Chemistry:Cresyl violet

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(9-dimethylamino-10-methyl-benzo[a]phenoxazin-5-ylidene)ammonium chloride
| |
| Other names
9-(Dimethylamino)-5-imino-10-methyl-5H-benzo[a]phenoxazine hydrochloride
Cresole violet | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3910949 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H18ClN3O | |
| Molar mass | 339.8187 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 245.5 °C (473.9 °F; 518.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cresyl violet is an organic compound with the chemical formula C19H18ClN3O. It is a basic dye and is used as a common stain in histology.
Cresyl violet stain
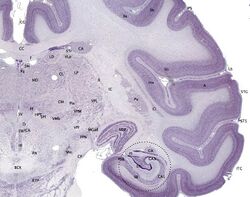
It is used in biology and medicine as a histological stain. Cresyl violet is an effective and reliable stain used for light microscopy sections. Initially, tissue sections are "defatted" by passing through graded dilutions of ethanol. Then, rehydrated by passing back through decreasing concentrations of ethanol. Lastly, back into water. The ethanol solutions act to differentiate the stain, causing myelin and other components to lose color whereas perikarya retain the color. It is also used to find Helicobacter pylori.[1]
Intestinal mucins also take up the stain although not as strongly as Campylobacter-like organisms.[2]
Cresyl violet is used to stain Heinz bodies in red blood corpuscles or for staining of the neurons in the brain and spinal cord. It is used to demonstrate the Nissl substance in the neurons and cell nuclei. In this role it is also often used as a counterstain to Luxol fast blue, which stains the myelin.
References
- ↑ "Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the natural history of duodenal ulcer disease". Arch. Dis. Child. 79 (6): 502–5. 1998. doi:10.1136/adc.79.6.502. PMID 10210995.
- ↑ "Cresyl fast violet staining method for Campylobacter like organisms". J. Clin. Pathol. 40 (3): 353. 1987. doi:10.1136/jcp.40.3.353-b. PMID 2435763. Free Full Text.
External links
- About stains - University of Western Australia.
 |

