Astronomy:NGC 2547
| NGC 2547 | |
|---|---|
 This image from the Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile, shows the bright open star cluster NGC 2547. | |
| Observation data (J2000.0 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Vela |
| Right ascension | 8h 09m 52.360s |
| Declination | −49° 10′ 35.01″ |
| Distance | 1.19 kly (364.0+46.8 −37.9[1] pc) |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.7 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 20′ |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mass | 201[1] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.61[1] ly |
| Estimated age | 37.7+5.7 −4.8[1] Myr |
| Other designations | NGC 2547, Cr 177, Mel 84, Dunlop 410, Lacaille III.2 |
NGC 2547 is a southern open cluster in Vela, discovered by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1751[2][3] from South Africa. The star cluster is young with an age of 20-30 million years.[4]
Observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope showed a shell around the B3 III/IV-type star HD 68478. This could be a sign of recent mass loss in this star.[5]
A study using Gaia DR2 data showed that NGC 2547 formed about 30 million years ago together with a new discovered star cluster, called [BBJ2018] 6.[6][7] The star cluster NGC 2547 has a similar age compared with Trumpler 10, NGC 2451B, Collinder 135 and Collinder 140. It was suggested that all these clusters formed in a single event of triggered star formation.[8]
NGC 2547 shows evidence for mass segregation down to 3 M☉.[9]
Cluster members with debris disks
Observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope have shown that ≤1% of the stars in NGC 2547 have infrared excess in 8.0 μm and 30-45% of the B- to F-type stars have infrared excess at 24 μm.[10]
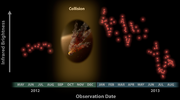
The system 2MASS J08090250-4858172, also called ID8 is located in NGC 2547 and showed substantial brightening of the debris disk at a wavelength of 3 to 5 micrometers, followed by a decay over a year. This was interpreted as a violent impact on a planetary body in this system.[11]
NGC 2547 contains nine M-dwarfs with 24 μm excess. These could be debris disks and the material could be orbiting close to the snow line of these stars, indicating that planet-formation is underway in these systems.[12] Later it was suggested that these M-dwarfs might contain Peter Pan Disks.[13] 2MASS 08093547-4913033, which is one of the M-dwarfs with a debris disk in NGC 2547 was observed with the Spitzer Infrared Spectrograph. In this system the first detection of silicate was made from a debris disk around an M-type star.[14]
Gallery
-
Asteroid collision - building planets near star NGC 2547-ID8 (artist concept)
-
Plot of IR brightness over time suggesting a collision of asteroids near star NGC 2547-0ID8 (2012–2013)
-
Zooming into the open star cluster NGC 2547 (in HD)
-
Pan sequence in the open star cluster NGC 2547 (in HD)
-
Infrared image of NGC 2547 taken with the Spitzer Space Telescope. Below the center HD 68478 and the shell around this star is seen.
-
Wide-field view of NGC 2547, created from DSS2 images.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bravi, L.; Zari, E.; Sacco, G. G.; Randich, S.; Jeffries, R. D.; Jackson, R. J.; Franciosini, E.; Moraux, E. et al. (July 2018). "The Gaia-ESO Survey: a kinematical and dynamical study of four young open clusters" (in en). Astronomy & Astrophysics 615: A37. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201832645. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2018A&A...615A..37B.
- ↑ "Full name of NGC discoverers". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. http://www.ngcicproject.org/erdmann/NGC_Discoverers_01.txt.
- ↑ Jones, K. G. (March 1969). "The search for the nebulae - VI". Journal of the British Astronomical Association 79: 213–222. Bibcode: 1969JBAA...79..213J.
- ↑ "Young, Hot and Blue - Stars in the cluster NGC 2547" (in en). https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1316/.
- ↑ Young, E. T.; Lada, C. J.; Teixeira, P.; Muzerolle, J.; Muench, A.; Stauffer, J.; Beichman, C. A.; Rieke, G. H. et al. (September 2004). "Spitzer Observations of NGC 2547: The Disk Population at 25 Million Years" (in en). The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 154 (1): 428. doi:10.1086/422688. ISSN 0067-0049. Bibcode: 2004ApJS..154..428Y.
- ↑ Beccari, Giacomo; Boffin, Henri M. J.; Jerabkova, Tereza; Wright, Nicholas J.; Kalari, Venu M.; Carraro, Giovanni; De Marchi, Guido; de Wit, Willem-Jan (November 2018). "A sextet of clusters in the Vela OB2 region revealed by Gaia" (in en). MNRAS 481 (1): L11–L15. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/sly144. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2018MNRAS.481L..11B. http://eprints.keele.ac.uk/5214/1/20180810_wright_sly144.pdf.
- ↑ "[BBJ2018 6"]. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=%5BBBJ2018%5D+6&submit=SIMBAD+search.
- ↑ Cantat-Gaudin, T.; Mapelli, M.; Balaguer-Núñez, L.; Jordi, C.; Sacco, G.; Vallenari, A. (January 2019). "A ring in a shell: the large-scale 6D structure of the Vela OB2 complex" (in en). Astronomy & Astrophysics 621: A115. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834003. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2019A&A...621A.115C.
- ↑ Littlefair, S. P.; Naylor, Tim; Jeffries, R. D.; Devey, C. R.; Vine, S. (November 2003). "Mass segregation in the young open cluster NGC 2547" (in en). MNRAS 345 (4): 1205–1211. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2966.2003.07035.x. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2003MNRAS.345.1205L.
- ↑ Gorlova, N.; Balog, Z.; Rieke, G. H.; Muzerolle, J.; Su, K. Y. L.; Ivanov, V. D.; Young, E. T. (November 2007). "Debris Disks in NGC 2547*" (in en). The Astrophysical Journal 670 (1): 516–535. doi:10.1086/521671. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2007ApJ...670..516G.
- ↑ Meng, Huan Y. A.; Su, Kate Y. L.; Rieke, George H.; Stevenson, David J.; Plavchan, Peter; Rujopakarn, Wiphu; Lisse, Carey M.; Poshyachinda, Saran et al. (August 2014). "Large impacts around a solar-analog star in the era of terrestrial planet formation" (in en). Science 345 (6200): 1032–1035. doi:10.1126/science.1255153. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 25170148. Bibcode: 2014Sci...345.1032M. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/49844/13/1503.05609.pdf.
- ↑ Forbrich, Jan; Lada, Charles J.; Muench, August A.; Teixeira, Paula S. (November 2008). "New M Dwarf Debris Disk Candidates in NGC 2547" (in en). The Astrophysical Journal 687 (2): 1107–1116. doi:10.1086/592035. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...687.1107F.
- ↑ Silverberg, Steven M.; Wisniewski, John P.; Kuchner, Marc J.; Lawson, Kellen D.; Bans, Alissa S.; Debes, John H.; Biggs, Joseph R.; Bosch, Milton K. D. et al. (2020-01-14). "Peter Pan Disks: Long-lived Accretion Disks Around Young M Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 890 (2): 106. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab68e6. Bibcode: 2020ApJ...890..106S.
- ↑ Teixeira, Paula S.; Lada, Charles J.; Wood, Kenneth; Robitaille, Thomas P.; Luhman, Kevin L. (July 2009). "Infrared Spectrograph Characterization of a Debris Disk Around an M-Type Star in NGC 2547" (in en). Astrophysical Journal 700 (1): 454–459. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/700/1/454. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...700..454T.
External links
- NGC 2547 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- SEDS – NGC 2547
Coordinates: ![]() 08h 10m 42s, −49° 16′ 00″
08h 10m 42s, −49° 16′ 00″
 |