Chemistry:Sirius Red
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
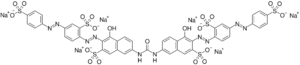
Hexasodium (3E)-4-oxo-7-[[(6E)-5-oxo-7-sulfonato-6-[[2-sulfonato-4-[(4-sulfonatophenyl)diazenyl]phenyl]hydrazinylidene]naphthalen-2-yl]carbamoylamino]-3-[[2-sulfonato-4-[(4-sulfonatophenyl)diazenyl]phenyl]hydrazinylidene]naphthalene-2-sulfonate
| |
| Other names
Direct Red 80; Picrosirius Red
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H26N10Na6O21S6 | |
| Molar mass | 1373.05 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Sirius Red F 3B (Direct Red 80) is an azo dye primarily used in staining methods for collagen and amyloid.[1] It has the molecular formula C45H26N10Na6O21S6.
In histology, sirius red staining is used in various domains of diagnostic to observe fibrosis levels in a lot of cases of inflammation induced by cancer, vascular or metabolic pathologies.[2]
In bright field microscopy the following can be observed:
- The nuclei in yellow
- The cytoplasm in yellow
- Collagen fibers in red
- Muscular fibers in yellow
- Red blood cells in yellow
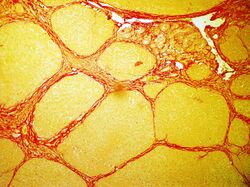
Sirius red staining in rat liver, where the red color indicates collagen deposition[3]
See also
- Collagen Hybridizing Peptide, a peptide that stains denatured collagen in tissues
References
- ↑ Dapson, Richard W.; Fagan, C.; Kiernan, John A.; Wickersham, T.W. (March 2011). "Certification procedures for sirius red F3B". Biotechnic & Histochemistry 86 (3): 133–9. doi:10.3109/10520295.2011.570277. PMID 21417582. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/50591278. Retrieved 2015-08-21.
- ↑ "Sirius red". http://www.histalim.com/accueil/activities/our-services/histology/sirius-red/.
- ↑ Dwivedi, Durgesh Kumar; Jena, G B (November 2018). "Glibenclamide protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic damage in Wistar rat: investigation on NLRP3, MMP-2, and stellate cell activation". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 391 (11): 1257–1274. doi:10.1007/s00210-018-1540-2. PMID 30066023.
 |

