Social:List of revolutions and rebellions

This is a list of revolutions, rebellions, insurrections, and uprisings.
BC
- Revolutionary/rebel victory
- Revolutionary/rebel defeat
- Another result (e.g. a treaty or peace without a clear result, status quo ante bellum, result unknown or indecisive)
- Ongoing conflict
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 2730 BCE | Set rebellion | Priests of Horus | Egypt divides into Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt | 
|
[1] | |
| c. 2690 BC | Nubian revolt | Nubians | Pharaoh Khasekhemwy quashed the rebellion, reuniting Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt | 
|
[2] | |
| c. 2380 BC | Sumerian revolt | Lagash, Sumer | Sumerians | The popular revolt deposed King Lugalanda and put the reformer Urukagina on the throne. | 
|
[3] |
| 1042–1039 BC | Rebellion of the Three Guards | China | Three Guards, separatists and Shang loyalists | Decisive Zhou loyalist victory, Fengjian system established, Resistance of Shang loyalists is broken. | 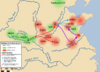
| |
| 842 BC | Compatriots Rebellion | China | Peasants and soldiers | King Li of Zhou was exiled and China was ruled by the Gonghe Regency until Li's death. | 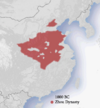
|
[4][5] |
| 626–620 BC | Revolt of Babylon | Neo-Assyrian Empire | Babylonians, led by Nabopolassar | The Babylonians overthrew Assyrian rule, establishing the Neo-Babylonian Empire, which ruled over the Near East for about a century. | 
|
[6] |
| 570 BC | Amasis revolt | Egyptian soldiers | Pharaoh Apries was overthrown and exiled, giving Amasis II the opportunity to seize the throne. Apries later attempted to retake Egypt, with Babylonian support, but was defeated and killed. | 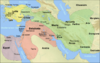
|
[7] | |
| 552–550 BC | Persian Revolt | Persis, Media | Persians, led by Cyrus the Great | Median rule overthrown, Persis and Media become part of the new Achaemenid Empire | 
|
|
| 531 BC | Phoenician revolt of 351 | Phoenicia | Tennes of Sidon, followed by rulers of Anatolia and Cyprus | Destruction of Sidon, execution of Tennes, and invasion of Egypt. | [8][9] | |
| 522 BC | Anti-Achaemeneid Rebellions | Assyrians, Babylonians, Egyptians, Elamites, Medians and Parthians | Darius the Great quashes all the rebellions within the space of a year. | 
|
[10] | |
| 510–509 BC | Roman Revolution | Republicans | The Roman monarchy was overthrown and in its place the Roman Republic was established. | [11] | ||
| 508–507 BC | Athenian Revolution | Democrats | The Tyrant Hippias was deposed and the subsequent aristocratic oligarchy overthrown, establishing Democracy in Athens. | 
| ||
| 499–493 BC | Ionian Revolt | Ionia, |
Greeks | The Achaemenid Empire asserts its rule over the city states of Ionia. | 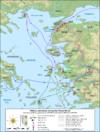
|
[12] |
| 494 BC | First secessio plebis | Plebeians | Patricians freed some of the plebs from their debts and conceded some of their power by creating the office of the Tribune of the Plebs. | 
|
[13] | |
| 484 BC | Bel-shimanni's rebellion | Babylon, |
Babylonians | Rebellion quickly defeated by Xerxes I. | [14] | |
| 482–481 BC | Shamash-eriba's rebellion | Babylon, |
Babylonians | Rebellion eventually defeated by Xerxes I, Babylon's forticiations were destroyed and its temples were ransacked. | [14] | |
| 464 BC | Third Messenian War | Messenian Helots | Slave revolt put down by Archidamus II, who called Sparta to arms in the wake of an earthquake. | [15] | ||
| 460–454 BC | Inaros' revolt | Egypt, |
Inaros II and his Athenian allies | Defeated by the Persian army led by Megabyzus and Artabazus, after a two-year siege. Inaros was captured and carried away to Susa where he was crucified. | 
|
[16][17] |
| 449 BC | Second Secessio plebis | Plebeians | The Senate forced the resignation of the Decemviri and restored both the office of Tribune of the Plebs and the right of appeal, which were suspended during the rule of the Decemvir. | 
|
[18][19] | |
| 445 BC | Third Secessio plebis | Plebeians | Intermarriage between Patricians and Plebeians was legalized and the position of Consular Tribune (a Tribune of the Plebs elected with the powers of a consul) was created. | [20][21] | ||
| 342 BC | Fourth Secessio plebis | Plebeians | [20] | |||
| 287 BC | Fifth Secessio plebis | Plebeians | The Lex Hortensia was implemented, establishing that the laws decided by the Plebeian Council were made binding on all Roman citizens, including patricians. This law finally eliminated the political disparity between the two classes, bringing the Conflict of Orders to an end after about two hundred years of struggle. | [22] | ||
| 241 BC | Revolt of the Falisci | Falisci | The Falisci were defeated and subjugated to Roman dominance, the town of Falerii was destroyed. | 
|
[23] | |
| 209 BC | Dazexiang uprising | China | Villagers led by Chen Sheng and Wu Guang | The uprising was put down by Qin forces, Chen and Wu were assassinated by their own men. | 
|
[24] |
| 206 BC | Liu Bang's Insurrection | China | Han forces | The Qin dynasty is overthrown in a popular revolt and after a period of contention, Liu Bang is crowned Emperor of the Han dynasty. | 
|
|
| 205–185 BC | Great revolt of the Egyptians | Egyptians, led by Hugronaphor and Ankhmakis | Revolt put down by the Ptolemaic Kingdom, cementing Greek rule over Egypt. | 
|
[25] | |
| 181–179 BC | First Celtiberian War | Hispania, |
Celtiberians | Revolt eventually subdued by the Romans. | 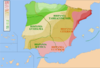
|
[26] |
| 167–160 BC | Maccabean Revolt | Judea, Coele-Syria, |
Sovereignty of Judea is secured, eventually the independent Hasmonean dynasty is established. | 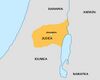
|
[27] | |
| 154 BC | Rebellion of the Seven States | China | Principalities led by Liu Pi | Rebellion crushed after 3 months, further centralization of imperial power. | 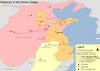
|
[28] |
| 154–151 BC | Second Celtiberian War | Hispania, |
Celtiberians | Rome increased its influence in Celtiberia | 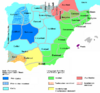
|
[29] |
| 143–133 BC | Numantine War | Hispania, |
Celtiberians | Expansion of the Roman territory through Celtiberia. | 
|
[30] |
| 155–139 BC | Lusitanian War | Lusitania, |
Lusitanians, led by Viriatus. | Pacification of Lusitania | 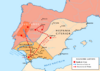
|
[31] |
| 135–132 BC | First Servile War | Sicily, |
Sicilian slaves, led by Eunus | After some minor battles won by the slaves, a larger Roman army arrived in Sicily and defeated the rebels. | 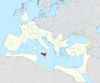
|
[32] |
| 125 BC | Fregellae's revolt | Fregellae, |
Fregellaeans | Fregellae was captured and destroyed by Lucius Opimius | 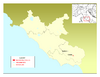
|
[33] |
| 104–100 BC | Second Servile War | Sicily, |
Sicilian slaves, led by Salvius Tryphon | The revolt was quelled, and 1,000 slaves who surrendered were sent to fight against beasts in the arena back at Rome for the amusement of the populace. To spite the Romans, they refused to fight and killed each other quietly with their swords, until the last flung himself on his own blade. | 
|
[34] |
| 91–88 BC | Social War | Italy, |
Italic peoples | Eventually resulted in a Roman victory. However, Rome granted Roman citizenship to all of its Italian allies, to avoid another costly war. | 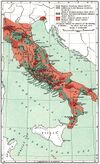
|
[35] |
| 88 BC | Sulla's first march on Rome | Italy, |
Populares | The Optimates were victorious and Sulla briefly took power in Rome. | 
|
[36] |
| 82–81 BC | Sulla's civil war | Italy, |
Populares | The Optimates were once again victorious and Sulla established himself as Dictator of Rome. | 
|
[37] |
| 80–71 BC | Sertorian War | Hispania, |
Populares | The war ended after the Populares leader Quintus Sertorius was assassinated by Marcus Perperna Vento, who was then promptly defeated by Pompey. | 
|
[38] |
| 77 BC | Lepidus' rebellion | Italy, |
Populares | Lepidus was defeated in battle and died from illness, other Populares fled to Spain to fight in the Sertorian War. | 
|
[39] |
| 73–71 BC | Third Servile War | Italy, |
Gladiators, led by Spartacus | The armies of Spartacus were defeated by the legions of Marcus Licinius Crassus. | 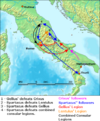
|
[40][41] |
| 65 BC | First Catilinarian conspiracy | Rome, |
Catiline | Lucius Aurelius Cotta and Lucius Manlius Torquatus remain in power as consuls. | 
|
[42] |
| 62 BC | Second Catilinarian conspiracy | Rome, |
Catiline | The plot was exposed, forcing Catiline to flee from Rome. Marcus Tullius Cicero and Gaius Antonius Hybrida remain in power as consuls. | 
|
[43] |
| 52–51 BC | Gallic Wars | Gaul | Gauls, led by Vercingetorix | The Gallic revolt was crushed by Julius Caesar | 
|
[44] |
| 49–45 BC | Great Roman Civil War | Populares, led by Julius Caesar | Caesar defeated the Optimates, assumed control of the Roman Republic and became Dictator in perpetuity. | 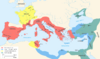
|
[45] | |
| 38 BC | Aquitanian revolt | Gallia Narbonensis, |
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa | Revolt suppressed by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa. | 
|
[46] |
| 29 BC | Theban revolt | Thebes, Egypt, |
Egyptians | Revolt suppressed by Cornelius Gallus | 
|
[47] |
1–999 AD
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3–6 | Gaetulian War | Mauretania, Roman Empire | Gaetuli | Revolt suppressed by Cossus Cornelius Lentulus | [48] | |
| 6 | Judas Uprising | Judea, Roman Empire | Zealots led by Judas of Galilee | Riots against the Roman census erupt throughout the country, but others are convinced by the High Priest of Israel to obey the census. | 
|
[49] |
| 6–9 | Bellum Batonianum | Illyricum, Roman Empire | Illyrian tribes | Revolt eventually suppressed by the Romans. | 
|
[50] |
| 9–16 | Germanic revolt | Germania | Alliance of Germanic tribes, led by Arminius | The Roman legions led by Publius Quinctilius Varus were defeated in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, temporarily halting further Roman occupation and colonization. | 
|
[51] |
| 14 | Mutiny of the legions | Germania and Illyricum, Roman Empire | Roman legions | Revolt suppressed by Germanicus and Drusus Julius Caesar respectively | 
|
[52] |
| 15–24 | Tacfarinas' revolt' | Mauretania, Roman Empire | Musulamii | Revolt suppressed by Publius Cornelius Dolabella | 
|
[53] |
| 17–23 | First Red Eyebrow Rebellion | China | Red Eyebrow and Lulin rebels | Xin dynasty overthrown and the Gengshi Emperor is instated on the throne. | 
| |
| 24–27 | Second Red Eyebrow Rebellion | China | Red Eyebrow rebels | Revolt suppressed by Liu Xiu's forces and the Eastern Han dynasty is established. | 
| |
| 21 | Gaulish debtors' revolt | Gaul, Roman Empire | Treveri and Aedui | The Treveri revolt was put down by Julius Indus and the Aedui revolt was put down by Gaius Silius. | 
|
[54] |
| 26 | Thracian revolt | Odrysian kingdom | Thracians | Revolt suppressed by Gaius Poppaeus Sabinus. | 
|
[55] |
| 28 | Revolt of the Frisii | Frisia | Frisii | The Roman Empire is driven out of Frisia. | 
|
[56] |
| 36 | Revolt of the Cietae | Cappadocia, Roman Empire | Cietae | Rebellion put down by Archelaus of Cilicia. | 
|
[57] |
| 40–43 | Trung sisters' rebellion | Lĩnh Nam | Vietnamese led by the Trung Sisters | After brief end to the First Chinese domination of Vietnam, the Han dynasty reconquers the country and begins the Second Chinese domination of Vietnam. | 
|
[58] |
| 40–44 | Mauretanian revolt | Mauretania, Roman Empire | Mauri led by Aedemon and Sabalus | Revolt suppressed by Gaius Suetonius Paulinus and Gnaeus Hosidius Geta, Mauretania is annexed directly into the empire and split into the Roman provinces of Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis. | 
|
[59] |
| 42 | Camillus' revolt | Dalmatia, Roman Empire | Roman legions led by Lucius Arruntius Camillus Scribonianus | Rebellion quickly collapses, Camillus flees to Vis where he takes his own life. | 
|
[60] |
| 46–48 | Jacob and Simon uprising | Galilee, Judea, Roman Empire | Zealots | Revolt suppressed, Jacob and Simon executed by Tiberius Julius Alexander. | File:First century Iudaea province.gif | [61] |
| 60–61 | Boudican revolt | Norfolk, Britain, Roman Empire | Celtic Britons led by Boudica | Revolt crushed by Gaius Suetonius Paulinus. | 
|
[62] |
| 66–73 | First Jewish–Roman War | Jewish people | Revolt crushed by the Roman Empire, Jerusalem and the Second Temple are destroyed in the process. | 
|
[63] | |
| 68 | Vindex's Revolt | Gallia Lugdunensis, Roman Empire | Gaius Julius Vindex | Vindex was defeated in battle by Lucius Verginius Rufus and committed suicide. | [64] | |
| 69 | Colchis uprising | Colchis, Roman Empire | Anicetus | Uprising put down by Roman forces. | 
|
[65] |
| 69–70 | Revolt of the Batavi | Batavia | Batavi | Revolt crushed by Quintus Petillius Cerialis and the Batavi again submitted to Roman rule, Batavia is incorporated into the Roman province of Germania Inferior. | 
|
[66] |
| 89 | Revolt of Saturninus | Germania Superior, Roman Empire | Lucius Antonius Saturninus | Revolt swiftly crushed by the Roman legions. | 
|
[67] |
| 115–117 | Kitos War | Eastern Mediterranean, Roman Empire | Zealots | Revolt crushed by the Roman legions and its leaders executed. | 
|
[68] |
| 117 | Mauretanian revolt | Mauretania, Roman Empire | Mauri | Revolt suppressed by Marcius Turbo | 
|
|
| 132–135 | Bar Kokhba revolt | Judea, Roman Empire | Jewish people led by Simon bar Kokhba | All-out defeat of the Jewish rebels, followed by wide-scale persecution and genocide of Jewish people and the suppression of Jewish religious and political autonomy. | 
|
[69] |
| 172 | Bucolic war | Egypt, Roman Empire | Egyptians led by Isidorus | Revolt suppressed by Avidius Cassius | 
|
[70] |
| 184–205 | Yellow Turban Rebellion | China | Yellow Turban Army led by Zhang Jue | The uprising eventually collapsed and was fully suppressed by various warlords of the Eastern Han dynasty. However, the large devolution of power to regional warlords led to the collapse of the Han dynasty not long after. | 
|
[71] |
| 185–205 | Heishan secession | Taihang Mountain, China | Heishan bandits | The autonomous confederacy eventually surrendered to the warlord Cao Cao. | 
|
[72] |
| 185 | Roman mutiny | Britain, Roman Empire | Roman legions | Mutiny suppressed by Pertinax. | 
|
[73] |
| 218 | Battle of Antioch | Antioch, Syria, Roman Empire | Elagabalus | Elagabalus overthrows Macrinus and is installed as Roman Emperor. | 
|
[74] |
| 225–248 | Lady Triệu's uprising | Vietnam | Vietnamese led by Lady Triệu | After several months of warfare Lady Triệu was defeated and committed suicide. The Second Chinese domination of Vietnam continues. | 
|
[75] |
| 227–228 | Xincheng Rebellion | Cao Wei, China | Meng Da | The revolt was suppressed by Sima Yi, Meng Da was captured and executed. | 
|
[76] |
| 251 | Wang Ling's Rebellion | Shouchon, Cao Wei, China | Wang Ling | Wang Ling surrendered to the Wei forces and later committed suicide. | 
|
[77] |
| 255 | Guanqiu Jian and Wen Qin's Rebellion | Shouchon, Cao Wei, China | Guanqiu Jian and Wen Qin | Cao Wei is victorious, Guanqiu Jian is slain, Wen Qin and his family fled to Eastern Wu. | 
|
[77] |
| 257–258 | Zhuge Dan's Rebellion | Shouchon, Cao Wei, China | Zhuge Dan | Cao Wei is victorious and the Sima clan cements control over the Wei government until its eventual demise. | 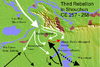
|
[77] |
| 284–286 | Gallic peasants' rebellion | Gaul, Roman Empire | Bagaudae | Rebellion crushed by Caesar Maximian, though the Bagaudae movement would persist until the Fall of the Western Roman Empire. | 
|
[78] |
| 286–296 | Carausian Revolt | Britain and northern Gaul, Roman Empire | Carausius and Allectus | Revolt suppressed, Britain and Gaul retaken. | 
|
[79] |
| 291–306 | War of the Eight Princes | China | Princes of the Sima clan | Sima Yue wins the war and gains influence over the Jin emperor but is killed a few years later. | 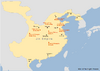
|
[80] |
| 304–316 | Uprising of the Five Barbarians | North China | Five Barbarians | Rebel victory in northern China; Fall of the Western Jin dynasty in northern China; Formation of the Eastern Jin dynasty in southern China; Rebel victory for Cheng Han's independence; Hubei southern Nanman Aboriginal uprising defeated. | 
|
[81] |
| 293 | Revolt of the Thebaid | Thebaid, Roman Empire | Busiris and Qift | Revolt suppressed by Galerius. | 
|
[82] |
| 351–352 | Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus | Syria Palaestina, Roman Empire | Jewish people | The Romans crush the revolt and destroy several Jewish cities. | 
| |
| 398 | Gildonic War | Africa, |
Comes Gildo | The revolt was subdued by Flavius Stilicho. | 
|
[83] |
| 484 | Justa uprising | Samaria, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Samaritans | Uprising suppressed by Zeno, who rebuilt the church of Saint Procopius in Neapolis and banned the Samaritans from Mount Gerizim. | 
|
[84] |
| 495 | Samaritan unrest | Samaria, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Samaritans | Uprising suppressed by the Byzantines. | 
|
[84] |
| 496 | Mazdak's Revolt | Template:Country data Sasanian Empire | Mazdakites | Mazdak successfully converted Kavadh I, before the latter was overthrown by the nobility and the former was executed. | 
| |
| 529–531 | Ben Sabar Revolt | Samaria, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Samaritans led by Julianus ben Sabar | The forces of Justinian I quelled the revolt with the help of the Ghassanids; tens of thousands of Samaritans died or were enslaved. The Christian Byzantine Empire thereafter outlawed the Samaritan faith. | 
|
[84] |
| 532 | Nika revolt | Constantinople, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Blue and Green demes | Revolt suppressed, its participants killed and Justinian I's rule over the Byzantine empire is strengthened. | 
|
[85] |
| 541 | Vietnamese uprising | Vạn Xuân | Vietnamese led by Lý Nam Đế | The Second Chinese domination of Vietnam is brought to an end, the country declares itself independent as the Kingdom of Vạn Xuân and crowns Lý Nam Đế as the first king of the Early Lý dynasty. | 
|
[86] |
| 556 | Samaritan revolt | Samaria, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Samaritans and Jewish people | Amantius, the governor of the East was ordered to quell the revolt. | 
|
[84] |
| 572–578 | Samaritan revolt | Samaria, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Samaritans and Jewish people | Revolt suppressed, the Samaritan faith was outlawed and from a population of nearly a million, the Samaritan community dwindled to near extinction. | 
|
[84] |
| 608–610 | Heraclian revolt | Exarchate of Africa, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Heraclius the Elder | Phocas executed and Heraclius the Younger is installed as Byzantine Emperor, establishing the Heraclian dynasty. | 
| |
| 611–617 | Anti-Sui rebellions | China | Former Sui officials and peasant rebels | The Sui dynasty is overthrown, followed by the rise of rebel leader Li Yuan, founder of the Tang dynasty. | 
|
[87] |
| 614–625 | Jewish revolt against Heraclius | Palaestina Prima, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Jewish people | After Palestine was retaken by the Byzantines, Jewish people were massacred and expelled from the region. | 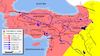
|
[88] |
| 623–626 | Slavic revolt | Avar Khaganate | Slavs led by Samo | Avar rule overthrown, Slavic tribes in the area unify to form Samo's Empire. | 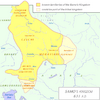
| |
| 632–633 | Ridda wars | Arabia, |
Arab tribes | Rebels forced to submit to the caliphate of Abu Bakr. | 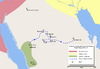
|
[89] |
| 656–661 | First Fitna | Umayyads | Hasan ibn Ali negotiates a treaty acknowledging Mu'awiya I as caliph, establishing the Umayyad Caliphate. | 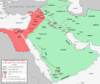
| ||
| 680–692 | Second Fitna | Zubayrids, Alids and Kharijites | The Umayyad Caliphate increases its own power, restructuring the army and Arabizing and Islamizing the state bureaucracy. | 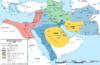
|
[90] | |
| 696–698 | Sufri revolt | Central Iraq, |
Sufri led by Shabib ibn Yazid al-Shaybani | Defeated by the caliphate, although Sufrism continued to be practiced in Mosul. | 
| |
| 700–703 | Ibn al-Ash'ath's rebellion | Iraq, |
Abd al-Rahman ibn Muhammad ibn al-Ash'ath | Revolt suppressed by the caliphate, signalling the end of the power of the tribal nobility of Iraq, which henceforth came under the direct control of the Umayyad regime's staunchly loyal Syrian troops. | 
|
[91] |
| 720–729 | Yazid's mutiny | Basra, |
Yazid ibn al-Muhallab | Revolt suppressed by the caliphate. | [92] | |
| 713–722 | Annam uprising | Vietnam | Vietnamese led by Mai Thúc Loan | The independent kingdom was put down by a military campaign at the order of the Emperor Xuanzong of Tang, continuing the Third Chinese domination of Vietnam | 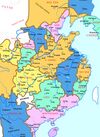
|
[93] |
| 734–746 | Harith's rebellion | Khurasan, |
Al-Harith ibn Surayj | Harith is killed and the rebellion crushed, although the revolt weakened Arab power in Central Asia and facilitated the beginning of the Abbasid Revolution. | [94] | |
| 740 | Zaidi Revolt | Kufa, |
Zayd ibn Ali | The Umayyad governor of Iraq managed to bribe the inhabitants of Kufa which allowed him to break the insurgence, killing Zayd in the process | 
|
[95] |
| 740–743 | Berber Revolt | Maghreb, |
Berbers led by Maysara al-Matghari | Umayyads expelled from the Maghreb and several independent Berber states are established in the area. | 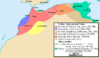
|
[96] |
| 744–747 | Third Fitna | Pro-Yaman Umayyads, Alids led by Abdallah ibn Mu'awiya, Kharijites led by Al-Dahhak ibn Qays al-Shaybani | Victory of Marwan II and the pro-Qays faction in the inter-Umayyad civil war and anti-Umayyad revolts crushed, although Umayyad authority was now permanently weakened. | 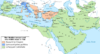
|
[97] | |
| 747–748 | Ibadi revolt | South Arabia, |
Ibadis | Umayyad victory in the Hijaz and the Yemen; though Ibadi autonomy is secured in Hadramawt. | 
| |
| 747–750 | Abbasid Revolution | Abbasids | Abbasid Caliphate established, bringing an end to the privileged status for Arabs and discrimination against non-Arabs. | 
|
[94] | |
| 752–760 | Mardaite revolts | Mount Lebanon and |
Lebanese Christians and Byzantine Empire | Christian inhabitants of parts of interior and coastal Lebanon expelled and replaced with Arab tribes. | 
| |
| 754 | Abdallah's rebellion | Syria, |
Abdallah ibn Ali | Abdallah's army is defeated by Abu Muslim. | 
| |
| 755 | Córdoban revolution | Almuñécar, al-Andalus, |
Umayyads led by Abd al-Rahman I | Umayyads take control of al-Andalus, establishing the Emirate of Córdoba. | 
|
[98] |
| 755–763 | An Lushan Rebellion | Yan, China | An Lushan | Yan defeated by the Tang imperial forces, although the Tang dynasty was weakened. | 
|
[99] |
| 762–763 | Alid Revolt | Hejaz and Southern Iraq, |
Alids led by Muhammad ibn Abdallah | Revolt suppressed by the caliphate, followed by a large-scaled reprisal campaign against the Alids. | [100] | |
| 772–804 | Saxon Wars | Saxony | Saxons | Saxony is annexed into the Frankish empire and the Saxons are forcibly converted from Germanic paganism to Catholicism. | 
|
[101] |
| 786 | Alid revolt | Mecca, Hejaz, |
Alids | Revolt crushed by the Abbasid army and members of the Alid house are executed. One of the Alids, Idris ibn Abdallah, fled the battlefield to the Maghreb, where he established the Idrisid dynasty. | [102] | |
| 791–802 | Phùng rebellion | Vietnam | Vietnamese led by Phùng Hưng | Briefly ruled the country before the Third Chinese domination of Vietnam is reestablished. | 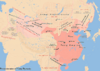
|
[103] |
| 793–796 | Qays–Yaman war | Syria, |
Qays | Revolt crushed by the Abbasids and their Yamani allies. | 
|
[104] |
| 794–795 | Al-Walid's rebellion | Jazira, |
Kharijites led by Al-Walid ibn Tarif al-Shaybani | Yazid ibn Mazyad al-Shaybani met the rebels in battle in late 795, at al-Haditha above Hit, and defeated al-Walid in single combat, killing him and cutting off his head. Yazid also killed a large number of the Kharijites and forced the remainder to disperse, and the revolt ended in defeat. | 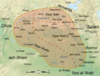
|
[105] |
| 811–838 | Fourth Fitna | Alids led by Muhammad ibn Ja'far al-Sadiq, Qays led by Nasr ibn Shabath al-Uqayli and Khurramites led by Babak Khorramdin | Al-Ma'mun takes power as Caliph, al-Sadiq is forced into exile, Qays territory is lost and Nasr surrenders to the caliphate, Babak is executed and the Tahirids begin their reign over Khorasan | 
| ||
| 814 | al-Ribad rebellion | Guadalquivir, Emirate of Córdoba | Clerics in al-Ribad | Rebellion crushed at Al-Hakam I | [106] | |
| 821–823 | Thomas the Slav's rebellion | Anatolia, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Thomas the Slav | Thomas is surrendered and executed by the Byzantines | [107] | |
| 824–836 | Tunisian mutiny | Tunisia, Ifriqiya, |
Arabs | Aghlabids put down the revolt with the help of the Berbers | 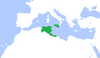
|
[108] |
| 822 | Aristocratic rebellion | Aristocrats led by Kim Heonchang | The royal faction was able to regain much of the territory that Heonchang's forces had taken. After the fall of Gongju, Gim Heon-chang took his own life. | 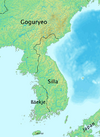
|
||
| 841–842 | Umayyad rebellion | Palestine, |
Umayyads led by Al-Mubarqa | Al-Hidari defeated al-Mubarqa's forces in a battle near Ramlah, al-Mubarqa taken prisoner and brought to the caliphal capital, Samarra, where he was thrown into prison and never heard of again. | 
| |
| 841–845 | Stellinga | Saxony, Carolingian Empire | Saxon freemen and freedmen | Revolt crushed by the Carolingians and their allies in the Saxon nobility. | 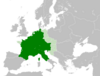
|
[109] |
| 845–846 | Jang Bogo's mutiny | Jang Bogo | Jang Bogo assassinated by an emissary from the Silla court. | 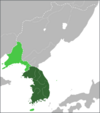
|
[110] | |
| 859–860 | Qiu's rebellion | Zhejiang, China | Peasants led by Qiu Fu | Rebellion was suppressed by the imperial general Wang Shi. | 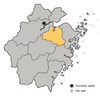
|
[111] |
| 861–876 | Saffarid revolution | Sistan, Khorasan, |
Saffarids led by Ya'qub ibn al-Layth al-Saffar | al-Saffar overthrows Abbasid rule over Iran and establishes the Saffarid dynasty. | 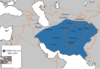
| |
| 864 | Alid uprising | Iraq, |
Alids led by Yahya ibn Umar | The Alids attacked Al-Musta'in's forces, but were defeated and fled, Umar was subsequently executed. | 
|
[112] |
| 865–866 | Fifth Fitna | Iraq, |
Al-Mu'tazz | Al-Musta'in deposed as Caliph and succeeded by Al-Mu'tazz. | 
|
[113] |
| 866–896 | Kharijite Rebellion | Jazira, |
Kharijites | It was finally defeated after the caliph al-Mu'tadid undertook several campaigns to restore caliphal authority in the region. | 
|
[114] |
| 869–883 | Zanj Rebellion | Sawad, |
Zanj | Revolt eventually suppressed by the Abbasids. | 
|
[115] |
| 874–884 | Qi rebellion | China | Wang Xianzhi and Huang Chao | Rebellions suppressed by the Tang dynasty, which later collapsed due to the destabilization caused by the rebellion. | 
|
[116] |
| 880–928 | Bobastro rebellion | Emirate of Córdoba | Muwallads and Mozarabs led by Umar ibn Hafsun | Ibn Hafsun died in 917, his coalition then crumbled, and while his sons tried to continue the resistance, they eventually fell to Abd-ar-Rahman III, who proclaimed the Caliphate of Córdoba. | 
|
[117] |
| 899–906 | The Qarmatian Revolution | Eastern Arabia, |
Qarmatians | Qarmatians successfully establish a republic in Eastern Arabia, becoming the most powerful force in the Persian Gulf. The Qarmatians were eventually reduced to a local power by the Abbasids in 976 and annihilated by the Seljuq-backed Uyunid Emirate in 1076. | ||
| 917–924 | Bulgarian–Serbian war | Balkans | Serbians led by Zaharija | Serbia is annexed into the First Bulgarian Empire. | 
| |
| 928–932 | Bithynian rebellion | Bithynia, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Basil the Copper Hand | The revolt was finally subdued by the imperial army and Basil was executed. | 
| |
| 943–947 | Ibadi Berber revolt | Ifriqiya, |
Ibadi Berbers led by Abu Yazid | Revolt suppressed by the Fatimids, Abu Yazid captured and killed. | 
|
[118] |
| 969–970 | First rebellion of Bardas Phokas the Younger | Caesarea, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Phokas family | Rebellion extinguished by Bardas Skleros, Phokas was captured and exiled to Chios, where he stayed for 7 years. | [119] | |
| 976–979 | Rebellion of Bardas Skleros | Anatolia, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Bardas Skleros | Bardas Phokas the Younger recalled from exile to put down Skleros' rebellion at the Battle of Pankaleia, Skleros seeks refuge in Baghdad. | 
|
[120] |
| 983 | Great Slav rising | Elbe, Germany, Template:Country data Holy Roman Empire | Polabian Slavs | Halt to Ostsiedlung. | 
|
[121] |
| 987–989 | Second Rebellion of Bardas Phokas the Younger | Anatolia, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Bardas Phokas the Younger and Bardas Skleros | Rebel armies surrendered after the death of Phokas. | 
|
[122] |
| 993–995 | Da Shu rebellion | Sichuan, China | Da Shu Kingdom | The Song dynasty was able to suppress the rebellion and restore their rule over the Shu region. | 
|
[123] |
| 996 | Peasants' revolt in Normandy | Norman peasants | Suppression of the rebellion | [124] | ||
| 996-998 | Revolt of Tyre (996–998) | Tyre, Lebanon, |
Tyrians and Byzantine Empire | Revolt suppressed and rebels killed or enslaved |
1000–1499
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1034–1038 | Serb revolt against the Byzantine Empire | Duklja, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Serbs led by Vojislav of Duklja | Revolt suppressed and Vojislav imprisoned, before starting another rebellion which eventually succeeded | ||
| 1040–1041 | Uprising of Peter Delyan | Balkan peninsula, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Bulgarians led by Peter Delyan | Rebellion suppressed by Emperor Michael IV | 
|
[125] |
| 1072 | Uprising of Georgi Voyteh | Balkan peninsula, Template:Country data Byzantine Empire | Bulgarians led by Georgi Voyteh | Revolt suppressed by Damianos Dalassenos | 
|
[126] |
| 1090 | Takeover of Alamut | Alamut, Seljuk Empire | Hashshashin led by Hassan-i Sabbah | Nizari Ismaili state founded, creating the Order of Assassins | 
|
|
| 1095 | Rebellion of northern nobles against William Rufus | England | Northern nobles led by Robert de Mowbray | Suppression of the rebellion | ||
| 1125 | Almohads against the Almoravids | Atlas Mountains | Masmuda tribes led by Ibn Tumart | Establishment of the Almohad Caliphate | ||
| 1156 | Hōgen Rebellion | Japan | Forces loyal to retired Emperor Sutoku | Rebellion suppressed by forces loyal to Emperor Go-Shirakawa. Established the dominance of samurai clans and eventually the first samurai-led government in the history of Japan | ||
| 1185 | Rebellion of Asen and Peter against Byzantine Empire | Balkan Mountains | Bulgarians and Vlachs | Creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire | ||
| 1209–1211 | Quách Bốc Rebellion | Lý dynasty | Army led by General Quách Bốc | Defeat of Emperor Lý Cao Tông and further weakening of the declining Lý dynasty | ||
| 1233–1234 | Stedinger revolt | Frisia | Stedingers | Revolt suppressed by a crusade called by Pope Gregory IX | ||
| 1237–1239 | Babai Revolt | Sultanate of Rum | Rebels | Revolt suppressed | ||
| 1242–1249 | The First Prussian Uprising | Pomerania | Teutonic Knights | Swantopolk II returned seized lands. Knights allowed safe passage in Pomerania. Treaty of Christburg (secured rights for Christians) | ||
| 1250 | Bahri revolt | Egypt | Bahri Mamluks | Mamluks consolidated power and established the Bahri dynasty | ||
| 1282 | Sicilian Vespers | Sicily | Sicilian rebels | Angevin regime overthrown | ||
| 1296–1328 | First Scottish War of Independence | Scotland | Kingdom of Scotland | Renewed Scottish independence | ||
| 1302 | Battle of the Golden Spurs | Flanders | County of Flanders | Flemish victory. French ousted | ||
| 1323–1328 | Peasant revolt in Flanders | Flanders | County of Flanders | Restoration of pro-French court. Repression of rebels | ||
| 1332–1357 | Second Scottish War of Independence | Scotland | Kingdom of Scotland | Treaty of Berwick. Renewed Scottish independence | ||
| 1342 | Zealots of Thessalonica | Byzantine Empire | Zealots of Thessalonica | Zealots ruled Thessalonica for 8 years | ||
| 1343–1345 | St. George's Night Uprising | Estonia | Local Estonians from the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek | Uprising suppressed | ||
| 1346-1347 | Rebellion of Ismail Mukh | Deccan, |
Ismail Mukh's forces | Rebellion victory, later establishment of the Bahmani Sultanate. | ||
| 1354 | Revolt of Cola di Rienzi | Rome | Cola di Rienzi and loyal forces (with help from Louis I)[127] | Successfully revolted. However, Cola eventually abdicated and left Rome | ||
| 1356–1358 | Jacquerie uprising | Northern France | Peasants | Revolt successfully repressed | ||
| 1368 | Red Turban Rebellions | China | Peasant Han Chinese led by Zhu Yuanzhang | Establishment of the Ming dynasty | ||
| 1378 | Revolt of the Ciompi | Florence | Laborers from Florence | City government seized. Demands met by laborers | ||
| 1378–1384 | Tuchin Revolt | Béziers | Locals from Béziers | Duc de Berry suppressed the revolt | ||
| 1381 | Peasants' Revolt. This was a rebellion in England led by Wat Tyler and John Ball, in which peasants demanded an end to serfdom. | England | Rebels led by Wat Tyler | Wat Tyler killed, revolt suppressed | 
|
|
| 1382 | Harelle | Rouen, Paris | Guild members of Rouen | Revolt leaders killed. City rights revoked | ||
| c. 1387 | Isfahan revolt | Isfahan | Local rebels | Revolt violently repressed[128] | ||
| 1400–1415 | Welsh revolt | Wales | Rebels headed by Owain Glyndŵr | England conquered Wales | ||
| 1404/1408/1413^ | Uprising of Konstantin and Fruzhin | Historical region of Bulgaria | Bulgarian nobles | Failure to liberate Bulgaria | ||
| 1418–1427 | Lam Sơn uprising | Northern Vietnam | Rebels led by Lê Lợi | Independence of Đại Việt | ||
| 1431–1435 | First Irmandiño revolt | Galicia | Peasantry and bourgeoisie | Revolt suppressed | ||
| 1434–1436 | Engelbrekt rebellion | Dalarna | Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson | Engelbrekt assassinated. Kalmar Union eroded | ||
| 1437 | Transylvanian peasants revolt | Kingdom of Hungary | Transylvanian peasants and petty nobles | Patrician victory | ||
| 1444–1468 | Skanderbeg's rebellion | Ottoman-ruled Albania | Skanderbeg and his forces | Skanderbeg agreed to peace and paid tribute to the Ottomans. | ||
| 1450 | Jack Cade's Rebellion | Kent, England | Rebels led by Jack Cade | Royal victory | ||
| 1462–1485 | Rebellion of the Remences | Catalonia | Peasants | Indecisive | ||
| 1467–1470 | Second Irmandiño revolt | Galicia | Peasantry and bourgeoisie | Irmandiño movement defeated | ||
| 1497 | Cornish rebellion of 1497 | England | Rebels mainly from Cornwall | Royal victory |
1500–1699
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1499–1501 | Rebellion of the Alpujarras | Kingdom of Granada | Muslims of Granada | Rebellion suppressed and mass forced conversions of all Muslims in Granada | ||
| 1501–1503 | War of Deposition against King Hans | Kalmar Union | Swedish separatists | Separatist victory, Kalmar Union de facto dissolved | ||
| 1501–1504 | Alvsson's rebellion against King Hans of Norway | Denmark and Norway | Norwegian separatists | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1514 | Peasants' war led by György Dózsa | Kingdom of Hungary | Peasants led by György Dózsa | Rebellion suppressed and György Dózsa was executed | ||
| 1515 | Slovene peasant revolt | Holy Roman Empire | Peasants | Revolt put down by Holy Roman Empire mercenaries | ||
| 1515–1523 | Arumer Zwarte Hoop | Habsburg Netherlands | Frisian rebels led by Pier Gerlofs Donia and Wijerd Jelckama. | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1516 | Trần Cảo Rebellion | Lê dynasty | Rebellion suppressed. Lê dynasty weakened by ensuing civil war | |||
| 1519–1523 | Revolt of the Brotherhoods | Valencia | Germanies autonomist rebels | Rebel leader L'Encobert killed and strongholds of the Germanies captured | ||
| 1520–1522 | Revolt of the Comuneros | Royalist Castilians | Comuneros rebels | Royalist victory | ||
| 1521–1522 | Santo Domingo Revolt | Enslaved Africans | Suppression of the revolt | |||
| 1521–1523 | Gustav Vasa's Rebellion | Template:Country data Kalmar Union | Rebels led by nobleman Gustav Vasa | Rebels successfully deposed King Christian II from the throne of Sweden | ||
| 1524–1525 | German Peasants' War | Suppression of revolt and execution of its participants | ||||
| 1526 | Slave revolt in San Miguel de Gualdape | Rebels | Inconclusive | |||
| 1531 | The Straccioni Rebellion, uprising in Lucca | Rebels | ||||
| 1532–1547 | Sebastián Lemba's rebellion | Rebels led by maroon Sebastián Lemba | ||||
| 1536 | Pilgrimage of Grace | Suppression of the uprisings, execution of the leading figures | ||||
| 1540–1542 | Mixtón War | Caxcanes | Spaniard and indigenous allied victory | |||
| 1542 | Dacke War | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1548 | Revolt of the Pitauds | French peasants against the salt tax | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1548–1582 | Bayano Wars | Enslaved Bayano rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1549 | Prayer Book Rebellion | Catholic rebels in Cornwall and Devon | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1549 | Kett's Rebellion | East Anglian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1550–1590 | Chichimeca War | Chichimeca Confederation | Chichimeca military victory | |||
| 1567–1872 | Philippine revolts against Spain | Rebels | ||||
| 1568–1571 | Morisco rebellions in Granada | Morisco rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1568–1648 | Eighty Years' War | Peace of Münster | ||||
| 1569–1570 | Rising of the North | Elizabeth I of England | Partisans of Mary, Queen of Scots and Northern English Catholics | Elizabethan victory | ||
| 1570–1618 | Gaspar Yanga's revolt against Spanish colonial rule in Mexico | Rebels led by Gaspar Yanga | Ended with the signing of a treaty with Spain | |||
| 1573 | Croatian–Slovene peasant revolt | Croatian, Styrian and Carniolan nobility and Uskoks | Croatian and Slovene peasants | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1590–1610 | Celali rebellions | Ottoman Empire | Celali rebels | Suppressed by Kuyucu Murad Pasha | ||
| 1591–1594 | Rappenkrieg | Basel | Peasants | Negotiations led to a restriction to tax increases. Insurgents were spared punishment | ||
| 1594–1595 | Croquant rebellion | Limousin | Rebels | Croquants disarmed | ||
| 1594–1603 | Nine Years' War | Irish alliance | English victory | |||
| 1594 | Banat Uprising | Ottoman Empire | Serb rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1596 | Club War | Nobility and army | Peasants and army | Nobility victory | ||
| 1596–1597 | Serb Uprising against the Ottomans | Ottoman Empire | Serb rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1597 | First Guale revolt developed in Florida against the Spanish missions and led by Juanillo | Rebels led by Juanillo | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1598 | First Tarnovo uprising | Ottoman Empire | Bulgarian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1600–1601 | Thessaly rebellion | Ottoman Empire | Greek rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1600–1607 | Acaxee Rebellion | Acaxee | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1606–1607 | Bolotnikov rebellion | Tsardom of Russia | Rebels led by Bolotnikov | Rebellion suppressed | 
|
|
| 1616–1620 | Tepehuán Revolt | Tepehuánes | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1618–1625 | Bohemian Revolt | Template:Country data Holy Roman Empire Habsburg monarchy
|
Template:Country data Bohemia Crown of Bohemia
|
Imperial victory | ||
| 1631–1634 | Salt Tax Revolt | Rebels in Biscay | Ringleaders arrested and executed | |||
| 1637–1638 | Shimabara Rebellion | Tokugawa shogunate | Japanese Catholics | Tokugawa victory | [129] | |
| 1639 | Revolt of the va-nu-pieds | Rebels in Normandy | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1640–1668 | Portuguese Revolt | Template:Country data Kingdom of Portugal | Portuguese victory | |||
| 1640–1652 | Catalan Revolt | Catalan defeat | ||||
| 1641–1642 | Irish Rebellion of 1641 | Irish victory and the Founding of the Irish Catholic Confederation | ||||
| 1641 | Acclamation of Amador Bueno in the Captaincy of São Vicente, Brazil | Captaincy of São Vicente | [130][131][132] | |||
| 1642–1652 | English Civil War | Parliamentarian victory, Execution of Charles I, establishment of the Commonwealth of England | ||||
| 1644 | Li Zicheng's Uprising | Ming dynasty | Rebels led by Li Zicheng | Overthrow of the Ming dynasty and the establishment of the Shun dynasty | ||
| 1647 | Naples Revolt | Neapolitan Republic | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1648 | Khmelnytsky uprising | Template:Country data Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth | Emergence of Cossack Hetmanate under Russian protection | |||
| 1648 | Moscow salt riot | Tsardom of Russia | Rebels | Arrest and execution of many of the leaders of the uprising | ||
| 1648–1653 | Fronde | Parlements | Rebellion suppressed | 
|
||
| 1658 | Revolt of Abaza Hasan Pasha | Ottoman Empire | Rebels led by Abaza Hasan Pasha | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1659 | Bakhtrioni uprising | Strategically inconclusive | ||||
| 1662–1664 | Bashkir rebellion | Tsardom of Russia | Bashkir rebels | Demands of the rebels met | ||
| 1664–1670 | Magnate conspiracy | Template:Country data Holy Roman Empire Habsburg monarchy | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1667–1668 | First Revolt of the Angelets | Vallespir | Anti-salt tax rebels | Compromise of Céret. Tax inspectors ended controls | ||
| 1668–1676 | Solovetsky Monastery uprising | Tsardom of Russia | Old Believer monks | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1670–1674 | Second Revolt of the Angelets | Conflent | Rebels against the salt tax | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1672 | Pashtun rebellion | Mughal Empire | Pashtun rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1672–1674 | Lipka rebellion | Template:Country data Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth | Tatars' privileges, payments and religious freedoms guaranteed | [133] | ||
| 1672–1678 | Messina Revolt | Sicilian rebels | ||||
| 1674–1680 | Trunajaya rebellion |
|
Rebel forces | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1675 | Revolt of the papier timbré, an anti-tax revolt in Brittany | Rebels in Brittany | ||||
| 1675–1676 | King Philip's War | Native Americans | Confederation victory | |||
| 1676 | Bacon's Rebellion | Colony of Virginia | Virginia colonists, indentured servants and slaves | Change in Virginia's Native American-Frontier policy | ||
| 1680–1692 | Pueblo Revolt | Puebloans | Pueblo victory, expulsion of Spanish settlers | |||
| 1681–1684 | Bashkir rebellion | Tsardom of Russia | Bashkir rebels | Demands of the rebels met | [134] | |
| 1682 | Moscow Uprising | Tsardom of Russia | Streltsy regiments | Sophia suppressed the Streltsy and Tararui in their attempts to remove her from power | 
|
|
| 1684 | Beckman's Revolt | Maranhão e Grão-Pará | Manoel Beckman and rebels | Rebellion suppressed | [135][136] | |
| 1685 | Monmouth Rebellion | Monmouth rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1685 | Argyll Rebellion | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1686 | Second Tarnovo uprising | Ottoman Empire | Bulgarian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1687–1689 | Revolt of the Barretinas | Catalan rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1688 | Chiprovtsi uprising | Ottoman Empire | Catholic Bulgarian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1688 | Siamese revolution of 1688 |
|
|
Victory for Phetracha's forces and his Dutch allies | ||
| 1688 | Glorious Revolution | Rebels | James II replaced as king by his daughter Mary II and her husband William III | |||
| 1688–1746 | Jacobite risings | Jacobites | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1689 | Karposh’s Rebellion | Ottoman Empire | Bulgarian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | [137] | |
| 1689 | Boston revolt | Dissolution of the Dominion of New England; ouster of officials loyal to James II | ||||
| 1693 | Second Brotherhood | Valencia | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1698 | Streltsy uprising | Tsardom of Russia | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed |
1700–1799
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1702–1715 | War of the Camisards | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1703–1711 | Rákóczi Uprising | Template:Country data Holy Roman Empire | Template:Country data Transylvania Kuruc (Kingdom of Hungary) | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1707–1709 | Bulavin Rebellion | Tsardom of Russia | Don Cossack rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1707–1709 | Newcomers' War | Captaincy of São Vicente, Brazil | Paulistas | Rebellion suppressed | [138][139] | |
| 1709 | Mirwais Hotak's rebellion against Gurgin Khan, the Persian governor of Kandahar | Rebels led by Mirwais Hotak | rebellion successful | |||
| 1709–1710 | Pablo Presbere's insurrection against Spanish colonial power | Rebels led by Pablo Presbere | ||||
| 1710–1711 | Peddlers' War | Pernambuco, Brazil | Rebels | [140][141] | ||
| 1711 | Cary's Rebellion | Rebels | ||||
| 1712 | Tzeltal Rebellion | indigenous rebels | ||||
| 1712 | New York Slave Revolt of 1712 | Rebel slaves | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1715 | First Jacobite rising |
|
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1720 | Vila Rica Revolt | Minas Gerais, Brazil | Rebels | [142][143] | ||
| 1722 | Afghan rebels defeated Shah Sultan Husayn and ended the Safavid dynasty. | Afghan rebels | rebellion successful | |||
| 1728–1740 | First Maroon War | Jamaican Maroons | Maroon victory, the British government offered peace treaties | |||
| 1729 | Natchez revolt | French colonists | the Natchez | |||
| 1731 | Samba rebellion | French Louisiana | Rebel slaves | |||
| 1733–1734 | slave insurrection on St. John | Rebel slaves | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1739 | Stono Rebellion | Escaped slaves | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1741 | New York Conspiracy of 1741 | slaves and poor whites | ||||
| 1743 | Fourth Dalecarlian rebellion | peasants' | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1744–1829 | Dagohoy rebellion | Boholano people | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1745–1746 | Jacobite rising |
|
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1747 | Orangist revolution | |||||
| 1748 | Uprising led by Juan Francisco de León in Panaquire, Venezuela, against monopoly interests and the dominance of the Royal Company Guipuzcoana in terms of trade cocoa | Rebels led by Juan Francisco de León | ||||
| 1749 | Conspiracy of the Slaves | Malta | Rebel slaves | |||
| 1751–1752 | Pima Revolt | |||||
| 1753 | The Lunenburg Rebellion | immigrant rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1755–1769 | The revolution that ended Genoese rule and established a Corsican Republic | Revolution was brought to an end by the French conquest of Corsica | ||||
| 1760 | Tacky's War | Enslaved "Coromantee" people | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1763 | Berbice slave uprising | Society of BerbiceSociety of SurinameBarbados NavyDutch NavyArawak and Carib allies | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1763–1766 | Pontiac's War | numerous North American Indian tribes | Military stalemate | |||
| 1765–1783 | American Revolution | Colonists in British America, Slaves, Native Americans | Independence of the United States of America from the British Empire | |||
| 1765 | Quito Revolt of 1765 | Rebels | ||||
| 1765 | Strilekrigen | Norwegian farmers | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1768 | Louisiana Rebellion of 1768 | Template:Country data New France Creole and German settlers | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1769–1773 | First Carib War | Carib inhabitants of Saint Vincent | ||||
| 1770 | Orlov revolt | Supported by: |
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1770 | Abdzakh revolution. The Circassians of the Abdzakh region started a great revolution in Circassian territory in 1770. Classes such as slaves, nobles and princes were completely abolished. The Abdzakh Revolution coincides with the French Revolution. While many French nobles took refuge in Russia, some of the Circassian nobles took the same path and took refuge in Russia | Circassians of the Abdzakh region | [144] | |||
| 1771–1785 | Tây Sơn wars | Tây Sơn Cham people Chinese Vietnamese (1771–1777) Pirates of the South China Coast |
Nguyễn lord Chinese Vietnamese (Hoà Nghĩa army) |
Nguyễn lord victory | ||
| 1773–1775 | Pugachev's Rebellion | Coalition of Cossacks, Russian Serfs, Old Believers, and non-Russian peoples | Rebellion suppressed | [145] | ||
| 1775 | Rising of the Priests | Template:Country data SMOM Order of Saint John | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1775–1783 | American Revolutionary War | Template:Country data Loyalist (American Revolution) |
Revolutionary victory | 
|
||
| 1780–1782 | José Gabriel Condorcanqui, known as Túpac Amaru II, raises an indigenous peasant army in revolt against Spanish control of Peru. Julián Apasa, known as Túpac Katari allied with Túpac Amaru and lead an indigenous revolt in Alto Peru (present-day Bolivia) nearly destroying the city of La Paz in a siege. | Túpac Amaru II | ||||
| 1780–1787 | The Patriot Revolt | Rebels | ||||
| 1781 | Revolt in Bihar | Rebels in Bihar | ||||
| 1781 | Revolt of the Comuneros | Rebels | ||||
| 1782 | Sylhet uprising | Bengali Muslim Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1782 | Geneva Revolution | Republic of Geneva | the third estate | |||
| 1786–1787 | Shays' Rebellion | Shaysites | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1786–1787 | Lofthusreisingen | Norway | Rebels | |||
| 1787 | Abaco Slave Revolt | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1788 | Kočina Krajina Serb rebellion | Serb rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1789–1799 | French Revolution | Revisionaries | Revolutionary victory
|
|||
| 1789–1790 | Brabant Revolution | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1789–1791 | Liège Revolution | Revolutionary victory
|
||||
| 1790 | Saxon Peasants' Revolt | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1790 | The first slave revolt | British Virgin Islands | Rebels | |||
| 1791 | Whiskey Rebellion | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1791 | Mina conspiracy | Rebels | ||||
| 1791–1804 | Haitian Revolution | 1791–1793
|
1791–1793
|
Haitian victory | 
| |
| 1792 | War in Defence of the Constitution | Template:Country data Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth | Polish defeat | |||
| 1793 | Slave rebellion produced in the Guadeloupe island following the outbreak of the French Revolution . | Rebels | ||||
| 1793 | Jumla rebellion | Kingdom of Nepal
Ranajit Kunwar |
Sobhan Shahi
People of Jumla |
|||
| 1793–1796 | War in the Vendée | Supported by: |
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1794 | Kościuszko Uprising | Template:Country data Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth | Template:Country data Kingdom of Prussia Kingdom of PrussiaTemplate:Country data Holy Roman Empire |
Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1794 | Whiskey Rebellion | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1794 | Stäfner Handel uprising | Republic of Zürich | Rebels | |||
| 1795 | Batavian Revolution | Supported by: |
Supported by: |
Revolutionary victory | ||
| 1795 | Curaçao Slave Revolt | Slave rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1795–1796 | 1795–1796: In those years broke out several slave rebellions in the entire Caribbean, influenced by the Haitian Revolution: in Cuba, Jamaica (Second Maroon War), Dominica (Colihault Uprising), Louisiana (Pointe Coupée conspiracy), Saint Lucia (Bush War, so-called "Guerre des Bois"), Saint Vincent (Second Carib War), Grenada (Fédon's rebellion), Curaçao (led by Tula), Guyana (Demerara Rebellion) and in Coro, Venezuela (led by José Leonardo Chirino) | [146] | ||||
| 1796 | Conspiracy of Equals | Template:Country data French First Republic | Rebels | Conspiracy discovered and repressed | ||
| 1796 | Boca de Nigua Revolt | Dominica | Slave rebels led by Francisco Sopo | |||
| 1796–1804 | White Lotus Rebellion | Qing dynasty | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||
| 1797 | Spithead and Nore mutinies | Mutineers | ||||
| 1797 | 1797 Rugby School Rebellion | Mutineers | ||||
| 1797 | Scottish Rebellion | Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1798 | Irish Rebellion of 1798 | Template:Country data First French Republic |
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1798 | The Maltese Revolt in September 1798 against French administration in Malta. The French capitulated in September 1800 after they were blockaded inside the islands' harbour fortifications for two years | Template:Country data French First Republic | Rebels | |||
| 1799–1800 | Fries's Rebellion | Rebels led by John Fries | ||||
1800–1849
| Date | Revolution/Rebellion | Location | Revolutionaries/Rebels | Result | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1896–1898 | Philippine Revolution | Revolutionary victory | |||||
| 1800 | Gabriel Prosser's suppressed slave rebellion in Virginia | Slave Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1800–1802 | A farmer rebellion in Lærdal, Norway against military conscription | Norway | Rebels | ||||
| 1803 | The rebellion of Robert Emmet in Dublin, Ireland against British rule | Rebels | |||||
| 1803 | The Igbo Landing, a slave ship revolt off the coast of St. Simons, Georgia, in which the enslaved Igbo people committed mass suicide rather than submit to slavery in the United States | Slave Rebels | |||||
| 1804 | Castle Hill convict rebellion | Convict rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1804–1817 | Serbian Revolution | Serb rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1804–1813 | First Serbian uprising |
|
Template:Country data Revolutionary Serbia Supported by: Template:Country data Wallachia (1807–12) |
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1805 | An unsuccessful slave rebellion at Chatham Manor | Slave Rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1817 | Tican's Rebellion | Serb rebels | |||||
| 1808 | Rum Rebellion | Colony of New South Wales | New South Wales Corps | ||||
| 1808 | Kruščica Rebellion | Serb rebels | |||||
| 1808 | Dos de Mayo Uprising | Template:Country data First French Empire | |||||
| 1807–1814 | Peninsular War |
Template:Country data Denmark-Norway (Evacuation of La Romana's division) |
Spanish and allied victory | 
|
|||
| 1808–1833 | Spanish American Wars of independence | Revolutionary victory | |||||
| 1809–1810 | The rebellion of Velu Thampi Dalawa of Travancore | Travancore | Rebels | ||||
| 1809 | Chuquisaca Revolution | Rebels | |||||
| 1819 | La Paz revolution, headed by Pedro Murillo | Rebels | |||||
| 1819 | Tyrolean Rebellion | Supported by: |
French Victory | 
|
|||
| 1809–1825 | Bolivian War of Independence | Royalists:
|
Patriots:
|
Patriot Victory | |||
| 1809–1826 | Peruvian War of Independence | Royalists: | Patriots:
Template:Country data Protectorate of Peru Co-belligerents Template:Country data United Provinces of the Río de la Plata |
Patriot Victory | |||
| 1810 | The House Tax Hartal was an occasion of nonviolent resistance to protest a tax in parts of British India, with a particularly noteworthy example of hartal (a form of general strike) in the vicinity of Varanasi | Demonstrators | |||||
| 1810 | The West Florida rebellion against Spain, eventually becomes a short-lived republic. | Rebels | |||||
| 1810–1821 | Mexican War of Independence | Template:Country data Spanish Empire | Insurgent victory | ||||
| 1810 | May Revolution | Template:Country data Spanish Empire | Primera Junta | Primera Junta victory | |||
| 1810–1818 | Argentine War of Independence | Royalists
|
Patriots:
Republiquetas |
Argentine victory and emancipation from Spanish colonial rule | |||
| 1810–1823 | Venezuelan War of Independence | Template:Country data Spanish Empire Royalists
|
1810:
1811–1816:
1816–1819:
1819–1823: |
Patriot victory | |||
| 1810–1826 | Chilean War of Independence | Royalists:
Mapuche allies of the Royalists |
Patriots:
Mapuche allies of the Patriots |
Chilean victory | |||
| 1811 | Paraguayan Revolt | Paraguayan Rebels | Revolt victory | ||||
| 1811 | German Coast uprising | Local planters
Militia and regulars |
Enslaved Africans | Suppression of uprising | |||
| 1811 | 1811 Independence Movement | Salvadoran revolutionaries | Rebellion suppressed | 
|
|||
| 1812 | The peasant rebellion of Hong Gyeong-nae | Joseon dynasty | Rebels | ||||
| 1812 | Aponte conspiracy | Template:Country data Spanish Empire
|
Cuban rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1812 | The rebellion in protest against slavery led by José Leocadio, Pedro de Seda, and Pedro Henríquez in Dominican Republic | ||||||
| 1814 | Norwegian War of Independence |
Supported by:
|
Swedish victory | ||||
| 1814 | Hadži Prodan's Revolt | Template:Country data Revolutionary Serbia Serbian rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1815 | George Boxley's slave rebellion in Spotsylvania County, Virginia | Slave rbels | |||||
| 1815–1817 | Second Serbian uprising | Strategic Serbian diplomatic victory; Establishment of the autonomous Principality of Serbia | |||||
| 1816 | Bussa's rebellion |
|
Slave rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1816–1858 | Seminole Wars | Seminole Yuchi Choctaw Freedmen |
American victory | ||||
| 1817 | Pernambucan Revolt | Portuguese victory and resulted in the creation of the short-lived Republic of Pernambuco (7 March 1817 – 20 May 1817). | |||||
| 1817 | Pentrich rising, | Rebels led by William Oliver | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1817 | Paika Rebellion | Bhoi dynasty | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1817–1818 | Uva-Wellassa Rebellion | Rebellion suppressed | |||||
| 1820 | The Revolutions of 1820 were a wave of revolutions attempting to establish liberal constitutional monarchies in Italy, Spain and Portugal. | ||||||
| 1820 | Radical War | Various Groups | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1820–1822 | Ecuadorian War of Independence | Royalists:
|
Patriot victory. Annexation of the territory to Gran Colombia. | ||||
| 1820–1824 | The revolutionary war of independence in Peru led by José de San Martín | ||||||
| 1821 | Marcos Xiorro's conspiracy to incite a slave revolt in Spanish Puerto Rico | Rebels | |||||
| 1821 | Wallachian uprising | Template:Country data Wallachia (revolutionary)
|
Ottoman military victory Wallachian political victory
End of the Phanariote Era |
||||
| 1821–1829 | Greek War of Independence | 1821:
After 1822: Military support:
Diplomatic support:
|
Greek victory | ||||
| 1822 | Denmark Vesey's suppressed slave uprising in South Carolina | Slave rebels | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1822–1823 | The republican revolution in Mexico overthrows Emperor Agustín de Iturbide | Rebels | Rebel victory | ||||
| 1822–1825 | Brazilian War of Independence |
|
Template:Country data Empire of Brazil |
Brazilian victory | |||
| 1823 | Demerara rebellion of 1823 |
|
Rebel slaves | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1824 | Chumash revolt of 1824 | Chumash Native Americans | |||||
| 1825 | Decembrist revolt | Northern Society of the Decembrists | Rebelion suppressed, Decembrists executed or deported to Siberia | ||||
| 1825–1830 | Java War | Template:Country data Dutch Empire
|
Javanese rebels | Dutch victory | |||
| 1826 | Janissary revolts | slave soldier rebels | |||||
| 1826–1827 | Fredonian Rebellion | Rebellion suppressed | |||||
| 1826–1828 | Lao rebellion | Military support: |
Siamese victory | ||||
| 1827–1828 | The failed conservative rebellion in Mexico led by Nicolás Bravo. | rebels led by Nicolás Bravo | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1828–1834 | Liberal Wars | Supported by:
|
Supported by:
|
Liberal victory | |||
| 1829 | Bathurst War | Wiradjuri | British victory | ||||
| 1829–1832 | War of the Maidens. Countrymen dressed as women resisted the new forestry law, which restricted their use of the forest | Template:Country data Bourbon Restoration France (Bourbon Restoration) (until 1830)
Template:Country data July Monarchy France (July Monarchy) (from 1830) |
rebels | ||||
| 1830 | The Revolutions of 1830 were a wave of Romantic nationalist revolutions in Europe | ||||||
| 1830–1831 | Belgian Revolution | Template:Country data United Kingdom of the Netherlands | Belgian victory | ||||
| 1830 | July Revolution | Template:Country data Bourbon Restoration France (Bourbon Restoration) | middle class against Bourbon King Charles X | Charles X which forced him out of office and replaced him with the Orleanist King Louis-Philippe (the "July Monarchy") | 
|
||
| 1830–1831 | November uprising | Congress Poland
|
Russian victory | ||||
| Ustertag revolution | Canton of Zurich | Rebels | |||||
| 1830 | Bathurst Rebellion |
|
Convict rebels | ||||
| 1830–1833 | Yagan's War | Noongar people | |||||
| 1830–1836 | Tithe War | Irish Demonstrators | |||||
| 1831 | Nat Turner's slave rebellion | Insurgents | Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1831 | Merthyr Rising | ||||||
| 1831, 1834, 1848 | Canut revolts | Template:Country data July Monarchy France (July Monarchy) | Lyonnais silk workers (French: canuts) | ||||
| 1831–1832 | Bosnian uprising | Ottoman victory | |||||
| 1831–1832 | Baptist War |
|
Slave rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1832 | June Rebellion | Template:Country data July Monarchy France (July Monarchy)
|
Rebellion suppressed | ||||
| 1832–1833 | Anastasio Aquino's Rebellion | Template:Country data Federal Republic of Central America
|
Indigenous rebels | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1832–1843 | Abdelkader's rebellion in French-occupied Algeria | Template:Country data July Monarchy France (July Monarchy) | Rebels led by Abdelkader | ||||
| 1833–1835 | Lê Văn Khôi revolt | Nguyễn dynasty | Lê Văn Khôi rebels
Supported by:
|
Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1834 | Flores' Rebellion | Nicaragua | rebels | ||||
| 1834–1859 | Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus | rebels | |||||
| 1835–1836 | Texas Revolution | De facto Texian independence from the Centralist Republic of Mexico | |||||
| 1835 | Malê revolt |
|
Malê slaves (primarily Nagôs) | Rebellion suppressed | |||
| 1835–1840 | The Cabanagem was a popular revolution and pro-separatist movement that occurred in the then province of Grão-Pará, Empire of Brazil | Template:Country data Empire of Brazil | Rebels | ||||
| 1835–1845 | Ragamuffin War |
Supported by:
|
Peace treaty between both parties
|
||||
- 1837: Revolt of 1837 (New Mexico), also known as the Chimayó Rebellion, against the Mexican governor of New Mexico
- 1837–1838: The Rebellions of 1837 and the Upper Canada Rebellion: failed republican revolutions against British rule in Canada.
- 1837-1838: The Sabinada was a revolt by military officer Francisco Sabino that occurred in Brazil's Bahia province.
- 1838-1841: The Balaiada was a social revolt between 1838 and 1841 in the interior of the Province of Maranhão, Brazil.
- 1839: The Amistad Rebellion, a slave ship revolt that was initially successful but ended with the eventual capture of the slaves by the United States .
- 1839–1843: The Rebecca Riots were a series of protests undertaken by farmers and agricultural workers in Wales, in response to perceived unfair taxation
- 1841: Creole revolt, a successful slave revolt aboard the Creole, ending with their arrival at Nassau, where slavery was abolished.
- 1841-1842: Dorr Rebellion in Rhode Island
- 1841–1842: The Afghan uprising. Hostile Afghan tribes massacred Elphinstone's British army including some 12,000 civilian dependents and camp followers.[152]
- 1842: The Slave Revolt in the Cherokee Nation, an attempted escape of slaves from the Cherokee, that ended with their capture.
- 1845 - 1872 The New Zealand Wars.
- 1846: The Greater Poland uprising against Austrian rule.
- The failed Kraków uprising ends in slaughter.
- 1846: Bear Flag Rebellion in Alta California, quickly subsumed in the U.S. military takeover of the territory
- 1847: The Caste War of Yucatán, revolt of Maya against the Mexican state.
- 1847: The Taos Revolt in New Mexico against the United States.
- 1847: The Sonderbund War, a revolt by the Swiss Confederation against the centralization of power by Catholic cantons, resulting in the rise of Switzerland as a federal state.
- 1848: The Revolutions of 1848 were a wave of failed liberal and republican revolutions that swept through Europe.
- The French Revolution of 1848 led to the creation of the French Second Republic.
- The Revolutions of 1848 in the Italian states.
- The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states.
- The Revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire
- The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 grew into a war for independence from Austrian Empire.
- The Slovak Uprising of 1848–49.
- The Revolutions of 1848 in the Danish States started in the German speaking cities of Altona and Kiel. It spilled into a peaceful revolution in Copenhagen, which abolished absolutism in favor of parliamentary constitutional monarchy, and a counter-revolutionary war against the German speaking minority.
- The March Unrest.
- The Czech Revolution of 1848.
- The Greater Poland uprising.
- The Young Irelander Rebellion of 1848 took place during the Great Famine.
- Serbian Revolution of 1848.
- Wallachian Revolution of 1848.
- Moldavian Revolution of 1848.
- 1848: Matale Rebellion A rebellion in Ceylon against British colonial rule.
- 1848-1849: Beach Rebellion (Revolução Praieira) in Pernambuco, Brazil.[153]
1850–1899
right|thumb|The current Puerto Rican Flag was flown for the first time in Puerto Rico by Fidel Vélez and his men during the "Intentona de Yauco" revolt
- 1851–64: The Taiping Rebellion by the God Worshippers against the Qing dynasty of China. In total between 20 and 30 million lives had been lost, making it the second deadliest war in human history.
- 1852: The Kautokeino rebellion in Kautokeino, Norway.
- 1852–62: The Herzegovina Uprising (1852–62) in Ottoman Herzegovina.
- 1853–55: The Small Knife Society rebellion in Shanghai, China.
- 1854: A revolution in Spain against the Moderate Party Government.
- 1854: The Eureka Rebellion (Eureka Stockade) in Ballarat, Victoria, Australia. Miners battled British Colonial forces against taxation policies of the Government.
- 1854–56: Peasant Rebel in Vietnam, led by Cao Ba Quat, against the Nguyễn dynasty.
- 1854–56: The Red Turban Rebellion (1854–1856) in Guangdong (Canton), China.
- 1854–73: The Miao Rebellion in China.
- 1854–55: The Revolution of Ayutla in Mexico.
- 1855–73: The Panthay Rebellion by Chinese Muslims against the Qing dynasty.
- 1857: The Indian rebellion against British East India Company, marking the end of Mughal rule in India. Also known as the 1857 War of Independence and, particularly in the West, the Sepoy Mutiny.
- 1858: The Mahtra War in Estonia.
- 1858: Pecija's First Revolt, in Ottoman Bosnia.
- 1858–61: The War of the Reform in Mexico.
- 1859: John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry, an effort by abolitionist John Brown to initiate an armed slave revolt in Southern states by taking over Harpers Ferry Armory in Virginia.
- 1859: The Second Italian War of Independence.
- 1861–65: The American Civil War in the United States, between the United States and the Confederate States of America, which was formed out of eleven southern states.
- 1863–65: A counter-rebellion occurred in the self-declared Free State of Jones in Mississippi.
- 1861–66: Quantrill's Raiders in Missouri.
- 1862: The Sioux Uprising in Minnesota.[154]
- 1862–77: The Muslim Rebellion by Chinese Muslims against the Qing dynasty.
- 1862: The 23 October 1862 Revolution was a popular insurrection which led to the overthrow of King Otto of Greece.
- 1863: The New York Draft riots.[155]
- 1863–65: The January Uprising was the Polish uprising against the Russian Empire.
- 1864–65: The Mejba Revolt was a rebellion in Tunisia against the doubling of an unpopular poll tax imposed by Sadok Bey.
- 1865: The Morant Bay rebellion.
- 1866: The Uprising of Polish political exiles in Siberia.
- 1866–68: The Meiji Restoration and modernization revolution in Japan. Samurai uprising leads to overthrow of shogunate and establishment of "modern" parliamentary, Western-style system.
- 1867: The Fenian Rising: an attempt at a nationwide rebellion by the Irish Republican Brotherhood against British rule.
- 1868: The Glorious Revolution in Spain deposes Queen Isabella II.
- 1868: The Grito de Lares was the first major revolt against Spanish rule in Puerto Rico. The rebels proclaimed the independence of Puerto Rico from Spain.
- Ten Years' War (1868–1878), also known as the Great War (Guerra Grande) and the War of '68, was part of Cuba's fight for independence from Spain, led by Cuban-born planters (especially by Carlos Manuel de Céspedes) and other wealthy natives.
- 1869–70: The Red River Rebellion, the events surrounding the actions of a provisional government established by Métis leader Louis Riel at the Red River Colony, Manitoba, Canada.
- 1870–72: The Revolution of the Lances, the National Party revolts against the Colorado Government in Uruguay.
- 1871: The Paris Commune.
- 1871–72: Porfirio Díaz rebels against President Benito Juárez of Mexico.
- 1871: The liberal revolution in Guatemala.
- 1873: The Petroleum Revolution in the First Spanish Republic.
- 1873–74: The Cantonal rebellion in the First Spanish Republic.
- 1875: The Deccan Riots.
- 1875: The Stara Zagora Uprising, a revolt by the Bulgarian population against Ottoman rule.
- 1875–76: The Svaneti uprising of 1875–1876
- 1875–78: The Great Eastern Crisis:
- 1875–77: The Herzegovinian rebellion, the most famous of the rebellions against the Ottoman Empire in Herzegovina; unrest soon spread to other areas of Ottoman Bosnia.
- 1876: The April uprising, a revolt by the Bulgarian population against Ottoman rule.
- 1876: The Razlovtsi insurrection, a revolt by the Bulgarian population against Ottoman rule, part of the April Uprising.
- 1876–78: Serbian-Turkish Wars (1876–1878)
- 1876–78: Montenegrin–Ottoman War (1876–78)
- 1877–78: Romanian War of Independence
- 1878: Kumanovo Uprising
- 1878: Kresna–Razlog uprising, a revolt by the Bulgarian population against Ottoman rule.
- 1878 Greek Macedonian rebellion
- Epirus Revolt of 1878
- Cretan Revolt (1878)
- 1876: The second rebellion by Porfirio Díaz against President Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada of Mexico.
- 1877: The Satsuma Rebellion of Satsuma ex-samurai against the Meiji government.
- 1879: Little War (Cuba) or Small War, second of three conflicts between Cuban rebels and Spain. It started on 26 August 1879 and ended in rebel defeat in September 1880.
- 1879–1882: The Urabi Revolt: an uprising in Egypt on 11 June 1882 against the Khedive and European influence in the country. It was led by and named after Colonel Ahmed Urabi.
- 1880–1881: The Brsjak revolt.
- 1883: The Timok Rebellion was a popular uprising that began in eastern Serbia.
- 1885: A peasant revolt in the Ancash region of Peru led by Pedro Pablo Atusparía succeeds in occupying the Callejón de Huaylas for several months.
- 1885–96: Cần Vương movement of Vietnam, led by emperor Hàm Nghi, against French colonialism
- 1885: The North-West Rebellion of Métis in Saskatchewan.
- 1885: Bulgarian unification - accomplished after revolts in Eastern Rumelian towns, followed by a coup.
- 1888: The Peasant Rebellion in Banten, Indonesia.
- 1890–1914: The Saminism Movement in Indonesia.
- 1890: Revolution of the Park, Argentina.
- 1893: Revolution of 1893, Argentina
- 1893: A liberal revolt brings José Santos Zelaya to power in Nicaragua.
- 1894–95: The Donghak Peasant Revolution: Korean peasants led by Jeon Bong-jun revolted against the Joseon dynasty; the revolt was crushed by Japanese and Chinese intervention, leading to First Sino-Japanese War.
- 1895: The revolution against President Andrés Avelino Cáceres in Peru ushers in a period of stable constitutional rule.
- 1895-1896: The War of Canudos was a conflict between the First Brazilian Republic and the residents of Canudos in the northeastern state of Bahia.
- 1895–1896: The First Italo-Ethiopian War in which Ethiopians fought against Italians colonizers.
- 1895–1898:Cuban War of Independence, the last of three liberation wars that Cuba fought against Spain, being initiated by José Martí.
- 1896: Yaqui Uprising in Sonora and Arizona
- 1896–98: The Philippine Revolution, a war of independence against Spanish rule directed by the Katipunan society.
- 1897: The Intentona de Yauco (Attempted Coup of Yauco), was the second and last major revolt against Spanish colonial rule in Puerto Rico, staged by Puerto Rico's pro-independence movement.
- 1898: The Dukchi Ishan (Andican Uprising): Kirgiz, Uzbek, and Kipcak peoples rebelled against Tsarist Russia in Turkestan (Fargana Valley).
- 1898: The Hut Tax War was a resistance in the newly annexed Protectorate of Sierra Leone to a new, severe tax imposed by the colonial military governor.
- 1898: The Dog Tax War was a confrontation between the Colony of New Zealand and a group of Northern Māori, led by Hone Riiwi Toia, opposed to the enforcement of a 'dog tax'.
- 1898: The Wilmington insurrection of 1898, A mob of white supremacists forced out the city government of Wilmington, North Carolina.[156]
- 1899: The tancament de caixes, a tax revolt in Barcelona.
- 1899–1902: The Philippine–American War, an insurgency against the imposition of colonial rule by the United States following the transfer of the Philippines from Spain to the U.S. in the Treaty of Paris which ended the Spanish–American War.
- 1899–1901: The Boxer Rebellion against foreign influence in areas such as trade, politics, religion and technology that occurred in China during the final years of the Qing dynasty, which was defeated by the Eight-Nation Alliance.
- 1899–1962: The Mau was a non-violent movement for Samoan independence from colonial rule (by Germany and then New Zealand) during the first half of the 20th century.
1900s
- 1901–1936: Holy Man's Rebellion.
- 1903: The Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising breaks out in the Ottoman Empire.
- 1904: Revolution of 1904
- 1904: A liberal revolution in Paraguay.
- 1904–1908: Macedonian Struggle.
- 1904–1908: Herero Wars.
- 1905: Argentine Revolution of 1905.
- 1905–1906: The Persian/Iranian constitutional revolution.
- 1905–1906: The Maji Maji Rebellion in German East Africa.
- 1905: Shoubak Revolt.
- 1905: Łódź insurrection.
- 1905–1907: Revolution in the Kingdom of Poland (1905–07).
- 1905–1906: 1905 Tibetan Rebellion.
- 1905–1907: 1905 Russian Revolution, which was abortive and ultimately crushed, though forming the critical precedent for the 1917 Russian Revolution.
- 1906: Bambatha Rebellion.
- 1906–1908: Theriso revolt.
- 1907: The Romanian Peasants' Revolt.
- 1908: The Young Turk Revolution: Young Turks force the autocratic ruler Abdul Hamid II to restore parliament and constitution in the Ottoman Empire.
- 1909: HNLMS De Zeven Provinciën (1909).
- 1909: Hauran Druze Rebellion.
1910s
- 1910–1920: The Mexican Revolution overthrows the dictator Porfirio Díaz; seizure of power by the National Revolutionary Party (later called Institutional Revolutionary Party).
- 1910: The republican revolution in Portugal.
- 1910: The Albanian Revolt of 1910 against Ottoman centralization policies in Albania.
- 1910–1911: The Sokehs Rebellion erupts in German-ruled Micronesia. Its primary leader, Somatau, is executed soon after being captured.
- 1911–1912: The Xinhai Revolution overthrows the ruling Qing dynasty and establishment of the Republic of China.
- 1911–1912: The East Timorese rebellion against colonial Portugal.
- 1912: The Albanian Revolt of 1912 against Ottoman Empire rule in Albania.
- 1912-1916: The Contestado War was a guerrilla war for land between settlers and landowners in South Brazil.
- 1913: The Second Revolution against President Yuan Shikai of China.
- 1914: The Ten Days War was a shooting war involving irregular forces of coal miners using dynamite and rifles on one side, opposed to the Colorado National Guard, Baldwin Felts detectives, and mine guards deploying machine guns, cannon and aircraft on the other, occurring in the aftermath of the Ludlow massacre. The Ten Days War ended when federal troops intervened.
- 1914–1915: The Boer Revolt against the British in South Africa.
- 1914: The revolt of Peasants of Central Albania overthrows Prince William of Wied.
- 1915: The Armenian revolt in city of Van against the Ottomans in Turkey.
- 1915–1916: The National Protection War against the Empire of China headed by Emperor Yuan Shikai. The Republic of China was restored.
- 1915–1916: The Tapani incident is the last major Chinese uprising in Taiwan during the Japanese colonial era.
- 1916: The Easter Rising in Dublin, Ireland during which the Irish Republic was proclaimed.
- 1916: An anti-French uprising in Algeria.
- 1916: The Central Asian Revolt started when the Russian Empire government ended its exemption of Muslims from military service.
- 1916: Cochinchina uprising of Vietnam against French colonialism
- 1916–1917: The Tuareg rebellion against French colonial rule of the area around the Aïr Mountains of northern Niger.
- 1916–1918: The Arab Revolt with the aim of securing independence from the Ottoman Empire.
- 1916–1923: The Irish War of Independence, the period of nationalist rebellion, guerrilla warfare, political change and civil war which brought about the establishment of the independent nation, the Irish Free State. Sparking the Irish Civil War between pro-treaty forces and pro-republic forces
- 1916–1947: The Indian people's struggle against the British for Indian Independence.
- 1917: The French Army Mutinies.
- 1917: Thái Nguyên uprising of Vietnam, led by Trinh Van Can, against French colonialism
- 1917: The February Revolution made Tsar Nicholas II abdicate and abolishes the Russian monarchy
- 1917: The Green Corn Rebellion takes place in rural Oklahoma.
- 1917: The October Revolution in Russia: Bolsheviks take over the provisional government of the Russian Republic, instituting the first socialist society in the world. The chaos leads to the final collapse of the Russian Empire as many peripheral territories declare independence and anti-Bolshevik forces rose in revolt against the new Soviet Russian order, sparking the Russian Civil War, eventually leading to the establishment of the Soviet Union.
- 1917–1921: The Ukrainian Revolution: Nationalists and Soviet allies both declare separate republics in Ukraine, fighting anarchists under Nestor Makhno as well as White forces loyal to the Ukrainian State, a German puppet state.
- 1918: The Finnish Civil War: Finnish Red Guards sympathetic to the Bolsheviks in Russia rise in revolt against the newly independent Finnish Whites, supported by the German Empire.
- 1918: The Wilhelmshaven mutiny.
- 1918: The German Revolution overthrows the Kaiser; establishment of the Weimar Republic after a brief socialist uprising by the Spartacists.
- 1918: Aster Revolution ends Habsburg rule in Hungary
- 1918–1919: A wave of strikes and student unrest shakes Peru. These events influence two of the dominant figures of Peruvian politics in the 20th century: Víctor Raúl Haya de la Torre and José Carlos Mariátegui.
- 1918–1919: The Greater Poland Uprising, Polish uprising against German authorities.
- 1918–1919: The 1919 Egyptian revolution against the British occupation of Egypt.
- 1918–1920: The Georgian–Ossetian conflict, the southern Ossetians revolted against Georgian rule.[157]
- 1918–1922: The Third Russian Revolution, a failed anarchist revolution against Bolshevism.
- 1918–1931: The Basmachi Revolt against Soviet Russia rule in Central Asia.
- 1919: The Christmas uprising in Montenegro: Montenegrins (Zelenaši) rebelled against unification of the Kingdom of Montenegro with the Kingdom of Serbia.
- 1919: The Sette Giugno (Malta).
- 1919-1920: The Biennio Rosso in Italy.
- 1919–1920: Iraqi revolt against the British and British-Indian troops, attempting to create a Muslim regime or the restoration of Ottoman rule.
- 1919–1921: The Tambov Rebellion, one of the largest peasant rebellions against the Bolshevik regime during the Russian Civil War.
- 1919–1921: The Silesian uprisings of the ethnic Poles against Weimar rule.
- 1919–1922: The Turkish War of Independence commanded by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
- 1919: Simko Shikak revolt in Persia.
- 1919: A revolution in Hungary, resulting in the short-lived Hungarian Soviet Republic.
- 1919: Counterrevolution in Hungary against the Hungarian Soviet Republic. After many failed attempts, legitimist and other far-right forces take over Transdunabia after the Soviet Republic falls to the Romanians.
- 1919: March 1st movement In Korea against the Japanese occupation (1910). Ultimately fails
1920s
- 1920: The Pitchfork uprising was a peasant uprising against the Soviet policy of the war communism in what is today Tatarstan.
- 1920: Kapp Putsch and the following Ruhr Uprising in Germany
- 1920–1922: Patagonia Rebelde, the uprising and violent suppression of a rural workers' strike in the Argentine province of Santa Cruz in Patagonia between 1920 and 1922.
- 1920–1922: Gandhi led Non-cooperation movement.
- 1920: The Husino uprising in Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- 1921: The Battle of Blair Mountain ten to fifteen thousand coal miners rebel in West Virginia, assaulting mountain-top lines of trenches established by the coal companies and local sheriff's forces in the largest armed, organized uprising in American labor history.
- 1921: The Kronstadt rebellion of Soviet sailors against the government of the early Russian SFSR.
- 1921: The Poplar Rates Rebellion.
- 1921: Brief communist takeover of Baranya county, declaring the Serbian-Hungarian Baranya-Baja Republic
- 1921: Uprising in West Hungary by far-right paramilitaries resisting the Hungarian handover of Burgerland to Austria
- 1921: Habsburg legitimist rebellion attempting to restore Charles IV to the throne of Hungary.
- 1921: The rebellion of Mirdita led by Markagjoni declares the independence of Republic of Mirdita from Albania.
- 1921–1922: The Karelian Uprising
- 1921–1923: The Yakut Revolt.
- 1921–1924: A revolution in (Outer) Mongolia re-establishes the country's independence and sets out to construct a Soviet-style socialist state.
- 1921: The Moplah rebellion, uprising against the colonial British authority and Hindu landlords in the Malabar in South India by Mappila Muslims, aftermath of a series of peasant uprising in the past centuries.
- 1921: March Action in Germany
- 1922: The March on Rome, organized mass demonstration which resulted in Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party acceding to power in the Kingdom of Italy.
- 1922: The Bondelswarts Rebellion by Khoikhoi people against the apartheid regime of South West Africa.
- 1922–1923: The Irish Civil War, between supporters of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the government of the Irish Free State and more radical members of the original Irish Republican Army who opposed the treaty and the new government.
- 1923: Bajram Curri attacks gendarmerie of Kruma, Albania.
- 1923: The founding of the Republic of Turkey by overthrow of the Ottoman Empire and introduction of Atatürk's Reforms.
- 1923: The Klaipėda Revolt in the Memel territory that had been detached from Germany after World War I.
- 1923: Küstrin Putsch in Germany
- 1923: The German October, communist revolutions across Germany, including the Hamburg Uprising and Reichsexekution in Saxony and Thuringia
- 1923-24: Rebellion in Pfalz, by Franz Joseph Heinz's Pfälzischen Corps
- 1923: The Adwan Rebellion in Jordan.
- 1924–1925: The Khost rebellion in Afghanistan.
- 1924: The August Uprising in Georgia against Soviet rule.
- 1925: The Sheikh Said Rebellion.
- 1925: The July Revolution in Ecuador.
- 1925–1927: The Great Syrian Revolt, a revolt initiated by the Druze and led by Sultan al-Atrash against French Mandate.
- 1926: Angry catholic peasants of Dukagjin, Shkodër fight against army and gendarmerie.
- 1926: The National Revolution in Portugal initiated a period known as the National Dictatorship.
- 1926–1929: The Cristero War in Mexico, an uprising against anti-clerical government policy.
- 1926–1927: The first Communist rebellion in Indonesia against colonialism and imperialism of Dutch colonial government.
- 1927-1937: First half of the Chinese Civil War.
- 1927: Sheikh Abdurrahman rebellion by Kurdish Zazas against Turkey.
- 1927–1930: The Wahhabi Rebellion of Ikhwan against Ibn Saud in Arabia.
- 1927–1931: The Ağrı Rebellion by Kurds against Turkey.
- 1927–1933: A rebellion led by Augusto César Sandino against the United States presence in Nicaragua.
- 1928–1931: A rebellion led by Bhagat Singh against the British Rule in India.
- 1929: The Women's War broke out when thousands of Igbo women traveled to the town of Oloko to protest against the Warrant Chiefs, whom they accused of restricting the role of women in the government.
1930s
- 1930: The Brazilian Revolution of 1930 led by Getúlio Vargas.
- 1930–1931: Nghe-Tinh Revolt in Vietnam, led by the Communist Party of Indochina, against French colonialism.
- 1930–1934: The Saya San Rebellion in British Burma, led by Saya San, against British rule in Burma.
- 1930: Yên Bái mutiny of Vietnam, led by Vietnamese Nationalist Party, against French Occupation.
- 1930: The Salt Satyagraha, a campaign of non-violent protest against the salt tax in British India.
- 1930: The Musha Incident led by the Seediq Indigenous group is the last major uprising in Japanese-controlled Taiwan.
- 1932: The Constitutionalist Revolution against provisional president Getúlio Vargas led Brazil to a short civil war.
- 1932: The Aprista revolt in Trujillo, Peru.
- 1932: The 1932 Salvadoran peasant uprising, known as La matanza ("The Slaughter"), Pipil and peasant rebellion led by Farabundo Martí
- 1932: The Siamese coup d'état of 1932, sometimes called the "Promoters Revolution", ends absolute monarchy in Thailand.
- 1933: The popular revolution against Cuban dictator Gerardo Machado.
- 1933: Dutch sailors on the cruiser HNLMS De Zeven Provinciën mutiny.
- 1933: Boworadet Rebellion in Thailand
- 1934: Latvian coup d’état by Latvian prime minister Kārlis Ulmanis against the parliamentary system in Latvia. Lasted until 1940.
- 1934: The Austrian Civil War between paramilitary forces of socialist Schutzbund and fascist Heimwehr
- 1934: The Spanish Revolutionary General Strike of October took place during the black biennium of the Second Spanish Republic.
- 1935: Muharrem Bajraktari, former Aide-de-camp of King Zog, led a revolt against government in North Albania.
- 1935: A secret anti-Zogist organization led an uprising against the Albanian government and King Zog in Fier and Lushnje.
- 1935: The Communist Uprising in Rio Grande do Norte, Pernambuco and Rio de Janeiro; Brazil .[158][159]
- 1935–1936: Iraqi Shia revolts against Hashemite central rule.
- 1935: Imam Reza shrine rebellion in Iran of Shi'ite radicals against Reza Shah.
- 1935–1936: Second Italo-Ethiopian War in which Ethiopians resisted Italian occupation.
- 1936: The Febrerista Revolution, led by Rafael Franco, ended oligarchic Liberal Party rule in Paraguay.
- 1936: The Spanish Revolution, a workers' social revolution that began during the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War.
- 1936: The Portuguese Naval revolt against the Estado Novo regime.
- 1936–1939: Arab revolt in Palestine against the British Mandate.
- 1936–1939: Spanish Civil War.
- 1936–1939: David Toro seizes power in Bolivia, initiating a period of so-called "military socialism", including nationalization of Standard Oil and passage of progressive labor laws, and establishing a corporative state in 1938.
- 1937–1938: The Dersim Rebellion, the most important Kurdish rebellion in modern Turkey.[160]
- 1937: The Fets de Maig or "May Days", a major strike in Catalonia, Spain.
- 1937: The Revolt of Delvina, a revolt of gendarmerie and local peasants against King Zog.
- 1938: Sudeten German uprising orchestrated by Sudeten German Party against Czechoslovakia.
- 1938: The Integralist Uprising in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil .[161]
- 1939–1965: Spanish Maquis insurgency
- 1939–1940: The Irish Republican Army attempt a sabotage campaign against British rule in Northern Ireland
- 1939–1945: Resistance during World War II
- 1939-1945: Polish resistance
1940s
- 1940–1948: The Insurgency in Chechnya.
- 1940: Cochinchina Uprising of Vietnam, led by Viet Minh, against French and Japanese Occupation
- 1940-1944: French Resistance
- 1940: Bac Son Uprising of Vietnam, led by Viet Minh, against French and Japanese Occupation
- 1940–1947: Mohammad Ali Jinnah's struggle for a separate state for the Muslims of India.
- 1941: The June Uprising against the Soviet Union in Lithuania.
- 1941: Legionnaires' rebellion and Bucharest pogrom, Romania
- 1941–1945: Yugoslav People's Liberation War against the Axis Powers in World War II.
- 1941–1944: Greek Resistance
- 1941: Do Luong Mutiny of Vietnam, led by Doi Cung, against French occupation
- 1942: Sri Lankan soldiers ignite the Cocos Islands Mutiny in an unsuccessful attempt to transfer the islands to Japanese control.
- 1942: The destruction of the German garrison in Lenin.
- 1942–1944: The Irish Republican Army tries to start a new campaign in Northern Ireland called the Northern Campaign and fails
- 1943: The Warsaw Ghetto uprising.
- 1943: The uprising at Treblinka extermination camp.
- 1943: Following the liberation of Albania, the Communist Party of Albania under Enver Hoxha consolidated its control and declared the People's Republic of Albania in January 1946.
- 1943: The uprising at Sobibór extermination camp.
- 1943: The Woyane Rebellion in northern Ethiopia threatens to topple the newly restored government, and is put down with British help.
- 1943–1945: Italian Resistance Movement against Nazi occupation and the Fascist Italian Social Republic, culminating in 25 April final insurrection in Northern Italy.
- 1944: The Guatemalan Revolution overthrows the dictator Federico Ponce Vaides by liberal military officers.
- 1944: The Warsaw uprising was an armed struggle during the Second World War by the Polish Home Army (Armia Krajowa) to liberate Warsaw from German occupation and Nazi rule. It started on 1 August 1944.
- 1944: The Paris Uprising staged by the French Resistance against the German Paris garrison.
- 1944: The Slovak National uprising against Nazi Germany.
- 1944: The uprising at Auschwitz extermination camp.
- 1944–1947: The Jewish insurgency in Palestine.
- 1944–1947: A Communist-friendly government was installed in Bulgaria following a coup d'état and the Soviet invasion.
- 1944–1949: The Greek Civil War.
- 1944-1953: Anti-communist resistance in Poland.
- 1944–1965: The Forest Brothers Rebellion in Baltic states against Soviet Union.
- 1945: The first anti-communist revolt in Eastern Europe in Koplik, Albania led by bayraktars and intellectuals.
- 1945–1949: The Indonesian National Revolution against Dutch after their independence from Japan. Led by Sukarno, Hatta, Tan Malaka, etc. with the Dutch led by Van Mook.
- 1945: The Prague uprising against German occupation during World War II.
- 1945: Ba To Uprising of Vietnam, led by Viet Minh, against French and Japanese Occupation
- 1945: The August Revolution led by Ho Chi Minh and Viet Minh declared the independence of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam from French rule.
- 1945: A democratic revolution in Venezuela, led by Rómulo Betancourt.
- 1945-1949: Second half of the Chinese Civil War.
- 1946: The Royal Indian Navy Mutiny takes place in Bombay, and spreads to different parts of British India, demanding Indian independence.
- 1946 — 1951: Telangana Rebellion a Communist-led Peasant rebellion in Telangana and Hyderabad, India , ("Telangana Peasants Armed Struggle") was a Peasant rebellion against the feudal lords of the Telangana region in the princely state of Hyderabad, and later the Indian government.
- 1946: Another attempt of anti-communist forces in Albania to take out the government takes place in Shkodër.
- 1946: The Battle of Athens, Tennessee (aka the McMinn County War); a local revolt against officials accused of rigging local elections.
- 1947: Three months after an abortive coup, civil war broke out in Paraguay. The rebellion was crushed by the government of dictator Higinio Morínigo.
- 1947 : Sardar Muhammad Ibrahim Khan waged and led a guerrilla war against the Maharaja Hari Singh of Kashmir and formed a revolutionary Government on 24 October under his Presidency. He captured a large area of Kashmir called Azad Kashmir.
- 1947–1952: In the Albanian Subversion, the intelligence services of the United States and Britain deployed exiled fascists, Nazis, and monarchists in a failed attempt to foment a counterrevolution in Communist-ruled Albania.
- 1947: Angami Zapu Phizo declared the independence of Nagaland from India only to be subdued by the Indian army.
- 1947: The 228 Massacre occurred following discontent and resentment of the native Taiwanese under the early rule of the KMT of the island.
- 1947: India wins independence from Britain.
- 1948: The Costa Rican Civil War precipitated by the vote of the Costa Rican Legislature, dominated by pro-government representatives, to annul the results of the presidential election of 1948.
- 1948: Following the liberation of Korea, Marxist former guerrillas under Kim Il Sung work to rapidly industrialize the country and rid it of the last vestiges of "feudalism.".
- 1948–1960: The Malayan Emergency.
- 1948-1989: The communist insurgency in Burma is launched.
- 1948: Al-Wathbah (the Leap) uprising in Iraq.
- 1948 : Second Communist rebellion in Indonesia. The Communists tried to establish the Indonesian Soviet Republic, but were crushed by the Indonesian National Armed Forces.
- 1949: Chinese Communist Revolution. A period of social and political revolution in China that culminated in the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949.
1950s
- 1950: The Cazin uprising in the town of Cazin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- 1950: The Puerto Rican Nationalist Party Revolts of the 1950s in Puerto Rico, attempt on the life of US president Harry S. Truman in the Blair House, and shooting at Congress, was a call for Puerto Rico's independence and uprising by the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party against United States Government rule of Puerto Rico.
- 1950s: The Mau Mau uprising.
- 1950: Republic of South Maluku (RMS) separatist rebellion. The rebellion was crushed by Indonesian National Armed Forces. Surviving RMS rebels founded government-in-exile in The Netherlands.
- 1951: A Revolution in Nepal introduced democracy in Nepal.
- 1952: A popular revolution in Bolivia led by Víctor Paz Estenssoro and the Revolutionary Nationalist Movement (MNR) initiates a period of multiparty democracy lasting until a 1964 military coup.
- 1952: The Rosewater Revolution in Lebanon.
- 1952: Egyptian Revolution of 1952
- 1953: The Vorkuta uprising was a major uprising of the Gulag inmates in Vorkuta in the summer of 1953. Like other camp uprisings it was bloodily quelled by the Red Army and the NKVD.[162]
- 1953: Uprising of 1953 in East Germany.
- 1953–1959: The Cuban Revolution led by Fidel Castro removes the government of General Fulgencio Batista. By 1962 Cuba had been transformed into a declared socialist republic.
- 1953–1975: The Laotian Civil War in Laos.
- 1954–1962: The Algerian War of Independence: an uprising against French colonialism.
- 1954–1968: The Civil rights movement in the United States was a struggle by African Americans to end legalized racial discrimination, disenfranchisement and racial segregation.
- 1954: The Kengir uprising in the Soviet prison labor camp Kengir.
- 1954: The Uyghur uprising against Chinese rule in Hotan.
- 1955–1960: The Guerrilla war against British colonial rule of Cyprus led by the EOKA (National Organisation of Cypriot Fighters).
- 1955–1972: The First Sudanese Civil War was a conflict between the northern part of Sudan and a south that demanded more regional autonomy.
- 1955–1958: The Revolución Libertadora in Argentina .
- 1956–1962: The Border Campaign led by the Irish Republican Army against the British, along the border of the independent Republic of Ireland and British Northern Ireland.
- 1956: De-Stalinization revolution in the Eastern Bloc:
- The Khrushchev Thaw
- The 1956 Georgian demonstrations
- The Poznań protests, a workers' uprising in the Polish People's Republic that was suppressed.
- The Polish October
- The Hungarian Revolution, a failed workers' and peasants' revolution against the Soviet-supported communist state in Hungary.
- The Bucharest student movement
- 1956: The Tibetan rebellions against Chinese rule broke out in Amdo and Kham.
- 1956: Quỳnh Lưu uprising against communist government in North Vietnam
- 1958: A popular revolt in Venezuela against military dictator Marcos Pérez Jiménez culminates in a civic-military coup d'état.
- 1958: The Iraqi Revolution (14 July Revolution) led by nationalist soldiers abolishes the British-backed monarchy, executes many of its top officials, and begins to assert the country's independence from both Cold War power blocs.
- 1959: The failed Tibetan uprising against Chinese rule led to the flight of the Dalai Lama.
- 1959–1962: In the Rwandan Revolution, the Tutsi king of Rwanda is forced into exile by Hutu extremists; racial pogroms follow an assassination attempt on Hutu leader Grégoire Kayibanda.
1960s
- 1960: A group of disaffected Ethiopian officers make an unsuccessful attempt to depose Emperor Haile Selassie and replace him with a more progressive government, but are defeated by the rest of the Ethiopian military.
- 1960: April Revolution erupts in South Korea, leading to the end of the First Republic of South Korea.
- 1961: The Legality Campaign (Campanha da Legalidade) in Brazil .[163][164]
- 1961: El Barcelonazo in Venezuela.
- 1961–1970: First Kurdish Iraqi War erupts as a result of Barzanji clan uprising.
- 1961–1991: The Eritrean War of Independence led by Isaias Afewerki against Ethiopia.
- 1961–1975: The Angolan War of Independence began as an uprising against forced cotton harvesting, and became a multi-faction struggle for control of Portugal's Overseas Province of Angola.
- 1962: El Carupanazo in Venezuela.
- 1962: El Porteñazo in Venezuela.
- 1962–1974: The leftist African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) wages a revolutionary war of independence in Portuguese Guinea. In 1973, the independent Republic of Guinea-Bissau is proclaimed, and the next year the republic's independence is recognized by the reformist military junta in Lisbon.
- 1962: The military coup of 1962 in Burma, led by General Ne Win, who became the country's strongman.
- 1962–present: Papua conflict.
- 1962: A revolution in northern Yemen overthrew the imam and established the Yemen Arab Republic.
- 1962–1975: Dhofar Rebellion in Oman.
- 1963: White Revolution in Iran.
- 1963: 1963 demonstrations in Iran.
- 1963 Dutch farmers' revolt.
- 1963: Syrian coup d'état in Syria that brought Ba'ath Party to power.
- 1963–1970: The Bale Revolt in southern Ethiopia, was a guerrilla war by local Somali and Oromo against Amhara settlers.
- 1963–1971: Ogaden Revolt in southern Ethiopia, a guerrilla war by Somalis seeking self-determination.
- 1964: Simba Rebellion in the Congo.
- 1964: The Zanzibar Revolution overthrew the 157-year-old Arab monarchy, declared the People's Republic of Zanzibar, and began the process of unification with Julius Nyerere's Tanganyika.
- 1964: 1964 Brazilian coup d'état led by Field Marshal Humberto Castelo Branco against president Joao Goulart.
- 1964–1979: The Rhodesian Bush War, also known as the Second Chimurenga, was a guerrilla war which lasted from July 1964 to 1979 and led to universal suffrage, the end of white minority rule in Rhodesia, and the creation of the Republic of Zimbabwe.
- 1964: The October Revolution in Sudan, driven by a general strike and rioting, forced President Ibrahim Abboud to transfer executive power to a transitional civilian government, and eventually to resign.
- 1964–1975: The Mozambican Liberation Front (FRELIMO), formed in 1962, commenced a guerrilla war against Portuguese colonialism. Independence was granted on 25 June 1975; however, the Mozambican Civil War complicated the political situation and frustrated FRELIMO's attempts at radical change. The war continued into the early 1990s after the government dropped Marxism as the state ideology.
- 1964–present: The Colombian Armed Conflict.
- 1965: 30 September Movement was a failed coup by the Communist Party to turn Indonesia into a Communist state.
- 1965: The March Intifada in Bahrain: a Leftist uprising demanding an end to the British presence in Bahrain.
- 1965-1983: The communist insurgency in Thailand is launched.
- 1966: Kwame Nkrumah is removed from power in Ghana by coup d'état.
- 1966–1990: A South African Police patrol clashes with militants of the South West African People's Organization in 1966, sparking the Namibian War of Independence. The conflict is part of the larger South African Border War and linked closely with South Africa's intervention in the Angolan Civil War. It largely ended with Namibia's first democratic elections in 1989.
- 1966–1993: A guerrilla warfare was conducted against the government of François Tombalbaye from the Sudan-based group FROLINAT.
- 1966–1976: Mao Zedong launches the Great Proletariat Cultural Revolution in the People's Republic of China, a sociopolitical movement to purge revisionist and bourgeois elements from the Chinese Communist Party and Chinese society at large through violent class struggle.
- 1966–1998: The Ulster Volunteer Force was recreated by militant Ulster Protestant loyalists in Northern Ireland to wage war against the Irish Republican Army and the Roman Catholic community at large.
- 1966: The year it is estimated the Black Power movement began, with no exact official end date.
- 1967–1970: Biafra: The former eastern Nigeria unsuccessfully fought for a breakaway republic of Biafra, after the mainly Igbo people of the region suffered pogroms in northern Nigeria the previous year.
- 1967: The Naxalite Movement begins in India, led by the AICCCR.
- 1967: Anguillans resentful of Kittitian domination of the island expelled the Kittitian police and declared independence from the British colony of Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. British forces retook the island in 1969 and made Anguilla a separate dependency in 1980. There was no bloodshed in the entire episode.
- 1967–1973: The Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War begins to turn violent, the violence later escalates. Incidents include the Weather High School Jailbreaks and the Greenwich Village townhouse explosion
- 1967: Pro-communist, anti-British riots in Hong Kong
- 1967: Long, hot summer of 1967 – a series of 159 race riots which occurred in major cities across the United States in the summer of 1967
- 1967 Buffalo riot (June 26 – July 1)
- 1967 Cairo riot (July 17)
- 1967 Cambridge riot (July 24, 1967)
- 1967 Detroit riot (July 23–28)
- 1967 Toledo riot (July 23–25)
- 1967 Milwaukee riot (July 30 – August 31)
- 1967 Newark riots (July 12–17)
- 1967 Plainfield riots (July 14–16)
- 1967 Saginaw riot (July 26)
- 1967 Albina riot (July 30)
- 1968–present: Moro conflict in the Philippines.
- 1968: The revolution in the Republic of Congo.
- 1968: The Protests of 1968:
- The May 1968 revolt: students' and workers' revolt against the government of Charles de Gaulle in France.
- A failed attempt by leader Alexander Dubček to liberalise Czechoslovakia in defiance of the Soviet-supported communist state culminates in the Prague Spring.
- The March of the One Hundred Thousand was a manifestation of popular protest against the military dictatorship in Brazil, which occurred in Rio de Janeiro.
- The 1968 movement in Italy
- Battle of Valle Giulia
- The 1968 student demonstrations in Yugoslavia
- The West German student movement
- A mass movement of workers, students, and peasants in Pakistan forced the resignation of President Mohammad Ayub Khan.
- The 1968 Polish political crisis
- The Mexican Movement of 1968
- Tlatelolco massacre
- King-assassination riots – a series of race riots following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
- 1968 Detroit riots
- 1968 New York City riot
- 1968 Washington D.C. riot
- 1968 Chicago riot
- 1968 Pittsburgh riots
- 1968 Baltimore riots
- 1968 Kansas City riot
- 1968 Wilmington riot
- 1968 Louisville riot
- 1968 Democratic National Convention protests
- Columbia University protests of 1968
- 1968: A coup by Juan Velasco Alvarado in Peru, followed by radical social and economic reforms.
- 1968–1969 Iraqi communists launched an insurgency in southern Iraq.[165]
- 1968–1969: The Egbe Agbekoya Revolt was an unsuccessful peasant revolt in Western Nigeria.
- 1969–present: Communist rebellion in the Philippines.
- 1969–1998: The Troubles: the Provisional Irish Republican Army and other Republican Paramilitaries waged an armed campaign against British Security forces and Loyalist Paramilitaries in an attempt to bring about a United Ireland.
- 1969: The Days of Rage occur, part of the Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War.
1970s
- 1970: The Black Power Revolution occurs in Trinidad.
- 1970: A rebellion in Guinea by what its government identified as Portuguese agents.
- 1970–1971: Black September in Jordan
- 1971: The Bangladesh Liberation War led by the Mukti Bahini establishes the independent People's Republic of Bangladesh from the former East Pakistan.
- 1971 Dutch farmers' revolt
- 1972–present: The Maoist insurgency in Turkey is launched.
- 1972: A revolution in Benin.
- 1972: A military-led revolution against the civilian government of President Philibert Tsiranana in the Malagasy Republic; a Marxist faction takes power in 1975 under Didier Ratsiraka, modeled on the North Korean juche theory developed by Kim Il Sung.
- 1973: 1973 Chilean coup d'etat led by Captain General Augusto Pinochet against President Salvador Allende in Chile .
- 1973: Wounded Knee Incident. American Indian Movement activists and Oglala Lakota besiege the small town of Wounded Knee in protest of government policies towards Native Americans and the corrupt Wilson Regime. Part of the Red Power movement
- 1973: Mohammad Daud Khan overthrows the monarchy and establishes a republic in Afghanistan.
- 1973: Worker-student demonstrations in Thailand force dictator Thanom Kittikachorn and two close associates to flee the country, beginning a short period of democratic constitutional rule.
- 1974: The Ethiopian Revolution overthrows Emperor Haile Selassie and installs the Derg junta.
- 1974–1975: The Carnation Revolution overthrows the right-wing dictatorship in Portugal. Leads to the independence of Angola, Cape Verde, Mozambique, São Tomé and Príncipe and Timor-Leste and recognition of Guinea-Bissau's self-proclaimed independence.
- 1975–1991: The Western Sahara War was a conflict between the Sahrawi national liberation movement named POLISARIO against the armies of their neighbours, Morocco and Mauritania, who have entered the territory when the Spanish colonizers troops fled.
- 1975: A revolution in Cambodia.
- 1975: Lebanese Civil War lasted from 1975 to 1990.
- 1975: 15 August, coup led by young military officers and the Assassination of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman in Bangladesh.
- 1975: Coup led by Brigadier Khaled Mosharraf and Colonel Shafaat Jamil in Bangladesh to depose President Khondaker Mostaq Ahmad. Three days later a counter-coup by Colonel Abu Taher puts Ziaur Rahman in power.
- 1975: Having become disillusioned with the rule of Leonid Brezhnev, Valery Sablin leads a mutiny in hopes of starting a Leninist revolution in the Soviet Union.
- 1976-1988: The "May-Revolution" by the Kurds in North-Iraq against the government.
- 1976: Student demonstrations and election-related violence in Thailand lead police to open fire on a sit-in at Thammasat University, killing hundreds. The military seizes power the next day, ending constitutional rule.
- 1976: The Gang of Four is removed from power in China in a coup led by Chairman Hua Guofeng with the support of senior officers of the People's Liberation Army, ending the Cultural Revolution.
- 1976: 1976 Argentine coup d'etat led by Lieutenant General Jorge Rafael Videla against President Isabel Perón.
- 1977: Egyptian Bread Riots the riots were a spontaneous uprising by hundreds of thousands of lower-class people, at least 79 people were killed and 800 wounded.
- 1977: The Market Women's Revolt in Guinea leads to a lessening of the state's role in the economy.
- 1977: A mutiny in Bangladesh Air Force occurs, with the goal of establishing a Marxist government,[166] resulting in the deaths of 11 air force officers. Subsequently, 1143 airmen and soldiers were executed for their alleged involvement in the uprising.[166]
- 1978: The Saur Revolution led by the Khalq faction of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan deposes and kills President Mohammad Daud Khan.
- 1979: New Jewel Movement led by Maurice Bishop launch an armed revolution and overthrow the government of Eric Gairy in Grenada.
- 1979: The popular overthrow of the Somoza dictatorship in the Nicaraguan Revolution.
- 1979: Anti-Communist Rebels in Nicaragua (aka) Contras start to form.
- 1979: The Iranian Revolution overthrows Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, resulting in the formation of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
- 1979: Cambodia is liberated from the Khmer Rouge regime by the Vietnam-backed Kampuchean People's Revolutionary Party.
- 1979: 1979 Equatorial Guinea coup d'état led by Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo against Francisco Macías Nguema.
- 1979–1992: Salvadoran Civil War
1980s

- 1980: National Socialist Council of Nagaland launches its struggle against Indian administration and the establishment of the greater Nagaland.
- 1980: 25 February. Suriname Government are put aside by a group of soldiers. The leader of the revolution is Desi Delano Bouterse.
- 1980: Gwangju uprising, alternatively called the "May 18 Democratic Uprising", in South Korea
- 1980: The Santo Rebellion in the Anglo-French condominium of New Hebrides
- 1980–2000: The Communist Party of Peru launched the internal conflict in Peru.
- 1980: First Entumbane uprising in Zimbabwe.
- 1981: Assassination of Ziaur Rahman in Bangladesh sparks protests and riots.
- 1981: Second Entumbane uprising in Zimbabwe.
- 1982: General Hussain Muhammad Ershad seizes power through a bloodless coup, deposing president Abdus Sattar in Bangladesh.
- 1983–1984: Diretas Já, a Brazil ian civil unrest movement that demanded direct presidential elections.
- 1983: Overthrow of the ruling Conseil de Salut du peuple (CSP) by Marxist forces led by Thomas Sankara in Upper Volta, renamed Burkina Faso in the following year.
- 1983: Prime Minister of Grenada, Maurice Bishop, overthrown and subsequently executed by high-ranking government officials.
- 1983–2009: Starting from 23 July 1983, an on-and-off civil war against the Government of Sri Lanka by the secessionist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam begins. The LTTE fight to establish an independent Tamil state in the Tamil-majority northeastern half of Sri Lanka. Fighting would last for nearly 26 years, resulting in the brutal defeat of the LTTE.
- 1983–2005: The Second Sudanese Civil War was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War, and one of the longest lasting and deadliest wars of the later 20th century.
- 1984–1999: Kurdish uprising for independence from the Republic of Turkey
- 1984–1985: Pro-independence Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front (FLNKS) forces in New Caledonia revolt following an election boycott and occupy the town of Thio from November 1984 to January 1985. Thio is retaken by the French after the assassination of Éloi Machoro, the security minister in the FLNKS provisional government and the primary leader of the occupation.[167]
- 1985: Soviet and Afghanistan P.O.W.s rose against their captors at Badaber base.
- 1986: The People Power Revolution peacefully overthrows Ferdinand Marcos after his two-decade rule in the Philippines .
- 1986–1991: Somali Rebellion as a result of military dictator Siad Barre beginning to attack clan-based dissident groups.
- 1986: Khalistan Commando Force started armed movement for the establishment of Khalistan, an independent Sikh homeland. The movement, as is the case with other Sikh nationalistic movements, was fueled in part by the Indian army's Operation Blue Star. The armed struggle resulted in thousands of mostly civilian deaths.
- 1987 : The June Struggle overthrew military dictatorship of South Korea.
- The rigged 1987 Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly election created a catalyst for the insurgency when it resulted in some of the state's legislative assembly members forming armed insurgent groups launches its struggle against Indian administration.
- 1987–1991: The First Intifada, or the Palestinian uprising, a series of violent incidents between Palestinians and Israelis.
- 1988–1991: The Pan-Armenian National Movement frees Armenia from Soviet rule.
- 1988–1991: The Singing Revolution, bloodless overthrow of communist rule in Soviet-occupied Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
- 1988: The 8888 Uprising In Burma or Myanmar.
- 1989: Armed resistance breaks out in the Kashmir valley against Indian administration.[168]
- 1989–1990 Dutch farmers' protests against wheat price reductions and environmental legislation.
- 1989–1997: The First Liberian Civil War in Liberia
- 1989: Revolutions of 1989 – a series of revolutions against Communist states around the world, especially in the Soviet satellite states of the Eastern Bloc
- Strikes by the Solidarity movement end in negotiations leading to the end of martial law and the peaceful overthrow of the Communist government in Poland
- Demonstrations in Hungary led to the peaceful overthrow of the Communist government and the dismantlement of the Hungarian border fence with Austria
- The Tiananmen Square protests, a series of street demonstrations led by students, intellectuals and labour activists in the People's Republic of China between 15 April and 4 June 1989, ends in a violent crackdown by the People's Liberation Army.
- Demonstrations in East Germany led to the fall of the Berlin Wall.
- Demonstrations in the People's Republic of Bulgaria led to the fall of the communist government there.
- The bloodless Velvet Revolution removes the communist government in Czechoslovakia.
- The Romanian Revolution kills the dictator Nicolae Ceauşescu and his wife, Elena Ceauşescu, in the Socialist Republic of Romania
- Baltic Way demonstrations against the Soviet occupation of the Baltic States in Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia; part of the Singing Revolution against Soviet rule leading to the independence of the Baltic States in 1991
1990s

- 1990: Oka Crisis
- 1990: People's Movement I was a revolution to restore democracy in Nepal and end the panchayat system in Nepal.
- 1990–present: United Liberation Front of Asom launch major violent activities against Indian rule in Assam. To date, the resulting clashes with the Indian army have left more than 10,000 dead.[169]
- 1990: 1990 Mass Uprising in Bangladesh Strikes and Protests topple the Bangladeshi military government and democracy is restored for the first time in nine years.
- 1990: The Poll tax riots were a series of riots in British towns and cities during protests against the Community Charge introduced by the government of Margaret Thatcher.
- 1990–1993: Rwandan Civil War
- 1990–1992: Anticommunist forces led a National Democratic Revolution that overthrew President Ramiz Alia and ended with an election victory by the Democratic Party of Albania, the biggest anticommunist party in Albania.
- 1990–1995: The Log Revolution in Croatia starts, triggering the Croatian War of Independence.
- 1990–1995: The First Tuareg Rebellion in Niger and Mali.
- 1991–2002: The Sierra Leone Civil War against the administration of president, Joseph Saidu Momoh.
- 1991: The Kurdish uprising against Iraqi President Saddam Hussein in Iraqi Kurdistan.
- 1991: The Shiite Uprising in Karbala, Iraq.
- 1991: The failed 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt takes place, leading to the dissolution of the Soviet Union
- 1991: Chechen Revolution leading to the Declaration of Sovereignty of the Chechen Republic.
- 1991: The Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front take control of Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia, after dictator Haile Mariam Mengistu flees the country, bringing an end to the Ethiopian Civil War
- 1991: Somali National Movement rebels establish the Somaliland administration in northwestern Somalia, and declare the region independent from the rest of the country.
- 1992: 1992 Los Angeles riots
- 1992: Black May (1992) Thailand popular protest in Bangkok against the government of General Suchinda Kraprayoon and the military crackdown that followed. Up to 200,000 people demonstrated in central Bangkok at the height of the protests.
- 1992–1995: Bosnian War
- 1992: Afghan uprising against the Taliban by United Islamic Front for the Salvation of Afghanistan, or the Northern Alliance.
- 1993: Waco siege.
- 1994: The 1990s Uprising in Bahrain, Shiite-led rebellion for the restoration of democracy in Bahrain.
- 1994: The Zapatista Rebellion: an uprising in the Mexican state of Chiapas demanding equal rights for indigenous peoples and in opposition to growing neoliberalism in North America.
- 1994–1996: The First Chechen Rebellion against Russia.
- 1996–2006: Nepalese Civil War
- 1996: Islamic movement in Afghanistan led by the Taliban established Taliban rule.
- 1996–1997: The First Congo War in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- 1997: The 1997 rebellion in Albania sparked by Ponzi scheme failures.
- 1997–1999: The Republic of the Congo Civil War
- 1998: The Indonesian Revolution of 1998 resulted the resignation of President Suharto after three decades of the New Order period.
- 1998–1999: The Kosovo War
- 1998–1999: The Guinea-Bissau Civil War against the administration and government of President Joao Bernardo Vieira.
- 1998–2003: The Second Congo War in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- 1999–2003: The Second Liberian Civil War against the government of Liberia.
- 1999–2009: The Second Chechen Rebellion against Russia.
- 1999: The Iran student protests, July 1999 were, at the time, the most violent protests to occur against the Islamic Republic of Iran.
- 1999–2000: The Cochabamba Water War in Bolivia.
2000s
- 2000–2005: The Second Intifada, a continuation of the First Intifada, between Palestinians and Israel.
- 2000: The bloodless Bulldozer Revolution, first of the four colour revolutions (in 2000, 2003, 2004, and 2005), overthrows Slobodan Milošević's régime in Yugoslavia.
- 2001: The 2001 Macedonia conflict.
- 2001-2021: The Taliban insurgency following the 2001 war in Afghanistan which overthrew Taliban rule.
- 2001: The 2001 EDSA Revolution peacefully ousts Philippine President Joseph Estrada after the collapse of his impeachment trial.
- 2001: Supporters of former Philippine President Joseph Estrada violently and unsuccessfully stage a rally, so-called the EDSA Tres, in an attempt of returning him to power.
- 2001: Cacerolazo in Argentina. Following mass riots and a period of civil unrest, popular protests oust the government and two additional interim presidents within months. December 2001 riots in Argentina
- 2003–2005: Bolivian gas conflict.
- 2003: The Rose Revolution, second of the colour revolutions, displaces the president of Georgia, Eduard Shevardnadze, and calls new elections.
- 2003–2011: The Iraqi insurgency refers to the armed resistance by diverse groups within Iraq to the U.S. occupation of Iraq and to the establishment of a liberal democracy therein.
- 2003–present: The Darfur rebellion led by the two major rebel groups, the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM/A) and the Justice and Equality Movement, recruited primarily from the land-tilling Fur, Zaghawa, and Massaleit ethnic groups.
- 2003–present: Conflict in the Niger Delta
- 2004–2004: The Shi'ite Uprising against the US-led occupation of Iraq.
- 2004–2005: The Orange Revolution in Ukraine. After pro-Russian prime minister Viktor Yanukovych was declared the winner of the presidential elections, people took to the streets in protest against mass fraud and vote falsification. Eventually, the country's Supreme Court ordered a recount, in which pro-Western opposition leader Viktor Yushchenko was declared the winner. This was the third colour revolution.
- 2005: A failed attempt at popular colour-style revolution in Azerbaijan, led by the groups Yox! and Azadlig.
- 2004: War in North-West Pakistan.
- 2004–present: The Naxalite insurgency in India, led by the Communist Party of India (Maoist).
- 2004–2013: The Kivu conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- 2005: The Cedar Revolution, triggered by the assassination of former Prime Minister Rafic Hariri, asks for the withdrawal of Syrian troops from Lebanon.
- 2005: The Tulip Revolution (a.k.a. Pink/Yellow Revolution) overthrows the President of Kyrgyzstan, Askar Akayev, and set new elections. This is the fourth colour revolution.
- 2005: Paraguayan People's Army insurgency.
- 2005: 15 April Intifada – Arab uprising in the Iranian province of Khuzestan.
- 2005: Ecuador experiences a nationwide and countrywide revolution, consisting of rallies and demonstrations, rioting and protests in March–April 2005 from indigenous tribes that started with a protest that mushroomed into a widespread uprising and popular movement that led to the overthrow of the government.
- 2006: 2006 democracy movement in Nepal was a revolution against Undemocratic rule of King Gyanendra.
- 2006: The 2006 Oaxaca protests demanding the removal of Ulises Ruiz Ortiz, the governor of Oaxaca state in Mexico.
- 2006–present: The Mexican drug war.
- 2007: The Lawyers' Movement in Pakistan emerged to restore a judge but eventually moved to rebel against the military dictatorship of General Pervez Musharraf.
- 2007–2015: The Civil war in Ingushetia.
- 2007–2009: The Second Tuareg Rebellion in Niger.
- 2007: The Burmese anti-government protests, including the Saffron Revolution of Burmese Buddhist monks.
- 2008: 2008 Armenian presidential election protests.
- 2008: 2008 Kashmir Unrest.
- 2008: A Shiite uprising in Basra.
- 2008: Attacks in Lanao del Norte in the Philippines by the Moro Islamic Liberation Front led by Kumander Bravo and Umbrfa Kato.
- 2008: Anti-austerity protests in Ireland
- 2008: 2008 Tibetan unrest.
- 2009: 2009 Iranian presidential election protests, leading to development of Iranian Green Movement
- 2009: 2009 Bangladesh Rifles revolt took place in Dhaka, Bangladesh killing 57 army officers.
- 2009–2011: A civil uprising popularly known as the Kitchenware Revolution brought down the Icelandic government after the collapse of the country's financial system in October 2008.
- 2009: The 2009 Malagasy political crisis in the Madagascar.
- 2009: The Dongo conflict In the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- 2009–present: Somali Civil War (2009–present).
- 2009–2015: South Yemen insurgency.
- 2009: 2009 Boko Haram uprising.
- 2009–2017: Insurgency in the North Caucasus.
2010s
- 2010 Thai political protests.
- 2010–2011: 2010–2011 Ivorian crisis.
- 2010–2012: Tajikistan insurgency.
- 2010: Kyrgyz Revolution of 2010.
- 2010: Kashmir Unrest 2010.
- 2010–2012: Anti-austerity movement in Greece
- 2010–2012: Arab Spring:
- The Tunisian Revolution (2010–2011) forces President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali to resign and flee the country, and sets free elections.
- The 2011 Egyptian revolution brings down the regime of President Hosni Mubarak.
- The 2011 Libyan Civil War in which rebel forces gradually take control of the country, and kill leader Muammar Gaddafi.
- 2011 Post-civil war violence in Libya.
- Syrian civil war.
- Bahraini uprising of 2011.
- 2011 Yemeni Revolution, the revolt that led to the eventual resignation of Ali Abdullah Saleh as President of Yemen.
- 2011–present: Sinai insurgency.
- 2011: Cherán uprising.
- 2011: Wukan protests in China.
- 2011–present: Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.
- 2011–2017: Syrian civil war spillover in Lebanon.
- 2011–present: Ethnic violence in South Sudan.
- Iraqi insurgency (2011–2013).
- 2011–2013 Maldives political crisis: Public protests and police mutiny led to resignation of President Mohamed Nasheed.
- 2011–2012: Occupy movement.
- 2012–present: Rojava Revolution in Syrian Kurdistan.
- 2012–2015: Northern Mali conflict.
- 2012–2012: 2012 Tuareg rebellion.
- 2012–present: Central African Republic conflict–François Bozizé, president of the Central African Republic, is overthrown by the rebel coalition Séléka, led by Michel Djotodia.
- 2012–2013: M23 rebellion.
- 2012–2015 unrest in Romania.
- 2013: 2013 Protests in Brazil
- 2013 Eritrean Army mutiny.
- 2013: Gezi Park protests in Turkey.
- 2013–present: Turkey–ISIL conflict.
- 2013 South Sudanese political crisis.
- 2013–14 Tunisian protests against the Ennahda-led government.
- 2013–2020: South Sudanese Civil War.
- RENAMO insurgency (2013–2019).
- 2013–2014: Euromaidan.
- 2014 Ukrainian Revolution.
- 2013–14 Thai political crisis.
- 2013–14 Cambodian protests.
- 2014–present: 2014 Protests in Venezuela.
- Iraqi Civil War (2014–2017).
- 2014–2020: Second Libyan Civil War.
- 2014: Abkhazian Revolution.
- 2014: The Umbrella Revolution of Hong Kong
- 2014 Burkinabé uprising.
- 2014: Ferguson unrest in Missouri
- 2015–present: Yemeni Civil War (2015–present).
- Burundian unrest (2015–18).
- 2015–present: Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present).
- 2015–present: ISIL insurgency in Tunisia.
- 2015: 2015 Baltimore protests
- 2016–present: 2016 Niger Delta conflict.
- 2016 Ethiopian protests.
- 2016 Mong Kok civil unrest, also known as "Fishball Revolution" in Mong Kok, Hong Kong
- 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt, a failed military coup.
- 2017–present: Anglophone Crisis, also known as the Ambazonia War, or the Cameroonian Civil War.
- 2016–17 South Korean protests, or Candlelight Revolution, in South Korea.
- 2016–17 Kashmir unrest.
- 2016–17: United States election protests – protests challenging the outcome of the 2016 United States presidential election.
- 2017 Ivory Coast mutiny.
- 2017: 2017 Military Police of Espírito Santo strike in Espírito Santo, Brazil .[170][171][172]
- 2017–18 Spanish constitutional crisis.
- 2017–2018 Romanian protests.
- 2017–2018 Iranian protests.
- 2018–present: 2018–19 Arab protests:
- 2018 Jordanian protests.
- 2018–2019: Sudanese Revolution, which resulted in the ouster of the President.
- 2019–2020 Algerian protests, also called Revolution of Smiles or Hirak Movement.
- 2019–present: 2019 Iraqi protests, also nicknamed the October Revolution, and 2019 Iraqi Intifada.
- 2019–present: 2019–20 Lebanese protests, also referred to as the Lebanese revolt.
- 2018 Armenian Velvet Revolution, which resulted in the ouster of the Prime Minister.
- 2018–2019 Gaza border protests, also referred to by organizers as the "Great March of Return".
- 2018–2020: 2018–20 Nicaraguan protests.
- 2018–2019: 2018–2019 Haitian protests.
- 2018–2019 Ingushetia protests
- 2018–present: Yellow vests protests.
- 2019–2020: 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests
- 2019 Papua protests.
- 2019 Indonesian protests and riots.
- 2019 Puerto Rico Anti-Corruption / Chat scandal Protest.
- 2019–present: Dutch farmers' protests.
- 2019 Ecuadorian protests.
- 2019–2020 Catalan protests.
- 2019–2022 Chilean protests, also called "Estallido social".
- 2019–2020 Iranian protests.
- 2019–2020: Citizenship Amendment Act protests, in India .
2020s
This section contains information of unclear or questionable importance or relevance to the article's subject matter. (July 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
- Protests against responses to the COVID-19 pandemic – a series of protests around the world against various governments' responses to the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly lockdowns.
- Strikes during the COVID-19 pandemic – strikes against wages or low hazard pay, insufficient workplace hazard controls such as a lack of personal protective equipment or social distancing, high rents or evictions, and the pandemic's general economic impact.
- 2020–2023 United States racial unrest – a series of protests against racial inequality and police brutality in the United States, sometimes in favor of abolishing or defunding the police.
- George Floyd protests.
- Breonna Taylor protests.
- Kenosha unrest.
- 2020–2023 Minneapolis–Saint Paul racial unrest.
- 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests – protests against Boyko Borisov's government.
- 2020–2021 Belarusian protests – protests against Alexander Lukashenko's government.
- 2020–2021 Thai protests – pro-democracy protests for reform to the Thai monarchy and against the 2017 Thai Constitution and Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha's government.
- 2020 Malian protests, also called "Malian Spring".
- 2020 Inner Mongolia protests
- 2020–2021 women's strike protests in Poland – protests against a Constitutional Tribunal ruling restricting abortion.
- End SARS protests – protests to abolish the Special Anti-Robbery Squad in Nigeria.
- 2020 Kyrgyz Revolution, also called the Third Kyrgyz Revolution.
- Indonesia omnibus law protests – protests against the Omnibus Law on Job Creation.
- 2020 Peruvian protests – protests against the impeachment and removal of Martín Vizcarra.
- 2020 Guatemalan protests
- 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest – protests against the 2020 Indian agriculture acts.
- Tigray War – the conflict started as an uprising in Ethiopia's Tigray region led by the TPLF, but then developed into a civil war in Northern Ethiopia.
- 2020-2021 United States election protests – protests challenging the legitimacy of the results in the 2020 United States presidential election.
- January 6 United States Capitol attack
- Attempts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential election
- 2021 Boğaziçi University protests
- 2021 Tunisian protests
- 2021 Russian protests
- 2021-present Myanmar protests, also called the Spring Revolution.
- 2021 Greek protests
- 2021 Bangladesh anti-Modi protests
- 2021 Northern Ireland riots
- 2021 Colombian protests
- 2021 Senegalese protests
- 2021-2023 Eswatini protests
- 2021 South African unrest
- 2021 Brazilian protests
- 2021 Cuban protests, also called the Cuba Libre movement.
- 2021–2022 Iranian protests
- Republican insurgency in Afghanistan
- 2021–2022 Afghan protests
- 2021 Solomon Islands unrest
- 2021–2022 Serbian environmental protests
- 2022 Kazakh unrest, also called Bloody January.
- Protests against the Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Anti-war protests in Russia (2022–present)
- Canada convoy protest
- 2022 Sri Lankan protests
- 2022 Corsica unrest
- 2022 Azadi March I
- 2022 Karakalpak protests
- 2022 Ecuadorian protests
- 2022 Peruvian economic protests
- 2022 Iranian food protests
- 2022 Iranian protests
- 2022-2023 Brazilian election protests
- 2023 Brazilian Congress attack
- 2022 Azadi March II
- 2022–present Moldovan protests
- 2022 Mongolian protests
- 2023 French pension reform unrest
- 2023 Georgian protests
- 2023 Israeli judicial reform protests
- War in Sudan (2023)
- Wagner Group rebellion
- Nahel Merzouk riots - major protests in France following the killing of 17-year old Nahel Merzouk by a police officer.
See also
- List of civil wars
- List of cultural, intellectual, philosophical and technological revolutions
- List of films about revolution
- List of guerrillas
- List of invasions
- List of peasant revolts
- List of rebellions in China
- List of riots
- List of strikes
- Uprisings led by women
- List of usurpers
- List of wars of independence (national liberation)
- List of women who led a revolt or rebellion
- Political history of the world
- Slave rebellion (including list of North American slave revolts)
Notes
- ↑ The Dutch Brigade
References
- ↑ P.E. Newberry, The Seth rebellion of the 2nd Dynasty, in Ancient Egypt., no. 7. 1922. pp. 40–46.
- ↑ Jimmy Dunn, "Khasekhem/Khasekhemwy of Egypt's 2nd Dynasty", Tour Egypt
- ↑ Finegan, Jack (2019) (in en). Archaeological History Of The Ancient Middle East. Routledge. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-429-72638-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=d72ZDwAAQBAJ&pg=PR43.
- ↑ Sources of Western Zhou History: Inscribed Bronze Vessels by Edward L. Shaughnessy
- ↑ Sima Qian. Records of the Grand Historian. 4.
- ↑ Lipschits, Oled (2005). The Fall and Rise of Jerusalem: Judah under Babylonian Rule. Eisenbrauns. pp. 13–18. ISBN 978-1575060958. https://books.google.com/books?id=78nRWgb-rp8C&q=fall+of+nimrud+medes&pg=PA18.
- ↑ Clayton, Peter A. (2006). Chronicle of the Pharaohs: The Reign-by-Reign Record of the Rulers and Dynasties of Ancient Egypt (Paperback ed.). Thames & Hudson. pp. 195–197. ISBN 0-500-28628-0.
- ↑ Jigoulov, Vadim S. (2016-04-08) (in en). The Social History of Achaemenid Phoenicia: Being a Phoenician, Negotiating Empires. Routledge. pp. 47. ISBN 978-1-134-93809-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=IbzsCwAAQBAJ&dq=%22Phoenician+revolt%22&pg=PA47.
- ↑ Rawlinson, George; Gilman, Arthur (1892) (in en). The Story of Ancient Egypt. G. P. Putnam. pp. 396. ISBN 978-0-8482-5897-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=a502AAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Briant, Pierre (2002). From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire. Eisenbrauns. pp. 115–116. ISBN 9781575061207. https://books.google.com/books?id=lxQ9W6F1oSYC&q=false.
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1.57
- ↑ Herodotus VI, 33
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita, Book 2
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Dandamaev, Muhammad A. (1993). "Xerxes and the Esagila Temple in Babylon". Bulletin of the Asia Institute 7: 41–45.
- ↑
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Tod, Marcus Niebuhr (1911). "Archidamus s.v. 2". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 367.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Tod, Marcus Niebuhr (1911). "Archidamus s.v. 2". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 367.
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 126
- ↑ Diodorus XI, 77
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita 3.55.13
- ↑ Cornell, T.J. (1995). The Beginnings of Rome. Routledge. p. 265.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Livy. "6-7". Ab urbe condita.
- ↑ Dionysius, xi. 60.
- ↑ Floro (1929). "X". Epitome of Roman History. https://archive.org/details/luciusannaeusflo0000unse.
- ↑ "Cassius Dio — Fragments of Book 12". https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Cassius_Dio/12*.html.
- ↑ Hong Liu (2015). The Chinese Strategic Mind. Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 145. ISBN 9781783474141. https://books.google.com/books?id=LbgkCwAAQBAJ&q=Dazexiang+uprising&pg=PA145.
- ↑ "The great revolt of the Egyptians (205–186 BC)". http://english.cri.cn/1702/2005-4-29/14@232828.htm.
- ↑ Livy, History of Rome from Its Foundation: Rome and the Mediterranean (Books 31-45), Penguin Classics, Reprint edition, 1976; ISBN:978-0140443189
- ↑ Schurer, Emil (1891). A History of the Jewish People in the Times of Jesus Christ. 1. Hendrickson Publishers. ISBN 1565630491.
- ↑ Rafe de Crespigny (1967). "An Outline of the Local Administrations of the Later Han Empire". Chung-chi Journal: 57–71. http://sunzi.lib.hku.hk/hkjo/view/7/700117.pdf.
- ↑ Appian. "6, The Spanish wars". Roman History, The foreign Wars.
- ↑ Appian. Foreign Wars. https://www.livius.org/ap-ark/appian/appian.html.
- ↑ Appian. History of Rome.. https://www.livius.org/ap-ark/appian/appian_spain_00.html.
- ↑ Mommsen, Theodor (1958). The History of Rome (Collins & Saunders ed.). Meridin Books.
- ↑ Conole, P. (1981). "Allied Disaffection and the Revolt of Fregellae1" (in en). Antichthon 15: 129–140. doi:10.1017/S0066477400004615. ISSN 0066-4774. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/antichthon/article/allied-disaffection-and-the-revolt-of-fregellae1/F5E621B58554048F46C3DED1BD961AB4.
- ↑ A. H. Beesely, The Gracchi, Marius, and Sulla Epochs of Ancient History, (Kindle edition), ch. VI., p. 57
- ↑ Beard, Mary (2008). Pompeii. Profile Books LTD. ISBN 978-1-86197-596-6.
- ↑ Plut. Sull. 9.3; Plut. Mar. 35.4
- ↑ Telford, Lynda. Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered.
- ↑ Dupuy and Dupuy, The Encyclopaedia of Military History, p. 93.
- ↑ Julius Exsuperantius, On the civil Wars of Marius, Lepidus and Sertorius, 38-42
- ↑ Appian, Civil Wars, 1:120
- ↑ Florus, Epitome, 2.8.
- ↑ Sallust, Bellum Catilinae XVIII.5; Asconius 92C; Dio Cassius XXXVI.44.3
- ↑ Crispus, Gaius Sallustius. The Conspiracy of Catiline.
- ↑ "Julius Caesar: The first triumvirate and the conquest of Gaul". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/88114/Julius-Caesar/9735/The-first-triumvirate-and-the-conquest-of-Gaul.
- ↑ Hornblower, S., Spawforth, A. (eds.) The Oxford Companion to Classical Civilization (1998) pp. 219–24
- ↑ Dio, 48.49
- ↑ Dio, Cassius. "23". Book LIII. https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Cassius_Dio/53*.html#23.
- ↑ Frontier and Society in Roman North Africa. Dr. David Cherry. Oxford University Press. 1998. pp. 38
- ↑ Raymond Brown, An Adult Christ at Christmas: Essays on the Three Biblical Christmas Stories, Matthew 2 and Luke 2 by Raymond E. Brown (Liturgical Press, 1978), page 17.
