Astronomy:Eta Cygni
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 19h 56m 18.37184s[1] |
| Declination | +35° 05′ 00.3224″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.889[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | red clump[3] |
| Spectral type | K0 III[4] |
| U−B color index | +0.881[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.035[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −26.57±0.34[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −34.165[1] mas/yr Dec.: −28.393[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 23.5482 ± 0.1078[1] mas |
| Distance | 138.5 ± 0.6 ly (42.5 ± 0.2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 0.74[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.9±0.1[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 10.2±0.3[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 60[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.36±0.08[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,783±20[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.02[6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 2.2 [8] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
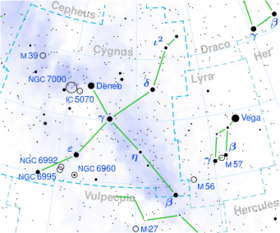
Eta Cygni (η Cygni) is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.889.[2] The star lies along the main body of the constellation, about midway between Gamma Cygni and Albireo.[10] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 23.55 mas,[1] it is located 138.5 light years from the Sun.
This is an evolved red clump[3] giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III.[4] It is presently on the horizontal branch and is generating energy through the nuclear fusion of helium at its core. The star has about 0.9 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 10 It radiates 60 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 4,780 K.[6]
Eta Cygni has five visual companions,[11] of which only component B appears to be physically associated. This magnitude 12.0 star lies at an angular separation of 7.80 arc seconds along a position angle of 206°, as of 2007.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Oja, T. (August 1986), "UBV photometry of stars whose positions are accurately known. III", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 65 (2): 405–409, Bibcode: 1986A&AS...65..405O.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Puzeras, E. et al. (October 2010), "High-resolution spectroscopic study of red clump stars in the Galaxy: iron-group elements", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 408 (2): 1225–1232, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17195.x, Bibcode: 2010MNRAS.408.1225P.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Morgan, W. W.; Keenan, P. C. (1973), "Spectral Classification", Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 11: 29–50, doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.11.090173.000333, Bibcode: 1973ARA&A..11...29M.
- ↑ Cardini, D. (January 2005), "Mg II chromospheric radiative loss rates in cool active and quiet stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics 430: 303–311, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041440, Bibcode: 2005A&A...430..303C.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Kallinger, T.; Beck, P. G.; Hekker, S.; Huber, D.; Kuschnig, R.; Rockenbauer, M.; Winter, P. M.; Weiss, W. W. et al. (2019-04-01), "Stellar masses from granulation and oscillations of 23 bright red giants observed by BRITE-Constellation" (in en), Astronomy & Astrophysics 624: A35, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834514, ISSN 0004-6361, Bibcode: 2019A&A...624A..35K
- ↑ Luck, R. Earle (September 2015), "Abundances in the Local Region. I. G and K Giants", The Astronomical Journal 150 (3): 23, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/3/88, 88, Bibcode: 2015AJ....150...88L.
- ↑ Massarotti, Alessandro et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal 135 (1): 209–231, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209, Bibcode: 2008AJ....135..209M.
- ↑ "eta Cyg". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=eta+Cyg.
- ↑ Marett-Crosby, Michael (2013), Twenty-Five Astronomical Observations That Changed the World: And How To Make Them Yourself, The Patrick Moore Practical Astronomy Series, Springer Science & Business Media, p. 231, ISBN 978-1461468004, https://books.google.com/books?id=0KRSphlvsqgC&pg=PA231.
- ↑ Mason, B. D. et al. (2014), "The Washington Visual Double Star Catalog", The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466–3471, doi:10.1086/323920, Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
External links
- Kaler, James B. (September 7, 2012), "Eta Cygni", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/etacyg.html, retrieved 2017-02-19.
Coordinates: ![]() 19h 56m 18s, +35° 05′ 00″
19h 56m 18s, +35° 05′ 00″
 |