Astronomy:HX Velorum
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Vela |
| Right ascension | 08h 42m 16.19252s[2] |
| Declination | −48° 05′ 56.7481″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.48 - 5.53[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B1.5V[4] |
| U−B color index | −0.9[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.17[4] |
| Variable type | ELL[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 42.0±4.5[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −3.714±0.128[2] mas/yr Dec.: 4.758±0.138[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.9479 ± 0.1121[2] mas |
| Distance | approx. 3,400 ly (approx. 1,100 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.32[6] |
| Details[4] | |
| Aa | |
| Mass | 8.5±1.7 M☉ |
| Radius | 5.0±0.3 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 8,700±1,500 L☉ |
| Temperature | 25,000±1,300 K |
| Ab | |
| Mass | 5.4±1.2 M☉ |
| Radius | 3.1±0.3 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,400±800 L☉ |
| Temperature | 20,000±2,500 K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
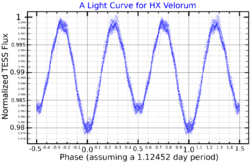
HX Velorum, also known as HR 3462 and HD 74455, is a star in the constellation Vela. It is a 5th magnitude star, so it will be faintly visible to the naked eye of an observer far from city lights. It is a variable star, whose brightness varies slightly from magnitude 5.48 to 5.53 over a period of 1.12 days.[3]
In 1981, Robert Shobbrook announced that HR 3462 is a variable star based on observations made in 1976. He correctly classified it as an ellipsoidal variable, but the period he derived, 0.56205±0.00005 days, was a factor of two too short because his data did not allow him to distinguish between primary and secondary minima in the light curve.[8] It was given the variable star designation HX Velorum in 1980.[9] In 1983, Christoffel Waelkens and Frédy Rufener published the correct period of variability, 1.124 days.[10]
HX Velorum is a triple star, consisting of a pair (components A, magnitude 5.5, and B, magnitude 8.28) separated by 0.5 arc seconds. Component A is itself a close binary pair (components Aa and Ab).[11][4] The system's brightness variation is caused by the ellipsoidal Aa and Ab components orbiting each other.[4]
HX Velorum is only about 2 arc minutes from the center of IC 2395, so it appears to be within that cluster. However the Gaia DR3 dataset lists the parallax of HX Velorum as 0.9479±0.1121 mas, yielding a distance of 3,400+500
−300 light years, while the distance to IC 2395 has been estimated to be 4,560±200[12] light years, so HX Velorum might be a foreground object rather than a true cluster member. Mark Blackford et al. concluded HX Velorum is a member of the cluster, but that conclusion was based in part on earlier, significantly different distance estimates for both the star and the cluster.[4]
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Samus', N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Blackford, M. G.; Erdem, A.; Sürgit, D.; Özkardeş, B.; Budding, E.; Butland, R.; Demircan, O. (July 2019). "Absolute parameters of young stars: HX Velorum". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 487 (1): 161–167. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1136. Bibcode: 2019MNRAS.487..161B.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Melnik, A. M.; Dambis, A. K. (2020). "Distance scale for high-luminosity stars in OB associations and in field with Gaia DR2. Spurious systematic motions". Astrophysics and Space Science 365 (7): 112. doi:10.1007/s10509-020-03827-0. Bibcode: 2020Ap&SS.365..112M.
- ↑ "V* HX Vel -- Double or Multiple Star". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V%2A+HX+Vel+--+Double+or+Multiple+Star.
- ↑ Shobbrook, R. R. (July 1981). "Short period variability of some early B stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 196 (2): 129–134. doi:10.1093/mnras/196.2.129. Bibcode: 1981MNRAS.196..129S.
- ↑ Kholopov, P. N.; Samus, N. N.; Kukarkina, N. P.; Medvedeva, G. I.; Perova, N. B. (February 1981). "65th Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1921: 1. Bibcode: 1981IBVS.1921....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/1901/1921.pdf. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- ↑ Waelkens, C.; Rufener, F. (May 1983). "An observational study of the influence of close companions on the pulsations of beta Cephei stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 121: 45–50. Bibcode: 1983A&A...121...45W.
- ↑ "The Washington Double Star Catalog". Georgia State University. http://www.astro.gsu.edu/wds/.
- ↑ Jaehnig, Karl; Bird, Jonathan; Holley-Bockelmann, Kelly (December 2021). "Membership Lists for 431 Open Clusters in Gaia DR2 Using Extreme Deconvolution Gaussian Mixture Models". The Astrophysical Journal 923 (1): 129. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac1d51. Bibcode: 2021ApJ...923..129J.
 |