Astronomy:GJ 1245
Coordinates: ![]() 19h 53m 54.492s, +44° 24′ 53.41″
19h 53m 54.492s, +44° 24′ 53.41″
Location of GJ 1245 in the constellation Cygnus | |
| Observation data {{#ifeq:J2000|J2000.0 (ICRS)|Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS)| Epoch J2000 [[Astronomy:Equinox (celestial coordinates)|Equinox J2000}} | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus[1] |
| GJ 1245 AC | |
| Right ascension | 19h 53m 55.142s[2] |
| Declination | +44° 24′ 44.39″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.46 / 16.75[3] |
| GJ 1245 B | |
| Right ascension | 19h 53m 55.141s[4] |
| Declination | +44° 24′ 54.15″[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 14.01[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M6V / M8V[5] / M6V[6] |
| Variable type | UV Cet[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 3.93±0.38[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 349.363(56)[4] mas/yr Dec.: −480.322(54)[4] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 214.5745 ± 0.0476[4] mas |
| Distance | 15.200 ± 0.003 ly (4.660 ± 0.001 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 15.12 / 18.41[5] / 15.72[3] |
| Orbit[8] | |
| Primary | GJ 1245 A |
| Companion | GJ 1245 C |
| Period (P) | 6,147±17 days |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.8267±0.0008″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.334±0.002 |
| Inclination (i) | 135.7±0.1° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 261.2±0.2° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 51506.8±2.1 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 36.1±0.2° |
| Details | |
| GJ 1245 A | |
| Mass | 0.120±0.001[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.146±0.007[5] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.0014[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 2,927[5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.07[5] dex |
| Age | ~300[citation needed] Myr |
| GJ 1245 C | |
| Mass | 0.081±0.001[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.087±0.004[5] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.0003[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 2,611[5] K |
| GJ 1245 B | |
| Mass | 0.115[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.142[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.00123[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 5.20[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 2,865[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.05[10] dex |
| Rotation | 0.71[11] days |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 7[11] km/s |
| Age | 3.1[10] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| GJ 1245 AC: G 208-44, LHS 3494, NLTT 48414, KIC 8451868, 2MASS J19535443+4424541[12] | |
| GJ 1245 B: G 208-45, LHS 3495, NLTT 48415, KIC 8451881, 2MASS J19535508+4424550[6] | |
| Database references | |
| AC | |
| B | |
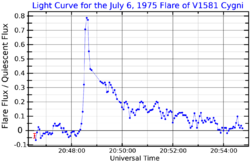
GJ 1245 (Gliese 1245) is a double star with components G 208-44 and G 208-45, located 15.2 light-years (4.7 parsecs) away in the constellation Cygnus. G 208-44 is itself a closer double star made up of two red dwarfs, while G 208-45 is also a red dwarf. GJ 1245 is the 43rd closest stellar system to the Solar System.[14] GJ 1245 A and B are both active flare stars,[15] and the pair are collectively designated V1581 Cygni.[16]
The largest of the three stars, GJ 1245 A (G 208-44 A) is only 12% the Sun's mass.[5] Of the other two stars, GJ 1245 C (G 208-44 B), is closest to star A at 2 AU away;[17] it is 8% of the Sun's mass.[5] The third star, GJ 1245 B (G 208-45), is 27 AU away from star A,[17] and is estimated to complete an orbit every 279 years.[18] It is slightly smaller and less luminous than GJ 1245 A.[9]
See also
- List of nearest stars
References
- ↑ Roman, Nancy G. (1987). "Identification of a constellation from a position". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 99 (617): 695. doi:10.1086/132034. Bibcode: 1987PASP...99..695R Constellation record for this object at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "The One Hundred Nearest Star Systems". RECONS. http://www.recons.org/TOP100.posted.htm.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 Dieterich, Serge B.; Simler, Andrew; Henry, Todd J.; Jao, Wei-Chun (April 2021). "The Solar Neighborhood. XLVII. Comparing M-dwarf Models with Hubble Space Telescope Dynamical Masses and Spectroscopy". The Astronomical Journal 161 (4): 172. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/abd2c2. Bibcode: 2021AJ....161..172D.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "G 208-45". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=G+208-45.
