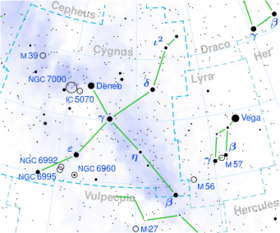
Astronomy:Delta Cygni
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 19h 44m 58.47854s[1] |
| Declination | +45° 07′ 50.9161″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 2.87[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0 IV[3] (B9 III + F1 V[4]) |
| U−B color index | −0.10[5] |
| B−V color index | −0.02[5] |
| Variable type | Suspected[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −20.1[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +44.07[1] mas/yr Dec.: +48.66[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 19.77 ± 0.48[1] mas |
| Distance | 165 ± 4 ly (51 ± 1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.74[8] |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Primary | A |
| Companion | B |
| Period (P) | 780.27 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 3.0″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.4670 |
| Details[10] | |
| Mass | 2.93 M☉ |
| Radius | 4.81±0.36[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 155 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.4±0.25[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 10400±400[11] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 142[11] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Delta Cygni is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from δ Cygni, and abbreviated Delta Cyg or δ Cyg. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, Delta Cygni is located roughly 165 light-years (51 parsecs) distant from the Sun.[1]
Delta Cygni's two components are designated Delta Cygni A (officially named Fawaris /fəˈwɛərɪs/)[12] and B. More widely separated is a faint third component, a 12th magnitude star that is moving along with the others. Together they form a triple star system.[13]
Nomenclature
δ Cygni (Latinised to Delta Cygni) is the binary's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as Delta Cygni A and B derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[14]
Traditionally, Delta Cygni had no proper name.[13] It belonged to the Arabic asterism al-Fawāris (الفوارس), meaning "the Riders" in indigenous Arabic,[15] together with Zeta, Epsilon, and Gamma Cygni, the transverse of the Northern Cross. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[16] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems.[17] It approved the name Fawaris for the component Delta Cygni A on 1 June 2018 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[12]
In Chinese, 天津 (Tiān Jīn), meaning Celestial Ford, refers to an asterism consisting of Delta Cygni, Gamma Cygni, 30 Cygni, Alpha Cygni (Deneb) and Nu, Tau, Upsilon, Zeta and Epsilon Cygni.[18] Consequently, the Chinese name for Delta Cygni itself is 天津二 (Tiān Jīn èr, English: the Second Star of Celestial Ford).[19]
Properties
The primary, Delta Cygni A, is a blue-white giant star of spectral class B9,[4] with a temperature of 10,400 K.[11] It is nearing the end of its main-sequence life stage with a luminosity 155 times that of the Sun,[10] a radius of 4.81 solar radii,[11] and a mass approximately 2.93 solar masses. Like many hot stars, it spins rapidly, at least 135 kilometers per second at the equator, about 60 times that of the Sun.[10]
The close companion Delta Cygni B is a yellow-white F-type main-sequence star of the sixth magnitude (6.33) with a luminosity about 6 times that of the Sun, and a mass about 1.5 times the Sun's. The two stars orbit each other at an average distance of 157 AU and a period of 780 years.[13]
The much more distant third companion is an orange (class K) twelfth magnitude star, and only two thirds as massive.[13]
The two main stars together appear with a spectral type of A0 IV.[3] As seen from Earth, the entire triple star system of Delta Cygni shines at a combined apparent magnitude of 2.87.[2] Both δ Cygni A and B have been suspected to vary in brightness. δ Cygni A was reported in 1951 as varying between magnitudes 2.85 and 2.89, and δ Cygni B was reported in 1837 to vary between magnitudes 6.3 and 8.5. The variability of the stars has not been confirmed.[6]
Pole Star
Delta Cygni is a visible star located within 3° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's North pole. For at least four centuries around 11,250 AD it will probably be considered a pole star, a title currently held by Polaris which is just 0.5° off of the precessional path.
| Preceded by | Pole Star | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| Deneb | ~11,000 AD to ~11,500 AD |
Vega |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Malagnini, M. L.; Morossi, C. (November 1990). "Accurate absolute luminosities, effective temperatures, radii, masses and surface gravities for a selected sample of field stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 85 (3): 1015–1019. Bibcode: 1990A&AS...85.1015M.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Zorec, J. et al. (July 2009). "Fundamental parameters of B supergiants from the BCD system. I. Calibration of the (λ_1, D) parameters into Teff". Astronomy and Astrophysics 501 (1): 297–320. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811147. Bibcode: 2009A&A...501..297Z.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Edwards, T. W. (April 1976). "MK classification for visual binary components". Astronomical Journal 81: 245–249. doi:10.1086/111879. Bibcode: 1976AJ.....81..245E.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Johnson, H. L. et al. (1966). "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory 4 (99): 99. Bibcode: 1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/GCVS. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Evans, D. S. (June 20–24, 1966). Batten, Alan Henry; Heard, John Frederick. eds. "The Revision of the General Catalogue of Radial Velocities". Determination of Radial Velocities and Their Applications, Proceedings from IAU Symposium No. 30 30: 57. Bibcode: 1967IAUS...30...57E.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Malkov, O. Yu. et al. (October 2012). "Dynamical masses of a selected sample of orbital binaries". Astronomy & Astrophysics 546: 5. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219774. A69. Bibcode: 2012A&A...546A..69M.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Challouf, M. et al. (2014). "Improving the surface brightness-color relation for early-type stars using optical interferometry⋆". Astronomy & Astrophysics 570: A104. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201423772. Bibcode: 2014A&A...570A.104C.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 Gordon, Kathryn D.; Gies, Douglas R.; Schaefer, Gail H.; Huber, Daniel; Ireland, Michael (2019). "Angular Sizes, Radii, and Effective Temperatures of B-type Stars from Optical Interferometry with the CHARA Array". The Astrophysical Journal 873 (1): 91. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab04b2. Bibcode: 2019ApJ...873...91G.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Naming Stars". IAU.org. https://www.iau.org/public/themes/naming_stars/.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Kaler, James B.. "Delta Cygni". Stars. University of Illinois. http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/deltacyg.html.
- ↑ Hessman, F. V.; Dhillon, V. S.; Winget, D. E.; Schreiber, M. R.; Horne, K.; Marsh, T. R.; Guenther, E.; Schwope, A.; Heber, U. (2010). "On the naming convention used for multiple star systems and extrasolar planets". arXiv:1012.0707 [astro-ph.SR].
- ↑ Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc.. pp. 193, 197. ISBN 978-0-486-21079-7.
- ↑ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". https://www.iau.org/science/scientific_bodies/working_groups/280/.
- ↑ "WG Triennial Report (2015-2018) - Star Names". p. 5. https://www.iau.org/static/science/scientific_bodies/working_groups/280/wg-starnames-triennial-report-2015-2018.pdf.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 4 日
 |