Astronomy:Margaret (moon)
 Discovery image of Margaret taken by the Subaru Telescope in August 2003 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery date | August 29, 2003[1][2] |
| Designations | |
Designation | Uranus XXIII |
| Pronunciation | /ˈmɑːrɡərət/[3] |
| Adjectives | Margaretian /ˌmɑːrɡəˈrɛtiən/[4] |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Mean orbit radius | 14,345,000 km[5][6] |
| Eccentricity | 0.6608[6] (mean) |
| Orbital period | 1687.01 d |
| Inclination | 57° (to the ecliptic)[5] |
| Satellite of | Uranus |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 10 km (estimate)[7] |
| Surface area | ~1,300 km2 (estimate) |
| Volume | ~4,200 km3 (estimate) |
| Mass | ~5.5×1015 kg (estimate) |
| Mean density | ~1.3 g/cm3 (assumed) |
| ~0.0023 m/s2 (estimate) | |
| ~0.0085 km/s (estimate) | |
| Rotation period | ? |
| Axial tilt | ? |
| Albedo | 0.04 (assumed)[7] |
| Physics | ~65 K (estimate) |
Margaret is the only known prograde irregular satellite of the moons of Uranus. It was discovered by Scott S. Sheppard, et al. in 2003 and given the provisional designation S/2003 U 3.[8]
Confirmed as Uranus XXIII, it was named after the servant of Hero in William Shakespeare's play Much Ado About Nothing.[1]
Orbit
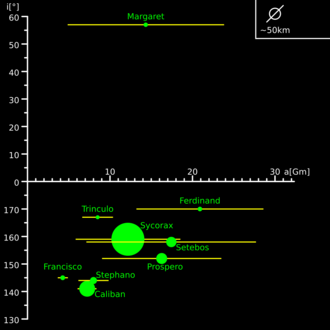
Margaret stands out as the only prograde irregular satellite of Uranus. The diagram illustrates the orbital parameters of Margaret, unique among the irregular satellites of Uranus, with inclination on the vertical axis and the eccentricity of the orbits represented by the segments extending from the pericentre to the apocentre.
Margaret's inclination of 57° is close to the limit of stability. The intermediate inclinations 60 < i < 140 are devoid of known moons due to the Kozai instability.[9] In this instability region, solar perturbations at apoapse cause the moons in this region to acquire large eccentricities that lead to collisions or ejection over 10 million to a billion years. Margaret's periapsis precession period (Pw) is almost 1.6 million years long.[6] Margaret itself may be ejected from the Uranian system in the far future.[10]
Margaret's orbit is subject to solar and planetary perturbations; thus, its orbital elements are variable over short timescales. Over a timescale of 8,000 years, the average orbital eccentricity of Margaret is 0.68. In 2010, its eccentricity grew to 0.81,[11] temporarily making Margaret with the most eccentric orbit of any moon in the Solar System, though Nereid's average eccentricity of 0.75 is greater.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Blue, Jennifer (2008-10-16). "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html#UranianSystem. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ Sheppard, Scott S.. "New Satellites of Uranus Discovered in 2003". Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawaii. http://www.dtm.ciw.edu/users/sheppard/satellites/uranus2003.html. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ Benjamin Smith (1903) The Century Dictionary and Cyclopedia
- ↑ Cathcart (1971) The Duchess of Kent
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sheppard, Jewitt & Kleyna 2005, p. 523, Table 3.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Jacobson, R.A. (2003) URA067 (2007-06-28). "Planetary Satellite Mean Orbital Parameters". JPL/NASA. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/?sat_elem#uranus. Retrieved 2008-01-23.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Sheppard, Jewitt & Kleyna 2005, p. 523, Table 3 ... ri (km) ... 10 ... i Radius of satellite assuming a geometric albedo of 0.04.
- ↑ IAU Circular 8217
- ↑ Sheppard, Jewitt & Kleyna 2005, pp. 524–525.
- ↑ Brozovic, M.; Jacobson, R. A. (4 March 2009). "The Orbits of the Outer Uranian Satellites". The Astronomical Journal 137 (4): 3834–42. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/137/4/3834. Bibcode: 2009AJ....137.3834B.
- ↑ "IAU-MPC Natural Satellites Ephemeris Service". IAU: Minor Planet Center. http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/iau/NatSats/NaturalSatellites.html. Retrieved 2008-01-26. (Select Uranian, deselect Ephemerides and select Orbital Elements)
- Sheppard, S. S.; Jewitt, D.; Kleyna, J. (2005). "An Ultradeep Survey for Irregular Satellites of Uranus: Limits to Completeness". The Astronomical Journal 129 (1): 518–525. doi:10.1086/426329. Bibcode: 2005AJ....129..518S.
External links
- Margaret Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- David Jewitt pages
- Uranus' Known Satellites (by Scott S. Sheppard)
- Ephemeris IAU-NSES
 |