Astronomy:Enceladus Life Signatures and Habitability

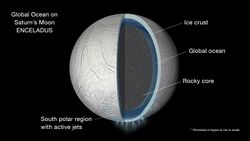
Enceladus Life Signatures and Habitability (ELSAH) is an astrobiology concept mission proposed in 2017 to NASA's New Frontiers program to send a spacecraft to Enceladus to search for biosignatures and assess its habitability.[1][2] The Principal Investigator is Christopher P. McKay, an astrobiologist at NASA Ames Research Center,[3] and the managing NASA center is Goddard Space Flight Center. No details of the mission have been made public, but observers speculate that it would be a plume-sampling orbiter mission.[4]
The two finalists, announced on 20 December 2017, are Dragonfly to Titan, and CAESAR (Comet Astrobiology Exploration Sample Return) which is a sample-return mission from comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko.[5]
Although ELSAH was not selected for launch in this instance, it received technology development funds to prepare it for future mission competitions.[6] The funds are meant to develop techniques that limit spacecraft contamination and thereby enable life detection measurements on cost-capped missions.[6]
See also
- Enceladus Explorer (En-Ex)
- Enceladus Life Finder (ELF)
- Explorer of Enceladus and Titan (E2T)
- Journey to Enceladus and Titan (JET)
- Life Investigation For Enceladus (LIFE)
- THEO
References
- ↑ "Proposed New Frontiers Missions". Future Planetary Exploration. 4 August 2017. http://futureplanets.blogspot.com/2017/08/proposed-new-frontiers-missions.html.
- ↑ McIntyre, Ocean (17 September 2017). "Cassini: The legend and legacy of one of NASA's most prolific missions". Spaceflight Insider. http://www.spaceflightinsider.com/missions/solar-system/cassini-legend-legacy-one-nasa-prolific-missions/.
- ↑ Chang, Kenneth (15 September 2017). "Back to Saturn? Five Missions Proposed to Follow Cassini". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/09/15/science/saturn-cassini-return.html.
- ↑ Back to Saturn? NASA Eyes Possible Return Mission as Cassini Ends. Mike Wall. Space. 17 September 2017.
- ↑ NASA's New Frontier Mission Will Search For Alien Life Or Reveal The Solar System's History. Elana Glowatz, IB Times. 20 December 2017.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 NASA Invests in Concept Development for Missions to Comet, Saturn Moon Titan. NASA News. 20 December 2017.
 |