Medicine:X-linked myotubular myopathy
| X-linked myotubular myopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | XLMTM |
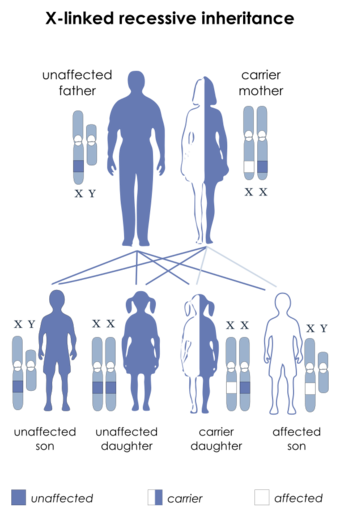 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. | |
X-linked myotubular myopathy (MTM) is a form of centronuclear myopathy (CNM) associated with mutations in the myotubularin 1 gene. It is found almost always in male infants. It is one of the severest congenital muscle diseases and is characterized by marked muscle weakness, hypotonia and feeding and breathing difficulties.[citation needed]
Genetics
This condition is caused by mutations in the myotubularin (MTM1) gene which is located on the long arm of the X chromosome (Xq28). Thus, almost all cases of X-linked MTM occurs in males. Females can be "carriers" for an X-linked genetic abnormality, but usually they will not be clinically affected themselves. Two exceptions for a female with a X-linked recessive abnormality to have clinical symptoms: one is a manifesting carrier and the other is X-inactivation. A manifesting carrier usually has no noticeable problems at birth; symptoms show up later in life. In X-inactivation, the female (who would otherwise be a carrier, without any symptoms), actually presents with full-blown X-linked MTM. Thus, she congenitally presents (is born with) MTM.[1]
Thus, although MTM1 mutations most commonly cause problems in boys, these mutations can also cause clinical myopathy in girls, for the reasons noted above. Girls with myopathy and a muscle biopsy showing a centronuclear pattern should be tested for MTM1 mutations.[1]
Abbreviations XL-MTM, XLMTM or X-MTM are sometimes used to emphasize that the mutation occurs on the X chromosome.
Research
Astellas Gene Therapies (earlier called Audentes Therapeutics) is developing an experimental gene therapy to treat the condition. A clinical trial was halted in 2020 after two boys participating in the trial died of liver inflammation and sepsis.[2]
References
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