- ↑ Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Benedict, G. F. et al. (November 2016). "The Solar Neighborhood. XXXVII: The Mass-Luminosity Relation for Main-sequence M Dwarfs". The Astronomical Journal 152 (5): 141. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/5/141. Bibcode: 2016AJ....152..141B.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Stassun, Keivan G. et al. (2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal 158 (4): 138. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467. Bibcode: 2019AJ....158..138S.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Mann, Andrew W.; Feiden, Gregory A.; Gaidos, Eric; Boyajian, Tabetha; von Braun, Kaspar (2015). "How to Constrain Your M Dwarf: Measuring Effective Temperature, Bolometric Luminosity, Mass, and Radius". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (1): 64. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/1/64. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804...64M.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Morin, J.; Donati, J. -F.; Petit, P.; Delfosse, X.; Forveille, T.; Jardine, M. M. (2010). "Large-scale magnetic topologies of late M dwarfs". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 407 (4): 2269. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17101.x. Bibcode: 2010MNRAS.407.2269M.
- ↑ "G 208-44". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=G+208-44.
- ↑ Cristaldi, S.; Rodonò, M. (April 1976). "Discovery of Flare Activity in the Visual Binary G 208-44/45". Astronomy and Astrophysics 48: 165. Bibcode: 1976A&A....48..165C.
- ↑ Reylé, Céline; Jardine, Kevin; Fouqué, Pascal; Caballero, Jose A.; Smart, Richard L.; Sozzetti, Alessandro (30 April 2021). "The 10 parsec sample in the Gaia era". Astronomy & Astrophysics 650: A201. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202140985. Bibcode: 2021A&A...650A.201R. Data available at https://gruze.org/10pc/
- ↑ Lurie, John C.; Davenport, James R. A.; Hawley, Suzanne L.; Wilkinson, Tessa D.; Wisniewski, John P.; Kowalski, Adam F.; Hebb, Leslie (2015). "Kepler Flares III: Stellar Activity on GJ 1245A and B". The Astrophysical Journal 800 (2): 95. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/800/2/95. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...800...95L.
- ↑ Kholopov, P. N.; Kukarkina, N. P.; Perova, N. B. (1978). "63rd Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1414: 1. Bibcode: 1978IBVS.1414....1K.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Salama, Maïssa et al. (September 2021). "Large Adaptive Optics Survey for Substellar Objects around Young, Nearby, Low-mass Stars with Robo-AO". The Astronomical Journal 162 (3): 102. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac0445. Bibcode: 2021AJ....162..102S.
- ↑ Tokovinin, Andrei (2018). "The Updated Multiple Star Catalog". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 235 (1): 6. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/aaa1a5. Bibcode: 2018ApJS..235....6T.
Further reading
- Harrington, R. S.; Dahn, C. C.; Kallarakal, V. V.; Guetter, H. H.; Riepe, B. Y.; Walker, R. L.; Pier, J. R.; Vrba, F. J. et al. (1993). "U.S. Naval Observatory photographic parallaxes - List IX". Astronomical Journal 105 (4): 1571–1580. doi:10.1086/116537. Bibcode: 1993AJ....105.1571H.
- Henry, Todd J.; Subasavage, John P.; Brown, Misty A.; Beaulieu, Thomas D.; Jao, Wei-Chun; Hambly, Nigel C. (2004). "The Solar Neighborhood. X. New Nearby Stars in the Southern Sky and Accurate Photometric Distance Estimates for Red Dwarfs". The Astronomical Journal 128 (5): 2460–2473. doi:10.1086/425052. Bibcode: 2004AJ....128.2460H.
- Smart, R. L.; Ioannidis, G.; Jones, H. R. A.; Bucciarelli, B.; Lattanzi, M. G. (2010). "Cool dwarfs stars from the Torino Observatory Parallax Program". Astronomy and Astrophysics 514: A84. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913424. Bibcode: 2010A&A...514A..84S.
- Dittmann, Jason A.; Irwin, Jonathan M.; Charbonneau, David; Berta-Thompson, Zachory K. (2014). "Trigonometric Parallaxes for 1507 Nearby Mid-to-late M Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal 784 (2): 156. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/784/2/156. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...784..156D. Table with parallaxes.
External links
- http://jumk.de/astronomie/near-stars/v1581-cygni.shtml
- http://www.answers.com/topic/list-of-nearest-stars?cat=travel
- http://www.richweb.f9.co.uk/astro/nearby_stars.htm
 |