Chemistry:Safranin
| |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
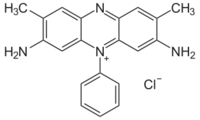
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,7-Diamino-2,8-dimethyl-5-phenylphenazin-5-ium chloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C20H19ClN4 | |||
| Molar mass | 350.85 g·mol−1 | ||
| Soluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   [1] [1]
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger[1] | ||
| H315, H318[1] | |||
| P264, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P310, P332+313, P362[1] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Safranin (Safranin O or basic red 2) is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and endospore staining. It can also be used for the detection of cartilage,[2] mucin and mast cell granules.
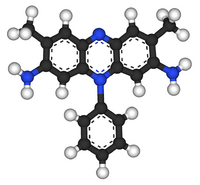
Safranin typically has the chemical structure shown at right (sometimes described as dimethyl safranin). There is also trimethyl safranin, which has an added methyl group in the ortho- position (see Arene substitution pattern) of the lower ring. Both compounds behave essentially identically in biological staining applications, and most manufacturers of safranin do not distinguish between the two. Commercial safranin preparations often contain a blend of both types.
Safranin is also used as redox indicator in analytical chemistry.
Safranines
Safranines are the azonium compounds of symmetrical 2,8-dimethyl-3,7-diaminophenazine. They are obtained by the joint oxidation of one molecule of a para-diamine with two molecules of a primary amine; by the condensation of para-aminoazo compounds with primary amines, and by the action of para-nitrosodialkylanilines with secondary bases such as diphenylmetaphenylenediamine. They are crystalline solids showing a characteristic green metallic lustre; they are readily soluble in water and dye red or violet. They are strong bases and form stable monacid salts. Their alcoholic solution shows a yellow-red fluorescence.[3]
Phenosafranine is not very stable in the free state[citation needed]; its chloride forms green plates[clarification needed]. It can be readily diazotized, and the diazonium salt when boiled with alcohol yields aposafranine or benzene induline, C18H12N3. Friedrich Kehrmann showed that aposafranine could be diazotized in the presence of cold concentrated sulfuric acid, and the diazonium salt on boiling with alcohol yielded phenylphenazonium salts. Aposafranone, C18H12N2O, is formed by heating aposafranine with concentrated hydrochloric acid. These three compounds are perhaps to be represented as ortho- or as para-quinones. The "safranine" of commerce is an ortho-tolusafranine. The first aniline dye-stuff to be prepared on a manufacturing scale was mauveine, which was obtained by Sir William Henry Perkin by heating crude aniline with potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid.[3]
Mauveine was converted to parasafranine (1,8-dimethylsafranine) by Perkin in 1878 by oxidative/reductive loss of the 7N-para-tolyl group.[4] Another well known safranin is phenosafranine (C.I. 50200, 3,7-diamino-5-phenylphenazinium chloride) widely used as a histological dye, photosensitizer and redox probe.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Safety Data Sheet: Safranin O". http://www.labchem.com/tools/msds/msds/75583.pdf.
- ↑ Rosenberg L (1971). "Chemical Basis for the Histological Use of Safranin O in the Study of Articular Cartilage" (abstract). J Bone Joint Surg Am 53 (1): 69–82. doi:10.2106/00004623-197153010-00007. PMID 4250366. http://www.ejbjs.org/cgi/content/abstract/53/1/69.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Safranine". Encyclopædia Britannica. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 1000.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Safranine". Encyclopædia Britannica. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 1000.
- ↑ W. H. Perkin F.R.S. (1879). "LXXIV.—On mauveine and allied colouring matters". J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 35: 717–732. doi:10.1039/CT8793500717. https://zenodo.org/record/2010519.
- ↑ Zucca, Paolo; Vinci, Carla; Rescigno, Antonio; Dumitriu, Emil; Sanjust, Enrico (14 April 2010). "Is the bleaching of phenosafranine by hydrogen peroxide oxidation catalyzed by silica-supported 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(sulfonatophenyl)porphine-Mn(III) really biomimetic?". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 321 (1–2): 27–33. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2010.01.015.
 |



