Astronomy:124 Alkeste
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters |
| Discovery date | 23 August 1872 |
| Designations | |
| (124) Alkeste | |
| Pronunciation | /ælˈkɛstiː/[1] |
| Named after | Alcestis |
| A872 QA | |
| Minor planet category | Main belt |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 143.65 yr (52468 d) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.8288 astronomical unit|AU (423.18 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.43166 AU (363.771 Gm) |
| 2.63022 AU (393.475 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.075491 |
| Orbital period | 4.27 yr (1558.1 d) |
| Average Orbital speed | 18.34 km/s |
| Mean anomaly | 343.779° |
| Mean motion | 0° 13m 51.816s / day |
| Inclination | 2.9573° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 187.991° |
| 61.413° | |
| Earth MOID | 1.41927 AU (212.320 Gm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 2.17851 AU (325.900 Gm) |
| TJupiter | 3.394 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 88.65±1.65 km 76.36±1.7 km |
| Mass | 4.7×1017 kg |
Equatorial surface gravity | 0.0214 m/s² |
Equatorial escape velocity | 0.0404 km/s |
| Rotation period | 9.921 h (0.4134 d) |
| Geometric albedo | 0.1728±0.008 |
| Physics | ~172 K |
| S | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 8.11,[2] 8.09[3] |
Alkeste (minor planet designation: 124 Alkeste) is a main-belt asteroid, and it is an S-type (silicaceous) in composition. C.H.F. Peters discovered the asteroid on August 23, 1872, from the observatory at Hamilton College, New York State. The name was chosen by Adelinde Weiss, wife of the astronomer Edmund Weiss, and refers to Alcestis, a woman in Greek mythology.[4]
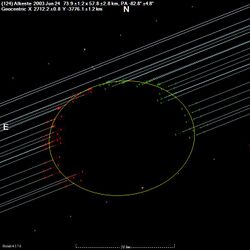
A 20 chord stellar occultation by Alkeste was observed when the asteroid passed in front of the third magnitude star Beta Virginis on June 24, 2003. The event was visible from Australia and New Zealand.[5]
The asteroid has been observed in 3 more stellar occultation events.[6]
Photometric observations of this asteroid in 2016 produced lightcurves indicating a rotation period of 9.9 hours with an amplitude variation of 0.18 in magnitude. This result matched previous determinations of the spin rate. The lightcurve was found to vary over the observation period as the viewing angle changed, suggesting the shadowing of topographic features.[7]
References
- ↑ 'Alceste' in Noah Webster (1884) A Practical Dictionary of the English Language
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yeomans, Donald K., "124 Alkeste", JPL Small-Body Database Browser (NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory), https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=124, retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ↑ Warner, Brian D. (December 2007), "Initial Results of a Dedicated H-G Project", The Minor Planet Bulletin 34: pp. 113–119, Bibcode: 2007MPBu...34..113W.
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. (2003). Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 27. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=KWrB1jPCa8AC&pg=PA27.
- ↑ Occultation by (124) Alkeste - 2003 Jun 24, Occultation Section, Royal Astronomical Society of New Zealand, May 23, 2003, http://www.occultations.org.nz/planet/2003/updates/030624au.htm, retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "Asteroid Data Sets". https://sbn.psi.edu/pds/resource/occ.html.
- ↑ Pilcher, Frederick (October 2016), "Three Asteroids with Changing Lightcurves: 124 Alkeste, 465 Alekto, and 569 Misa", The Minor Planet Bulletin 43 (4): 296–299, Bibcode: 2016MPBu...43..296P.
External links
- 124 Alkeste at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 124 Alkeste at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |