Astronomy:Xi Octantis
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox (celestial coordinates) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Octans |
| Right ascension | 22h 50m 22.8139s[1] |
| Declination | −80° 07′ 25.8418″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.32 - 5.36[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | main sequence[3] |
| Spectral type | B6 V[4] (B5/7 V)[5] |
| U−B color index | −0.48[6][7] |
| B−V color index | −0.13[6] |
| Variable type | SPB[8] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 22.1±0.5[9] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +20.003[1] mas/yr Dec.: −12.607[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.35 ± 0.0644[1] mas |
| Distance | 514 ± 5 ly (157 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.57[10] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 4.02±0.05[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.0±0.5[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 360+24−22[3] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.09[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 14,050[12] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.1[12] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 30[13] km/s |
| Age | 46+25−16[14] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Xi Octantis, Latinized from ξ Octantis, is a solitary[17] variable star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5.3, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye; however, this varies slightly. Located 514 light years away, the object is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 22 km/s.
Xi Octantis has a stellar classification of B6 V,[4] indicating that it is an ordinary B-type main-sequence star. Hintler et al. gives it a luminosity class IV (subgiant)[19] while Houk and Cowley gives a classification intermediate between a B5 and B7 dwarf.[5] Nevertheless, it has 4 times the mass of the Sun[3] and is 3 times larger.[11] It shines with a luminosity of 360 solar luminosity[3] from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 14,050 K,[12] giving it a whitish blue glow. Xi Octantis is 46 million years old[14] – 64.8% through its short main sequence lifetime[12] – and spins modestly with a projected rotational velocity of 30 km/s.[13]
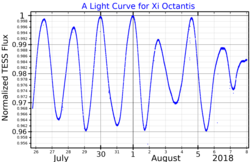
When the Hipparcos catalogue was released in 1997, Xi Octantis was found to vary in magnitude[20] — ranging from 5.32 to 5.36 based on data from the International Variable Star Index.[2] It has since been classified as a Slowly pulsating B-dwarf with a period of 1.78 days.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Watson, C. L.; Henden, A. A.; Price, A. (May 2006). "The International Variable Star Index (VSX)". Society for Astronomical Sciences Annual Symposium 25: 47. Bibcode: 2006SASS...25...47W.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (January 2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Cucchiaro, A.; Macau-Hercot, D.; Jaschek, M.; Jaschek, C. (October 1977). "Spectral classification from the ultraviolet line features of S2/68 spectra. II. Late B-type stars.". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 30: 71–79. ISSN 0365-0138. Bibcode: 1977A&AS...30...71C.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975). University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations -90_ to -53_ƒ0.. Bibcode: 1975mcts.book.....H.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P. et al. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 355: L27–L30. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ↑ Reed, B. Cameron (May 2003). "Catalog of Galactic OB Stars". The Astronomical Journal 125 (5): 2531–2533. doi:10.1086/374771. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2003AJ....125.2531R.
- ↑ Samus’, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (January 2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. ISSN 1063-7729. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. ISSN 1063-7737. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation" (in en). Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331–346. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. ISSN 1063-7737. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 De Cat, P.; Aerts, C. (October 2002). "A study of bright southern slowly pulsating B stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 393 (3): 965–981. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021068. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2002A&A...393..965D.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Smith, K. C.; Dworetsky, M. M. (July 1993). "Elemental abundances in normal late-B and HgMn stars from co-added IUE spectra. I. Iron-peak elements.". Astronomy and Astrophysics 274: 335–355. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 1993A&A...274..335S.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Levato, H.; Grosso, M. (June 2004). "New Projected Rotational Velocities of All Southern B-type Stars of the Bright Star Catalogue". Astronomical Society of the Pacific 215: 51. Bibcode: 2004IAUS..215...51L.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Grosbol, P. J. (June 1978). "Space velocities and ages of nearby early-type stars.". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 32: 409–421. ISSN 0365-0138. Bibcode: 1978A&AS...32..409G.
- ↑ "ksi Oct". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=ksi+Oct.
- ↑ Gould, Benjamin Apthorp (1878). "Uranometria Argentina : brillantez y posicion de las estrellas fijas, hasta la septima magnitud, comprendidas dentro de cien grados del polo austral : con atlas". Resultados del Observatorio Nacional Argentino 1. Bibcode: 1879RNAO....1.....G.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (11 September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ Hiltner, W. A.; Garrison, R. F.; Schild, R. E. (July 1969). "MK Spectral Types for Bright Southern OB Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 157: 313. doi:10.1086/150069. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 1969ApJ...157..313H.
- ↑ Perryman, M. A. C.; Lindegren, L.; Kovalevsky, J.; Hoeg, E.; Bastian, U.; Bernacca, P. L.; Crézé, M.; Donati, F. et al. (July 1997). "The HIPPARCOS Catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics 323: L49–L52. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 1997A&A...323L..49P.
 |