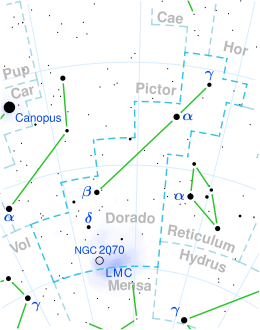
Astronomy:Beta Doradus
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Dorado |
| Right ascension | 05h 33m 37.51253s[1] |
| Declination | −62° 29′ 23.3231″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.46 to 4.08[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F4-G4Ia-II[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.55[3] |
| B−V color index | +0.70[4] |
| R−I color index | +0.48[4] |
| Variable type | δ Cephei[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +7.2[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +0.800[1] mas/yr Dec.: +9.458[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.14 ± 0.16[6] mas |
| Distance | 1,040 ± 50 ly (320 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.91±0.11[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 7.7±0.2[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 67.8±0.7[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 3,200[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.3[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 5,445[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.13[10] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 0[3] km/s |
| Age | 42.5±2.7[8] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Beta Doradus, Latinized from β Doradus, is the second brightest star in the southern constellation of Dorado.[12] It is a Classical Cepheid variable, with an apparent magnitude that varies between 3.46 and 4.08.[2] Based upon parallax measurements with the Hubble Space Telescope, it is located at a distance of 1,040 light-years (320 parsecs) from Earth.[6]
Characteristics

Beta Doradus is a Cepheid variable that regularly changes magnitude from a low of 4.08 to a high of 3.46[2] over a period of 9.84318 days.[14] The light curve of this magnitude change follows a nearly regular saw-tooth pattern, with average amplitude variations period to period about 0.005 magnitude from average amplitude of 0.62 magnitude.[14] During each radial pulsation cycle, the radius of the star varies by 3.9 R☉ around a mean of 67.8 R☉.[9] Its spectral type and luminosity class are likewise variable, from F-type to G-type and from a supergiant to a bright giant.[3]
Far ultraviolet emissions have been detected from this star with the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer, while X-ray emissions were detected with the XMM-Newton space telescope. The X-ray luminosity is about 1 × 1029 erg/s and the emission varies with the pulsation period, suggesting a connection with the pulsation process. The peak X-ray emissions are in the 0.6–0.8 keV energy range, which occurs for plasmas with temperatures of 7–10 million K.[15]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 bet Dor, database entry, The combined table of GCVS Vols I-III and NL 67-78 with improved coordinates, General Catalogue of Variable Stars , Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow, Russia. Accessed on line September 9, 2008.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 HR 1922, database entry, The Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Preliminary Version), D. Hoffleit and W. H. Warren, Jr., CDS ID V/50. Accessed on line September 9, 2008.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Turner, D. G. (April 1980), "The reddening of Beta Doradus", Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada 74: 64–69, Bibcode: 1980JRASC..74...64T
- ↑ Evans, D. S. (June 20–24, 1966), Batten, Alan Henry; Heard, John Frederick, eds., "The Revision of the General Catalogue of Radial Velocities", Determination of Radial Velocities and their Applications, Proceedings from IAU Symposium no. 30 (University of Toronto: International Astronomical Union) 30: p. 57, Bibcode: 1967IAUS...30...57E
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Benedict, G. Fritz et al. (April 2007), "Hubble Space Telescope Fine Guidance Sensor Parallaxes of Galactic Cepheid Variable Stars: Period-Luminosity Relations", Astronomical Journal 133 (4): 1810–1827, doi:10.1086/511980, Bibcode: 2007AJ....133.1810B.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Turner, David G. (April 2010), "The PL calibration for Milky Way Cepheids and its implications for the distance scale", Astrophysics and Space Science 326 (2): 219–231, doi:10.1007/s10509-009-0258-5, Bibcode: 2010Ap&SS.326..219T
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (January 2011), "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 410 (1): 190–200, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x, Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Taylor, Melinda M.; Booth, Andrew J. (August 1998), "The bright southern Cepheid beta Doradus: the radial velocity curve, distance and size", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 298 (2): 594–600, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01670.x, Bibcode: 1998MNRAS.298..594T
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Romaniello, M. et al. (September 2008), "The influence of chemical composition on the properties of Cepheid stars. II. The iron content", Astronomy and Astrophysics 488 (2): 731–747, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065661, Bibcode: 2008A&A...488..731R
- ↑ "V* bet Dor". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V%2A+bet+Dor.
- ↑ Kaler, James B., "Beta Doradus", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/betador.html, retrieved 2012-01-01
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Plachy, E. et al. (2021), "TESS Observations of Cepheid Stars: First Light Results", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 253 (1): 11, doi:10.3847/1538-4365/abd4e3, Bibcode: 2021ApJS..253...11P
- ↑ Engle, Scott G. et al. (May 2009), "The Secret XUV Lives of Cepheids: FUV/X-ray observations of Polaris and β Dor", Future Directions in Ultraviolet Spectroscopy: A Conference Inspired by the Accomplishments of the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer Mission, AIP Conference Proceedings, 1135, pp. 192–197, doi:10.1063/1.3154048, Bibcode: 2009AIPC.1135..192E
Coordinates: ![]() 05h 33m 37.5177s, −62° 29′ 23.371″
05h 33m 37.5177s, −62° 29′ 23.371″
 |