Chemistry:Sudan III

| |
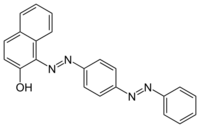
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-{[4-(Phenyldiazenyl)phenyl]diazenyl}naphthalen-2-ol | |
| Other names
Sudan Red BK, Fat Ponceau G, Cerasin Red, C.I. 26100, Solvent Red 23, Solvent Red 164, Sudan Red, Sudan Red III, Sudan V, Sudan Red B, Sudan G, Scarlet B, and Tony Red
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H16N4O | |
| Molar mass | 352.397 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 199 °C (390 °F; 472 K) |
| Hazards[1] | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich Sudan III |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H318, H319, H335, H413 | |
| P101, P102, P103, P270, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sudan III is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye. It is structurally related to azobenzene.[2]
Uses
It is used to color nonpolar substances such as oils, fats, waxes, greases, various hydrocarbon products, and acrylic emulsions. Its main use is as a fuel dye in the United States of America mandated by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to distinguish low-taxed heating oil from automotive diesel fuel, and by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to mark fuels with higher sulfur content; it is a replacement for Solvent Red 26 with better solubility in hydrocarbons.[3] The IRS requires "a concentration spectrally equivalent to at least 3.9 pounds of... Solvent Red 26 per thousand barrels of fuel" (11.1 mg/L);[4] the concentrations required by EPA are roughly 5 times lower. It should be stored at room temperature.[5]
Biological staining
Sudan III is a dye used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Oil Red O, Sudan IV, and Sudan Black B. They are used for staining of triglycerides in frozen sections, and some protein bound lipids and lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of reddish brown crystals and a maximum absorption at 507(304) nm.[6] It has a more orange shade than Oil Red O, lending to its less popular status. In botany, it is used with Light Green SF Yellowish to differentiate between suberized and cutinized plant tissue.[5]
Safety
Sudan I, Sudan III, and Sudan IV have been classified as category 3 carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer.[7]
References
- ↑ "Safety Data Sheet Sudan III". https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=S25593&productDescription=SUDAN+III+10G&vendorId=VN00115888&countryCode=US&language=en.
- ↑ Hunger, Klaus; Mischke, Peter; Rieper, Wolfgang; Raue, Roderich; Kunde, Klaus; Engel, Aloys (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_245.
- ↑ "L2_3_9_rf". http://www.chevron.com/products/prodserv/fuels/bulletin/diesel/L2_3_9_rf.htm.
- ↑ "Publication 510: Excise Taxes (Including Fuel Tax Credits and Refunds)". IRS.gov. February 2020. p. 9. https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p510.pdf. Retrieved February 10, 2021.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Sudan III". https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/documents/225/689/s4131pis.pdf.
- ↑ R. D. Lillie. Conn's Biological Stains. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD., U.S.A.
- ↑ "The induction of cytochrome P450 1A1 by Sudan dyes". J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 22 (2): 77–84. 2008. doi:10.1002/jbt.20220. PMID 18418879.
- Susan Budavari, Editor, (1996). The Merck Index, Ed. 12. Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA
- Edward Gurr, (1971). Synthetic Dyes in Biology, Medicine and Chemistry. Academic Press, London, England.
External links
- Stains File entry
 |