- ↑ Suetonius (2007). "The Life of Tiberius". The Life of The Twelve Caesars. Penguin Classics. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-0140455168. https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/home.html.
- ↑ Wells, Peter S. (2003), The Battle That Stopped Rome, Norton, p. 204, ISBN 9780393326437
- ↑ Pettinger, Andrew (2012), The Republic in Danger: Drusus Libo and the Succession of Tiberius, Oxford University Press, pp. 189–190, ISBN 978-0-19-960174-5
- ↑ Tacitus (100), "II.52", Annales
- ↑ Tacitus, Annales III:40-42.
- ↑ Diana Bowder (1984). Who was who in the Roman world. New York: Washington Square Press. p. 435.
- ↑ Tacitus (117). "IV.72–74". Annales.
- ↑ Tacitus, Annals, 6.41
- ↑ Bielestein, Hans (1987). "Wang Mang, the restoration of the Han dynasty, and Later Han". The Cambridge History of China, Volume 1: The Ch'in and Han Empires, 221 B.C.–A.D. 220. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 271. ISBN 9780521243278.
- ↑ Cassius Dio, Roman History 60:9
- ↑ Cassius Dio, lx. 15.
- ↑ Flavius Josephus, Antiquities 20.5.2 102
- ↑ Jason Burke, "Dig uncovers Boudicca's brutal streak" , The Observer, 3 December 2000
- ↑ "datesofhistory.com". http://www.datesofhistory.com/Rebellion-Roman-Empire.event.html.
- ↑ H. H. Scullard, From the Gracchi to Nero, p. 330
- ↑ Tacitus, Histories, 3. pp. 47–48
- ↑ Tacitus, Historiae IV.17
- ↑ Suetonius, "Life of Domitian, 6.2". https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Domitian*.html#6.2., "7.3". https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Domitian*.html#7.3.
- ↑ Ta'anit 18b; Yer. Ta'anit 66b
- ↑ "Legio VIIII Hispana". livius.org. https://www.livius.org/le-lh/legio/ix_hispana.html.
- ↑ Dio Cassius, Epitome 72
- ↑ Ropp, Paul S (10 June 2010). China in World History. Oxford University Press. p. 40. ISBN 9780199798766.
- ↑ de Crespigny, Rafe (2007). A biographical dictionary of Later Han to the Three Kingdoms (23–220 AD). Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-15605-0.
- ↑ Dio, 74:4
- ↑ Cassius Dio (1927). "79.40.5.". Roman History. Harvard University Press. p. 431. ISBN 0-674-99196-6.
- ↑ Taylor, Jay (1983), The Birth of the Vietnamese, University of California Press, p. 70
- ↑ Chen, Shou (3rd century). Records of the Three Kingdoms (Sanguozhi).
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 77.2 Chen, Shou. Records of the Three Kingdoms (Sanguozhi).
- ↑ E.M. Wightman, Gallia Belgica (London: Batsford) 1985.
- ↑ Casey, P. J. (1994). Carausius and Allectus: The British Usurpers (Repr. ed.). Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780203974353.
- ↑ di Cosmo, Nicola (2009), Military Culture in Imperial China, Harvard University Press
- ↑ Li, Bo; Zheng Yin (Chinese) (2001) 5000 years of Chinese history, Inner Mongolian People's publishing corp, ISBN:7-204-04420-7
- ↑ Rees, Diocletian and the Tetrarchy, p. 14, citing William Leadbetter, "Galerius and the Revolt of the Thebaid, 293/4," Antichthon 34 (2000) 82–94.
- ↑ Edward Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, (The Modern Library, 1932), chap. XXIX., p. 1,040
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 84.2 84.3 84.4 Kohen, E. (2007). History of the Byzantine Jews: A Microcosmos in the Thousand Year Empire. University Press of America. pp. 26–31. ISBN 9780761836230. https://books.google.com/books?id=r-9qJRP20MIC. Retrieved 2015-04-10.
- ↑ Norwich, John Julius (1999). A Short History of Byzantium. New York: Vintage Books, A Division of Random House, Inc.. p. 64. ISBN 0-679-77269-3. https://archive.org/details/shorthistorybyza00norw.
- ↑ Taylor, Keith Weller. (1983). The Birth of Vietnam (illustrated, reprint ed.). University of California Press. ISBN:0520074173. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ↑ Xiong, Victor Cunrui (2006), Emperor Yang of the Sui Dynasty: His Life, Times, and Legacy, Albany: State University of New York Press, ISBN 9780791482681, https://books.google.com/books?id=-1PSb8wp-woC
- ↑ Elli Kohen (2007). History of the Byzantine Jews: A Microcosmos in the Thousand Year Empire. University Press of America. ISBN 9780761836230. https://books.google.com/books?id=r-9qJRP20MIC. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ↑ Elias S. Shoufani: Al-Riddah and the Muslim conquest of Arabia. Toronto, 1973. ISBN:0-8020-1915-3
- ↑ Template:The Prophet and the Age of the Caliphates
- ↑ Template:The Arab Kingdom and its Fall
- ↑ Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, v. 23 "The Zenith of the Marwanid House," transl. Martin Hinds, SUNY, Albany, 1990; v. 24 "The Empire in Transition," transl. David Stephen Powers, SUNY, Albany, 1989
- ↑ Chapuis, Oscar (1995). A history of Vietnam: from Hong Bang to Tu Duc Numéro 5 de Contributions in Asian studies. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 35. ISBN 0-313-29622-7.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Shaban, M. A. (1979). The ʿAbbāsid Revolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-29534-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=1_03AAAAIAAJ.
- ↑ Blankinship, Khalid Yahya (1994). "Khārijī and Shī'ī Revolts in Iraq and the East". The End of the Jihād State. Albany: State University of New York Press. pp. 190–191. ISBN 9780791418277. https://books.google.com/books?id=Jz0Yy053WS4C&pg=PA190.
- ↑ Ibn Khaldun (1852 transl.) Histoire des Berbères et des dynasties musulmanes de l'Afrique, Algiers.
- ↑ Hawting, Gerald R. (2000). The First Dynasty of Islam: The Umayyad Caliphate AD 661–750 (2nd ed.). London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-24072-7.
- ↑ Kennedy, Hugh (1996). Muslim Spain and Portugal: A Political History of al-Andalus (First ed.). London: Taylor and Francis. p. 32. ISBN 0-582-49515-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=NFfJAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA32.
- ↑ Beckwith, Christopher I. (2009): Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN:978-0-691-13589-2
- ↑ Lewis (1960). "ʿAlids". in Gibb, H. A. R.. The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume I: A–B. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 401–403. OCLC 495469456. http://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-of-islam-2/alids-SIM_0543.
- ↑ Jennifer R. Davis (2015), Charlemagne's Practice of Empire (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), p. 179. The Royal Frankish Annals record battles in the years 772–80, 782–85, 793–99, 802 and 804.
- ↑ Template:The History of al-Tabari
- ↑ Anh Thư Hà, Hò̂ng Đức Trà̂n A brief chronology of Vietnam's history 2000 Page 27 "BỐ Cái Đại Vương (Phùng Hưng) (766-802) Phùng Hưng was initially a notable in Đường Lâm (Ba Vì, Hà Tây province). His father was a man of talent and good ethics, who took part in the rebellion led by Mai Hắc Đế. As a man of unusual..."
- ↑ Levy-Rubin, Milka; Kedar, Benjamin Z (2001). "A Spanish Source on mid-Ninth Century Mar Saba and a Neglected Sabaite Martyr". in Patrich, Joseph. The Sabaite Heritage in the Orthodox Church from the Fifth Century to the Present. Peeters Publishers. pp. 63–83. ISBN 978-90-429-0976-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=O4pj9YNdgJYC&pg=PA63.
- ↑ Eisenstein, H. (2002). "Al-Walid b. Tarif". The Encyclopedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume XI: W–Z. Leiden and New York: BRILL. pp. 129–130. ISBN 90-04-12756-9. http://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-of-islam-2/al-walid-b-tarif-SIM_7849.
- ↑ Nagendra Kr Singh, International encyclopaedia of Islamic dynasties, Anmol Publications PVT. LTD., 2002
- ↑ Template:ODB
- ↑ Barbara M. Kreutz, Before the Normans: Southern Italy in the Ninth and Tenth Centuries, (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1991), 26-27.
- ↑ Goldberg, Eric J. "Popular Revolt, Dynastic Politics, and Aristocratic Factionalism in the Early Middle Ages: The Saxon Stellinga Reconsidered." Speculum, Vol. 70, No. 3. (Jul., 1995), pp 467–501.
- ↑ Il-yeon: Samguk Yusa: Legends and History of the Three Kingdoms of Ancient Korea, translated by Tae-Hung Ha and Grafton K. Mintz. Book Two, page 103. Silk Pagoda (2006). ISBN:1-59654-348-5
- ↑ Zizhi Tongjian, vols. 248, 249, 250, 251, 252.
- 任士英 (2005) 正說唐朝二十一帝 Taipei (台北): 聯經. ISBN:978-957-08-2943-3
- ↑ The crisis of the ʻAbbāsid Caliphate, By Ṭabarī, George Saliba, pg.15-19
- ↑ Template:The History of al-Tabari
- ↑ Template:The History of al-Tabari
- ↑ Waines, David, ed (1992). The History of al-Ṭabarī, Volume XXXVI: The Revolt of the Zanj, A.D. 869–879/A.H. 255–265. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-0764-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=-ctgf6WSCPMC.
- ↑ Zizhi Tongjian, vols. 252, 253, 254.
- 任士英 (2005) 正說唐朝二十一帝 Taipei (台北): 聯經. ISBN:978-957-08-2943-3
- ↑ Houtsma, M. Th. et al. (eds.) (1913–1936) Encyclopaedia of Islam: dictionary of the geography, ethnography and biography of the Muhammadan peoples (1st ed. in 4 vol.) E. J. Brill, London. "'OMAR b. ḤAFṢŪN", p. 981-2; reprinted in facsimile edition as E.J. Brill's first encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913-1936 in 1987
- ↑ Brett, Michael (2017). The Fatimid Empire. The Edinburgh History of the Islamic Empires. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-4076-8.
- ↑ Psellus, Michael (1966). Fourteen Byzantine Rulers: The Chronographia of Michael Psellus. New York: Penguin Classics. pp. 400. ISBN 978-0-14-0441697. https://archive.org/details/fourteenbyzantin00psel/page/400.
- ↑ Psellus, Michael (1966). Fourtten Byzantine Rulers: The Chronographia of Michael Psellus. New York: Penguin Classics. pp. 32. ISBN 978-0-14-044169-7. https://archive.org/details/fourteenbyzantin00psel/page/32.
- ↑ Helmold: Chronica Slavorum. Neu übertragen und erläutert von Heinz Stoob. In: Ausgewählte Quellen zur deutschen Geschichte des Mittelalters. Wiss. Buchgesellschaft, Darmstadt 1963, 2. Auflage 1973.
- ↑ Kaldellis, Anthony (2017). Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood: The Rise and Fall of Byzantium, 955 A.D. to the First Crusade. Oxford University Press. p. 45. ISBN 978-0190253226.
- ↑ "Die Nördliche Song-Dynastie". http://german.cri.cn/other/chinageschichte/72.htm.
- ↑ Gowers, Bernard (2013). "996 and all that: The Norman peasants' revolt reconsidered". Early Medieval Europe 21: 71–98. doi:10.1111/emed.12010.
- ↑ A world history of tax rebellions: an encyclopedia of tax rebels, revolts, and riots from antiquity to the present, David F. Burg, Taylor & Francis, 2004, ISBN:0-415-92498-7, pp. 74–75.
- ↑ Dennis P. Hupchick, pp. 324-325.
- ↑
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Holland, Arthur William (1911). "Rienzi, Cola di". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 323.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Holland, Arthur William (1911). "Rienzi, Cola di". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 323.
- ↑ Chaliand, Gerard; Arnaud Blin (2007). The History of Terrorism: From Antiquity to Al Qaeda. University of California Press. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-520-24709-3. https://archive.org/details/historyofterrori00grar. "isfahan Timur."
- ↑ "Shimabara Rebellion". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/eb/topic-540634/Shimabara-Rebellion. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ↑ "Aclamação de Amador Bueno - 1641" (in pt-br). https://mundoeducacao.uol.com.br/historiadobrasil/aclamacao-amador-bueno.htm.
- ↑ "Aclamação de Amador Bueno (1641)" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/aclamacao-amador-bueno.htm.
- ↑ "Aclamação de Amador Bueno – São Paulo | Revoltas | Impressões Rebeldes". https://www.historia.uff.br/impressoesrebeldes/?revoltas_categoria=1640-aclamacao-amador-bueno.
- ↑ http://zahid.fm.interia.pl/ , "Tatarzy Polscy" (Polish Tatars), [1] (PDF)
- ↑ "История башкиро-татарских восстаний в XVII векевто — Реальное время". https://m.realnoevremya.ru/articles/66289-istoriya-bashkiro-tatarskih-vosstaniy-v-xvii-veke.
- ↑ "Revolta de Beckman: causas, participantes, fim" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/revolta-beckman.htm.
- ↑ "Beckman Revolt | Encyclopedia.com". https://www.encyclopedia.com/humanities/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/beckman-revolt.
- ↑ "P. Petrov - Karposhovoto vystanie, 1". http://macedonia.kroraina.com/pp/pp_1.htm.
- ↑ "War of the Emboabas | Brazilian history" (in en). https://www.britannica.com/event/War-of-the-Emboabas.
- ↑ "Guerra dos Emboabas: contexto, causas, consequências" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/guerra-dos-emboabas.htm.
- ↑ "Guerra dos Mascates (1710)" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/guerra-dos-mascates.htm.
- ↑ Kidd, Gray Fielding (2019). "Neither peddlers nor war: unraveling 180 years of historical literature on Pernambuco's "Peddlers' War," 1710-1711" (in en). CLIO: Revista de Pesquisa Histórica 37 (2): 300–325. doi:10.22264/clio.issn2525-5649.2019.37.2.07. ISSN 2525-5649. https://periodicos.ufpe.br/revistas/revistaclio/article/view/239101.
- ↑ "Vila Rica Revolt". https://forma-slova.com/en/articles/25065-vila-rica-revolt.
- ↑ "Revolta de Vila Rica" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/revolta-vila-rica.htm.
- ↑ "Diskussion zu den Referaten von Prof. Dr. Hanno Kube, LL.M. und Prof. Dr. Peter Essers", Erneuerung des Steuerrechts (Köln: Verlag Dr. Otto Schmidt): pp. 394–404, 2014, doi:10.9785/ovs.9783504384128.394, ISBN 978-3-504-38412-8, http://dx.doi.org/10.9785/ovs.9783504384128.394, retrieved 2021-02-02
- ↑ "The Slave Revolts by Herbert Aptheker". http://www.nybooks.com/articles/4503.
- ↑ THE FÉDONS OF GRENADA, 1763–1814 . Posted by Curtis Jacobs. Retrieved 10 March 2013, to 18: 25 pm.
- ↑ Rivera Vivanco, Gabriel (2011). "El apoyo de Chile a la independencia de las Provincias Unidas del Río de la Plata en 1811" (in es). Cuaderno de Historia Militar (7): 7–19.
- ↑ Hormazábal Espinosa, Pedro Edo. (2007). "Soldados chilenos en Argentina, la primera cooperación militar en el proceso independentista a partir de 1811" (in es). Revista de Historia Militar (6): 45–50.
- ↑ Arana, M., 2013, Bolivar, New York: Simon & Schuster, ISBN:9781439110195, pp. 186
- ↑ Sakalis, Alex (25 March 2021). "The Italians Who Fought for Greek Independence". Italics Magazine. https://italicsmag.com/2021/03/25/the-italians-who-fought-for-greek-independence/.
- ↑ "Belgian Corps 1832-35 in Portugal's Liberal Wars". 11 June 2006. http://balagan.info/belgian-corps-1832-35-in-portugals-liberal-wars.
- ↑ "British Library". https://www.bl.uk/collections/afghan/summary1838to1842.html.
- ↑ "Revolução Praieira: contexto, estopim, desfecho" (in pt-br). https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiab/revolucao-praieira.htm.
- ↑ Kunnen-Jones, Marianne (21 August 2002). "Anniversary Volume Gives New Voice To Pioneer Accounts of Sioux Uprising". University of Cincinnati. http://www.uc.edu/news/sioux.htm.
- ↑ Renowned author to speak about 1863 New York draft riots at Fairfield University's DiMenna-Nyselius Library press release Fairfield University
- ↑ How The Only Coup D'Etat In U.S. History Unfolded. NPR/Weekend Edition Sunday, 17 August 2008.
- ↑ Analysis: roots of the conflict between Georgia, South Ossetia and Russia
- ↑ "Communist Revolts of 1935 | Encyclopedia.com". https://www.encyclopedia.com/humanities/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/communist-revolts-1935.
- ↑ "A revolta comunista de 1935 | CPDOC". https://cpdoc.fgv.br/producao/dossies/FatosImagens/RevoltaComunista.
- ↑ Paul J. White, Primitive rebels or revolutionary modernizers?: the Kurdish national movement in Turkey, Zed Books, 2000, p. 79.
- ↑ "Levante Integralista | CPDOC". https://cpdoc.fgv.br/producao/dossies/AEraVargas1/anos37-45/PoliticaAdministracao/LevanteIntegralista.
- ↑ "I. Baltic Prisoners of the Gulag Revolts of 1953 – L. Latkovskis". lituanus.org. http://www.lituanus.org/2005/05_3_1Latkovskis.htm.
- ↑ "Há 60 anos, a "Campanha da Legalidade" impedia um golpe" (in pt-BR). 2021-09-05. https://congressoemfoco.uol.com.br/colunas-destaque/ha-60-anos-a-campanha-da-legalidade-impedia-um-golpe/.
- ↑ Santos, Patricia Fachin e João Vitor. "Campanha da Legalidade e o Brasil de hoje. Defesa da Constituição, senso de oportunidade política e mobilização popular. Alguns legados" (in pt-br). http://www.ihu.unisinos.br/159-noticias/entrevistas/612394-defesa-da-constituicao-senso-de-oportunidade-politica-e-mobilizacao-popular-legados-da-campanha-da-legalidade-para-o-brasil-de-hoje-algumas-analises.
- ↑ Tripp, Charles (2005). A History of Iraq. Cambridge University Press. pp. 188–189, 196. ISBN 978-0-521-70247-8. https://archive.org/details/historyofiraq00trip/page/188.
- ↑ 166.0 166.1 Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh : a legacy of blood.. Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN 0-340-39420-X. OCLC 242251870. http://worldcat.org/oclc/242251870.
- ↑ Tripp, Charles (2005). A History of Iraq. Cambridge University Press. pp. 116–126. ISBN:978-0-521-70247-8
- ↑ "India Pakistan – Timeline". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm.
- ↑ "Five killed in Assam bomb blasts". Dawn. 2 January 2009. http://www.dawn.com/2009/01/02/top6.htm.
- ↑ "Civil Police in Espírito Santo Sets Deadline for Governor to Meet Demands and Avoid a Strike". https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/internacional/en/brazil/2017/02/1857533-civil-police-in-espirito-santo-set-deadline-for-governor-to-meet-demands-and-avoid-a-strike.shtml.
- ↑ "Jamaica Observer Limited". https://www.jamaicaobserver.com/news/Brazilian-army-sends-paratroopers-to-chaotic-state_89091.
- ↑ ES, Do G1 (2017-02-08). "Sem PMs nas ruas, Espírito Santo registra 90 mortes, diz sindicato" (in pt-br). http://g1.globo.com/espirito-santo/noticia/2017/02/sem-pms-nas-ruas-espirito-santo-registra-87-mortes-diz-associacao.html.
 |




































