Chemistry:Ethyl pentanoate
From HandWiki
Revision as of 13:14, 2 April 2021 by imported>TextAI2 (fix)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
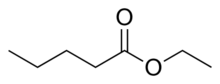
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl pentanoate | |
| Other names
Ethyl valerate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.18 g/mol |
| Density | 0.877 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −91 °C (−132 °F; 182 K) |
| Boiling point | 145 to 146 °C (293 to 295 °F; 418 to 419 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl pentanoate, also commonly known as ethyl valerate, is an organic compound used in flavors. It is an ester with the molecular formula C7H14O2. This colorless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with organic solvents.
As is the case with most volatile esters, it has a pleasant aroma and taste. It is used as a food additive to impart a fruity flavor, particularly of apple.
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 10042
 |


