Triacontatetragon
| Regular triacontatetragon | |
|---|---|
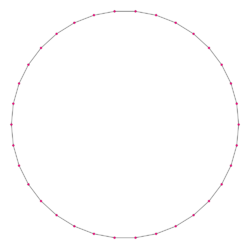 A regular triacontatetragon | |
| Type | Regular polygon |
| Edges and vertices | 34 |
| Schläfli symbol | {34}, t{17} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Dihedral (D34), order 2×34 |
| Internal angle (degrees) | 169.412° |
| Dual polygon | Self |
| Properties | Convex, cyclic, equilateral, isogonal, isotoxal |
In geometry, a triacontatetragon or triacontakaitetragon is a thirty-four-sided polygon or 34-gon.[1] The sum of any triacontatetragon's interior angles is 5760 degrees.
Regular triacontatetragon
A regular triacontatetragon is represented by Schläfli symbol {34} and can also be constructed as a truncated 17-gon, t{17}, which alternates two types of edges.
One interior angle in a regular triacontatetragon is (2880/17)°, meaning that one exterior angle would be (180/17)°.
The area of a regular triacontatetragon is (with t = edge length)
and its inradius is
The factor is a root of the equation .
The circumradius of a regular triacontatetragon is
As 34 = 2 × 17 and 17 is a Fermat prime, a regular triacontatetragon is constructible using a compass and straightedge.[2][3][4] As a truncated 17-gon, it can be constructed by an edge-bisection of a regular 17-gon. This means that the values of and may be expressed in terms of nested radicals.
Symmetry
The regular triacontatetragon has Dih34 symmetry, order 68. There are 3 subgroup dihedral symmetries: Dih17, Dih2, and Dih1, and 4 cyclic group symmetries: Z34, Z17, Z2, and Z1.
These 8 symmetries can be seen in 10 distinct symmetries on the icosidigon, a larger number because the lines of reflections can either pass through vertices or edges. John Conway labels these by a letter and group order.[5] The full symmetry of the regular form is labeled r68 and no symmetry is labeled a1. The dihedral symmetries are divided depending on whether they pass through vertices (d for diagonal) or edges (p for perpendiculars), and i when reflection lines path through both edges and vertices. Cyclic symmetries n are labeled as g for their central gyration orders.
Each subgroup symmetry allows one or more degrees of freedom for irregular forms. Only the g34 subgroup has no degrees of freedom but can seen as directed edges.
The highest symmetry irregular triacontatetragons are d34, an isogonal triacontatetragon constructed by seventeen mirrors which can alternate long and short edges, and p34, an isotoxal triacontatetragon, constructed with equal edge lengths, but vertices alternating two different internal angles. These two forms are duals of each other and have half the symmetry order of the regular triacontatetragon.
Dissection

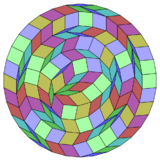
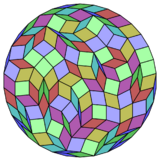
Coxeter states that every zonogon (a 2m-gon whose opposite sides are parallel and of equal length) can be dissected into m(m-1)/2 parallelograms.[6] In particular this is true for regular polygons with evenly many sides, in which case the parallelograms are all rhombi. For the regular triacontatetragon, m=17, it can be divided into 136: 8 sets of 17 rhombs. This decomposition is based on a Petrie polygon projection of a 17-cube.

|

|

|
|
|
Triacontatetragram
A triacontatetragram is a 34-sided star polygon. There are seven regular forms given by Schläfli symbols {34/3}, {34/5}, {34/7}, {34/9}, {34/11}, {34/13}, and {34/15}, and nine compound star figures with the same vertex configuration.
 {34/3} |
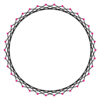 {34/5} |
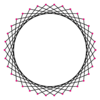 {34/7} |
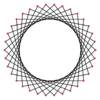 {34/9} |
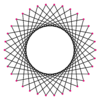 {34/11} |
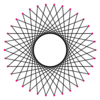 {34/13} |
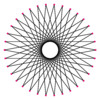 {34/15} |
Many isogonal triacontatetragrams can also be constructed as deeper truncations of the regular heptadecagon {17} and heptadecagrams {17/2}, {17/3}, {17/4}, {17/5}, {17/6}, {17/7}, and {17/8}. These also create eight quasitruncations: t{17/9} = {34/9}, t{17/10} = {34/10}, t{17/11} = {34/11}, t{17/12} = {34/12}, t{17/13} = {34/13}, t{17/14} = {34/14}, t{17/15} = {34/15}, and t{17/16} = {34/16}. Some of the isogonal triacontatetragrams are depicted below, as a truncation sequence with endpoints t{17}={34} and t{17/16}={34/16}.[7]
 t{17}={34} |

|

|

|
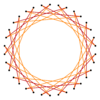
|
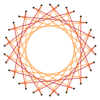
|

|

|

|
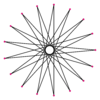 t{17/16}={34/16} |
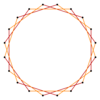 t{17/3}={34/3} |
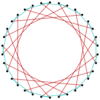
|
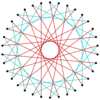
|

|
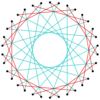
|
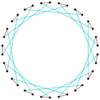
|
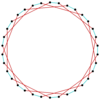
|

|

|
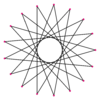 t{17/14}={34/14} |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination t{17/5}={34/5} |
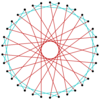
|
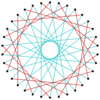
|
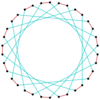
|
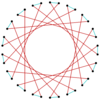
|
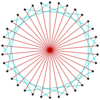
|
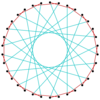
|
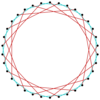
|
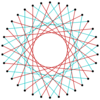
 t{17/12}={34/12} |
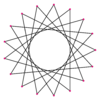 t{17/12}={34/12} |
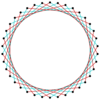 t{17/7}={34/7} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 t{17/10}={34/5} |
 t{17/9}={34/9} |
|
|
|
|
|
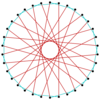
|

|
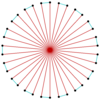
|
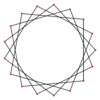 t{17/8}={34/8} |
References
- ↑ "Ask Dr. Math: Naming Polygons and Polyhedra". http://mathforum.org/dr.math/faq/faq.polygon.names.html.
- ↑ W., Weisstein, Eric. "Constructible Polygon" (in en). http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ConstructiblePolygon.html.
- ↑ Chepmell, C. H. (1913-03-01). "A construction of the regular polygon of 34 sides" (in en). Mathematische Annalen 74 (1): 150–151. doi:10.1007/bf01455349. ISSN 0025-5831. https://zenodo.org/record/1428274/files/article.pdf.
- ↑ White, Charles Edgar (1913) (in en). Theory of Irreducible Cases of Equations and Its Applications in Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry. pp. 79. https://books.google.com/books?id=O5Y5AQAAMAAJ.
- ↑ John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, (2008) The Symmetries of Things, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 20, Generalized Schaefli symbols, Types of symmetry of a polygon pp. 275-278)
- ↑ Coxeter, Mathematical recreations and Essays, Thirteenth edition, p.141
- ↑ The Lighter Side of Mathematics: Proceedings of the Eugène Strens Memorial Conference on Recreational Mathematics and its History, (1994), Metamorphoses of polygons, Branko Grünbaum
