Medicine:Legius syndrome
| Legius syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Neurofibromatosis 1-like syndrome[1] |
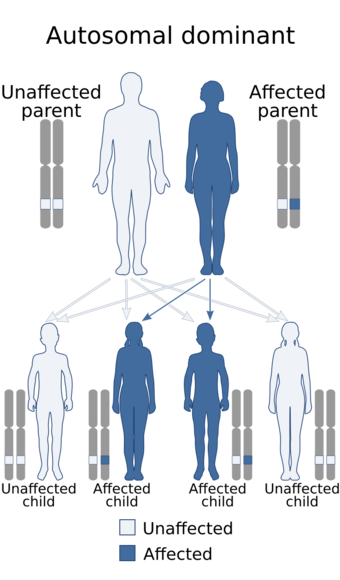 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
| Symptoms | café au lait spots; +/- learning disabilities[2] |
| Usual onset | at birth |
| Causes | Mutations in the SPRED1 gene[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Clinical findings, Genetic test[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | neurofibromatosis type I |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, Speech therapy[2][1] |
| Prognosis | good |
| Frequency | rare (estimated at 1:46,000-1:75,000)[2] |
Legius syndrome (LS) is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by cafe au lait spots.[3] It was first described in 2007 and is often mistaken for neurofibromatosis type I. It is caused by mutations in the SPRED1 gene.[5][6] It is also known as neurofibromatosis type 1-like syndrome.[1]
Symptoms and signs
Nearly all individuals with Legius syndrome show multiple café au lait spots on their skin.[7] Symptoms may include:[2]
- Freckles in the axillary and inguinal skin fold
- Lipomas, developing in adulthood
- Macrocephaly
- Learning disabilities
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Developmental delay
Features common in neurofibromatosis – like Lisch nodules (iris hamartomas diagnosed on slit lamp exam), bone abnormalities, neurofibromas, optic pathway gliomas and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors – are absent in Legius syndrome.[1]
Cause
Legius syndrome is a phakomatosis[8] and a RASopathy, a developmental syndrome due to germline mutations in genes.[7][9] The condition is autosomal dominant in regards to inheritance and caused by mutations to the SPRED1 gene at chromosome 15, specifically 15q14 (or (GRCh38): 15:38,252,086-38,357,248).[10][11] The gene in question demonstrates almost 100 mutations.[1]
Mechanism
A mutated SPRED1 protein adversely regulates Ras-MAPK signaling, which is a chain of proteins in a cell that sends signals from the surface of a cell to the nucleus which in turn causes the symptoms of this condition.[2][12]
Diagnosis
Genetic testing is necessary to identify the syndrome. The DNA test is necessary sometimes, because symptoms may not be sufficient to definitely diagnose this condition.[4][1][13]
Differential diagnosis
The symptoms of Legius syndrome and neurofibromatosis type I are very similar; An important difference between Legius syndrome and neurofibromatosis type I is the absence of tumor growths Lisch nodules and neurofibromas which are common in neurofibromatosis type I.[2]
A genetic test is often the only way to make sure a person has Legius syndrome and not neurofibromatosis type I; the similarity of symptoms stem from the fact that the different genes affected in the two syndromes code for proteins that carry out a similar task in the same reaction pathway.
Treatment
Management of Legius syndrome is done via the following:[2][1]
- Physical therapy
- Speech therapy
- Pharmacologic therapy (e.g. methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder)[14]
The prognosis of this condition is generally considered good with appropriate treatment.[citation needed]
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
- List of genes mutated in cutaneous conditions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Legius syndrome" (in en). http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=137605.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Stevenson, David; Viskochil, David; Mao, Rong (1993). "Legius Syndrome". GeneReviews. PMID 20945555. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK47312/. Retrieved 1 June 2017.update 2015
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Legius syndrome", Genetics Home Reference, National Institutes of Health
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Legius syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center" (in en). https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10714/legius-syndrome.
- ↑ "SPRED1", Genetics Home Reference, National Institutes of Health
- ↑ "Legius Syndrome Often Mistaken for Neurofibromatosis Type 1", by Allison Gandley, November 18, 2009, Medscape
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "OMIM Entry - # 611431 - LEGIUS SYNDROME" (in en-us). https://omim.org/entry/611431.
- ↑ Rosser, Tena (February 2018). "Neurocutaneous Disorders". Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn.) 24 (1, Child Neurology): 96–129. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000562. ISSN 1538-6899. PMID 29432239. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29432239/.
- ↑ Tidyman, William (2009). "The RASopathies: Developmental syndromes of Ras/MAPK pathway dysregulation". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 19 (3): 230–236. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.001. PMID 19467855.
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - * 609291 - SPROUTY-RELATED EVH1 DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 1; SPRED1" (in en-us). https://www.omim.org/entry/609291.
- ↑ "Homo sapiens sprouty related EVH1 domain containing 1 (SPRED1), RefSeq - Nucleotide - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/212549731.
- ↑ Molina, Julian R.; Adjei, Alex A. (2006-01-01). "The Ras/Raf/MAPK Pathway". Journal of Thoracic Oncology 1 (1): 7–9. doi:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9. PMID 17409820.
- ↑ "SPRED1 sprouty related EVH1 domain containing 1 - Gene - GTR - NCBI" (in en). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/genes/161742/.
- ↑ Storebø, Ole Jakob; Storm, Maja Rosenberg Overby; Pereira Ribeiro, Johanne; Skoog, Maria; Groth, Camilla; Callesen, Henriette E.; Schaug, Julie Perrine; Darling Rasmussen, Pernille et al. (2023-03-27). "Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023 (3): CD009885. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009885.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 36971690.
Further reading
- MD, Robert P. Erickson; PhD, Anthony J. Wynshaw-Boris MD (2016) (in en). Epstein's Inborn Errors of Development: The Molecular Basis of Clinical Disorders of Morphogenesis. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780190275426. https://books.google.com/books?id=cHd9DAAAQBAJ&q=Legius+syndrome&pg=PA639. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- Zhang, Jia (2016). "Molecular screening strategies for NF1-like syndromes with café-au-lait macules". Molecular Medicine Reports 14 (5): 4023–4029. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5760. PMID 27666661. Review
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |


