Medicine:Endocrine disease
| Endocrine glands | |
|---|---|
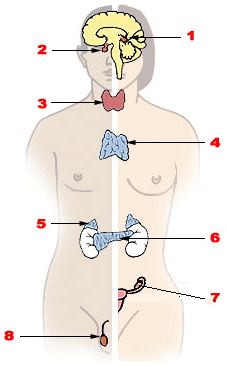 | |
| Major endocrine glands. (Male left, female right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8. Testes |
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:[1]
- Endocrine gland hypofunction/hyposecretion (leading to hormone deficiency)
- Endocrine gland hyperfunction/hypersecretion (leading to hormone excess)
- Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands
Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of hyperthyroidism are associated with an excess of thyroid hormone and a low level of thyroid stimulating hormone.[2]
List of diseases
Glucose homeostasis disorders
- Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
- Mature Onset Diabetes of the Young
- Diabetic myopathy[3][4]
- Hypoglycemia[citation needed]
- Idiopathic hypoglycemia
- Insulinoma
- Glucagonoma
Thyroid disorders
- Goitre
- Hyperthyroidism
- Graves-Basedow disease
- Toxic multinodular goitre
- Thyrotoxic myopathy
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroid myopathies[5]
- Kocher-Debre-Semelaigne syndrome
- Hoffmann syndrome
- Myasthenic syndrome
- Atrophic form
- Hypothyroid myopathies[5]
- Thyroiditis
- Thyroid cancer
- Thyroid hormone resistance
Calcium homeostasis disorders and Metabolic bone disease
- Parathyroid gland disorders
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroid myopathy[6]
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hypoparathyroid myopathy[6]
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoporosis
- Osteitis deformans (Paget's disease of bone)
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
Pituitary gland disorders
Posterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary
- Hypopituitarism (or Panhypopituitarism)
- Pituitary tumors
- Pituitary adenomas
- Prolactinoma (or Hyperprolactinemia)
- Acromegaly, gigantism, dwarfism
- Cushing's disease
Adrenal gland disorders
- Addison's disease
- Adrenal crisis
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Adrenal tumour
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Hypercortisolism (Cushing's disease)
- Hypoaldosteronism
- Hyperaldosteronism
Sex hormone disorders
- Disorders of sex development or intersex disorders
- Hermaphroditism
- Gonadal dysgenesis
- Androgen insensitivity syndromes
- Hypogonadism (Gonadotropin deficiency)
- Inherited (genetic and chromosomal) disorders
- Acquired disorders
- Ovarian failure (also known as Premature Menopause)
- Testicular failure
- Disorders of Puberty
- Menstrual function or fertility disorders
Tumours of the endocrine glands not mentioned elsewhere

- Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- MEN type 1
- MEN type 2a
- MEN type 2b
- Carcinoid syndrome
See also separate organs
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes
- Incidentaloma - an unexpected finding on diagnostic imaging, often of endocrine glands
Endocrine emergencies
In endocrinology, medical emergencies include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, hypoglycemic coma, acute adrenocortical insufficiency, phaeochromocytoma crisis, hypercalcemic crisis, thyroid storm, myxoedema coma and pituitary apoplexy.[7]
Emergencies arising from decompensated pheochromocytomas or parathyroid adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization).[8][9] It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols.[10][11][12]
See also
- List of MeSH codes (C19)
- List of ICD-9 codes 240-279: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases, and immunity disorders
- Diabetes self-management
References
- ↑ "Endocrine Disorders". webmd. http://diabetes.webmd.com/endocrine-system-disorders.
- ↑ "Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism: Overactivity of the Thyroid Gland". endocrineweb. http://www.endocrineweb.com/conditions/hyperthyroidism/diagnosing-hyperthyroidism-overactivity-thyroid-gland.
- ↑ D'Souza, Donna M.; Al-Sajee, Dhuha; Hawke, Thomas J. (2013-12-20). "Diabetic myopathy: impact of diabetes mellitus on skeletal muscle progenitor cells". Frontiers in Physiology 4: 379. doi:10.3389/fphys.2013.00379. ISSN 1664-042X. PMID 24391596.
- ↑ Sharma, Vikas; Borah, Papori; Basumatary, Lakshya J.; Das, Marami; Goswami, Munindra; Kayal, Ashok K. (July 2014). "Myopathies of endocrine disorders: A prospective clinical and biochemical study". Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology 17 (3): 298–302. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.138505. ISSN 0972-2327. PMID 25221399.
- ↑ Fariduddin, Maria M.; Bansal, Nidhi (2023), "Hypothyroid Myopathy", StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing), PMID 30137798, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519513/, retrieved 2023-08-25
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Rodolico, Carmelo; Bonanno, Carmen; Pugliese, Alessia; Nicocia, Giulia; Benvenga, Salvatore; Toscano, Antonio (September 2020). "Endocrine myopathies: clinical and histopathological features of the major forms". Acta Myologica: Myopathies and Cardiomyopathies 39 (3): 130–135. doi:10.36185/2532-1900-017. ISSN 2532-1900. PMID 33305169.
- ↑ Savage, M W; P Mah; A Weetman; J Newell-Price (1 September 2004). "Endocrine emergencies". Postgraduate Medical Journal 80 (947): 506–515. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2003.013474. PMID 15356351.
- ↑ Brouwers, FM; Eisenhofer, G; Lenders, JW; Pacak, K (December 2006). "Emergencies caused by pheochromocytoma, neuroblastoma, or ganglioneuroma.". Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America 35 (4): 699–724, viii. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2006.09.014. PMID 17127142. http://jcem.endojournals.org/content/98/2/581.short.
- ↑ Tahim, AS; Saunders, J; Sinha, P (2010). "A parathyroid adenoma: benign disease presenting with hyperparathyroid crisis.". Case Reports in Medicine 2010: 1–4. doi:10.1155/2010/596185. PMID 21209735.
- ↑ Newell, KA; Prinz, RA; Pickleman, J; Braithwaite, S; Brooks, M; Karson, TH; Glisson, S (August 1988). "Pheochromocytoma multisystem crisis. A surgical emergency.". Archives of Surgery 123 (8): 956–9. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400320042007. PMID 2899426.
- ↑ Scholten, A.; Cisco, R. M.; Vriens, M. R.; Cohen, J. K.; Mitmaker, E. J.; Liu, C.; Tyrrell, J. B.; Shen, W. T. et al. (2 January 2013). "Pheochromocytoma Crisis Is Not a Surgical Emergency". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 98 (2): 581–591. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-3020. PMID 23284003.
- ↑ Phitayakorn, R; McHenry, CR (June 2008). "Hyperparathyroid crisis: use of bisphosphonates as a bridge to parathyroidectomy.". Journal of the American College of Surgeons 206 (3): 1106–15. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.11.010. PMID 18501807.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
- Endocrine+system+diseases at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Template:MedlinePlusOverview
Template:Disease of the pancreas and glucose metabolism Template:Hypothalamic disease Template:Pituitary disease Template:Thyroid disease Template:Parathyroid disease Template:Adrenal gland disorder Template:Gonadal disorder Template:Growth disorder Template:Disorders involving multiple endocrine glands Template:Disease groups
 |
