Astronomy:(277475) 2005 WK4
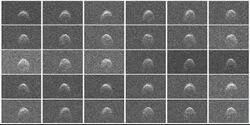 2005 WK4 imaged 30 times by radar at Goldstone on 8 August 2013 | |
| Discovery[1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Siding Spring Srvy. |
| Discovery site | Siding Spring Obs. |
| Discovery date | 27 November 2005 |
| Designations | |
| (277475) 2005 WK4 | |
| 2005 WK4 | |
| Minor planet category | Apollo · NEO · PHA[1][2] |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 8.71 yr (3,180 days) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 1.2506 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.7707 AU |
| 1.0106 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.2374 |
| Orbital period | 1.02 yr (371 days) |
| Mean anomaly | 81.040° |
| Mean motion | 0° 58m 12.36s / day |
| Inclination | 9.8433° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 138.14° |
| 74.063° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0037 AU · 1.4 LD |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 0.25±0.05 km[lower-alpha 1] 0.284 km (calculated)[3] |
| Rotation period | 2.595±0.002 h[4] 2.7±0.1 h[lower-alpha 1] 2.73±0.05 h[5] |
| Geometric albedo | 0.20 (assumed)[3] |
| Sk[6] · S (assumed)[3] B–V = 0.677±0.025[6] V–R = 0.446±0.019[6] V–I = 0.750±0.024[6] | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 20.1[1][3] |
(277475) 2005 WK4, provisional designation 2005 WK4, is a stony, sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group that passed Earth within 8.2 lunar distances on 8 August 2013.[7] It was discovered on 27 November 2005, by astronomers of the Siding Spring Survey at Siding Spring Observatory, Australia.[2]
Description
In August 2013, 2005 WK4 was radar-imaged by the Deep Space Network dish at Goldstone Observatory, United States,[7] and had been observed previously at Arecibo Observatory in July 2012 (this was not a close approach though).[8]
Physical characteristics
2005 WK4 measures approximately 250 meters in diameter, and has a rotation period of 2.595 hours.[3][4][lower-alpha 1] Its spectral type is that of an Sk-subtype, which transitions from the stony S-type to the uncommon K-type asteroids.[6]
See also
- List of asteroid close approaches to Earth in 2013
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Benner (2013): radiometric observations: mean-diameter 0.25±0.05 km; rotation period 2.7±0.1 hours. Summary figures at the LCDB; also see NASA news report
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 277475 (2005 WK4)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2277475. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "277475 (2005 WK4)". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=277475. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "LCDB Data for (277475)". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). http://www.minorplanet.info/PHP/generateOneAsteroidInfo.php?AstInfo=277475%7C. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Stephens, Robert D. (January 2014). "Asteroids Observed from CS3: 2013 July-September". The Minor Planet Bulletin 41 (1): 13–15. ISSN 1052-8091. Bibcode: 2014MPBu...41...13S. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/bib_query?bibcode=2014MPBu...41...13S. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (277475)". Geneva Observatory. http://obswww.unige.ch/~behrend/page5cou.html#277475. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Hicks, M.; Buratt, B.; Carcione, A.; Borlase, R. (August 2013). "Broadband Photometry Of The Potentially Asteroid 277475 (2005 WK4) and Corrected 52762 (1998 MT24) Colors.". The Astronomer's Telegram 5311 (5311): 1. Bibcode: 2013ATel.5311....1H. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/bib_query?bibcode=2013ATel.5311....1H. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Radar Images of Asteroid 2005 WK4". http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/asteroids/news/asteroid20130815.html#.Ug58vPJJqOI.
- ↑ 2005WK4 - Background
External links
- Radar images
- Radar Images of Asteroid 2005 WK4, NASA news, 15 August 2013
- Optical image, virtualtelescope.eu
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info )
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- (277475) 2005 WK4 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- (277475) 2005 WK4 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (277475) 2005 WK4 at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |




