12 A000129 Jacobsthal sequence 18 A001045 Narayana's cows sequence 10 A000930 Padovan sequence 15 A000931 Third-order Pell sequence 20 A008998 Tribonacci sequence 30 A000073 Tetranacci sequence 210 A000288
Semi-Fibonacci sequence
The semi-Fibonacci sequence (sequence A030067 in the OEIS) is defined via the same recursion for odd-indexed terms and , but for even indices , . The bisection A030068 of odd-indexed terms therefore verifies and is strictly increasing. It yields the set of the semi-Fibonacci numbers
- 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 11, 16, 17, 23, 26, 35, 37, 48, 53, 69, 70, 87, 93, 116, 119, 145, 154, ... (sequence A030068 in the OEIS)
which occur as .
References
- ↑ Triana, Juan (2019). "Negafibonacci numbers via matrices". Bulletin of TICMI 23 (1): 19–24. http://www.viam.science.tsu.ge/others/ticmi/blt/vol23_1/3_triana.pdf.
- ↑ "What is a Fibonacci Number? -- from Harry J. Smith". 2009-10-27. http://geocities.com/hjsmithh/Fibonacc/FibWhat.html.
- ↑ Pravin Chandra and Eric W. Weisstein. "Fibonacci Number". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/FibonacciNumber.html.
- ↑ Morrison, D. R. (1980), "A Stolarsky array of Wythoff pairs", A Collection of Manuscripts Related to the Fibonacci Sequence, Santa Clara, CA: The Fibonacci Association, pp. 134–136, http://www.math.ucsb.edu/~drm/papers/stolarsky.pdf, retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ Gardner, Martin (1961). The 2nd Scientific American Book of Mathematical Puzzles & Diversions. New York: Simon and Schuster.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Tuenter, Hans J. H. (October 2023). "In Search of Comrade Agronomof: Some Tribonacci History". The American Mathematical Monthly 130 (8): 708–719. doi:10.1080/00029890.2023.2231796.
- ↑ Podani, János; Kun, Ádám; Szilágyi, András (2018). "How Fast Does Darwin's Elephant Population Grow?". Journal of the History of Biology 51 (2): 259–281. doi:10.1007/s10739-017-9488-5. PMID 28726021. http://real.mtak.hu/72652/1/Podani_etal_DarwinElephants.pdf.
- ↑ Miller, W. J. C., ed (1892). Mathematical Questions and Solutions from the "Educational Times". 57. London: Francis Hodgson.
- ↑ Agronomof, M. (1914). "Sur une suite récurrente". Mathesis 4: 125–126.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Feinberg, Mark (October 1963). "Fibonacci-Tribonacci.". Fibonacci Quarterly 1 (3): 71–74. doi:10.1080/00150517.1963.12431573. https://www.fq.math.ca/Scanned/1-3/feinberg.pdf.
- ↑ Simon Plouffe, 1993
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 Wolfram, D. A. (May 1998). "Solving Generalized Fibonacci Recurrences". Fibonacci Quarterly 36 (2): 129–145. doi:10.1080/00150517.1998.12428948. http://www.fq.math.ca/Scanned/36-2/wolfram.pdf.
- ↑ Eric W. Weisstein. "Coin Tossing". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/CoinTossing.html.
- ↑ Hoggatt, Jr., V. E.; Bicknell-Johnson, Marjorie (April 1977). "Fibonacci Convolution Sequences". Fibonacci Quarterly 15 (2): 117–122. doi:10.1080/00150517.1977.12430465. http://www.fq.math.ca/Scanned/15-2/hoggatt1.pdf.
- ↑ Sloane, N. J. A., ed. "Sequence A001629". OEIS Foundation. https://oeis.org/A001629.
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Tribonacci number", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4, https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=p/t130190
 |
