Astronomy:R Cygni
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 19h 36m 49.35633s[1] |
| Declination | +50° 11′ 59.7198″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.1 - 14.4[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[3] |
| Spectral type | S2.5,9e-S6,9e(Tc)[4] |
| Variable type | Mira[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −3.158[1] mas/yr Dec.: −5.755[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 1.4835 ± 0.0963[1] mas |
| Distance | 2,200 ± 100 ly (670 ± 40 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.85[5] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 11,700[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.50[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 2,538[5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.50[5] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
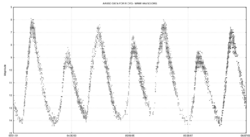
R Cygni is a variable star of the Mira type in the constellation Cygnus, less than 4' from θ Cygni. This is a red giant star on the asymptotic giant branch located around 2,200 light years away. It is an S-type star ranging between spectral types S2.5,9e to S6,9e(Tc).[4]
Stars at this mass range and evolutionary stage are pulsationally unstable, displaying a variation in their light output.[8] R Cygni has a maximum magnitude of 6.1 and a minimum magnitude of 14.4, with a period of 426.45 days.[2] The variation of this star was discovered by English astronomer N. R. Pogson in 1852, and it has a history of recorded brightness measurements stretching back more than a century.[8] R Cygni shows distinct period-doubling, where alternate maxima are of different brightness, hence the real period of pulsation could be considered to be twice that from one maximum to the next.[8]
The Catalog of Components of Double and Multiple Stars lists 10th magnitude BD+49 3065 as a companion to R Cygni, at a separation of 91", and both stars lie at approximately the same distance. The Washington Double Star Catalog additionally lists a 15th magnitude star as a companion at a separation of about 14".[9]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus', N. N; Kazarovets, E. V; Durlevich, O. V; Kireeva, N. N; Pastukhova, E. N (2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ Andriantsaralaza, M.; Ramstedt, S.; Vlemmings, W. H. T.; De Beck, E. (2022). "Distance estimates for AGB stars from parallax measurements". Astronomy and Astrophysics 667: A74. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243670. Bibcode: 2022A&A...667A..74A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 BSJ (4 January 2010). "R Cygni". American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=10921.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Anders, F.; Khalatyan, A.; Queiroz, A. B. A.; Chiappini, C.; Ardevol, J.; Casamiquela, L.; Figueras, F.; Jimenez-Arranz, O. et al. (2022). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: StarHorse2, Gaia EDR3 photo-astrometric distances (Anders+, 2022)". Vizier Online Data Catalog. Bibcode: 2022yCat.1354....0A.
- ↑ Guandalini, R; Francis, Charles (2010). "Infrared photometry and evolution of mass-losing AGB stars. III. Mass loss rates of MS and S stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 513: A4. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200911764. Bibcode: 2010A&A...513A...4G.
- ↑ "R Cyg". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=R+Cyg.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Kiss, L. L.; Szatmáry, K. (August 2002). "Period-doubling events in the light curve of R Cygni: Evidence for chaotic behaviour". Astronomy and Astrophysics 390 (2): 585–596. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020744. Bibcode: 2002A&A...390..585K.
- ↑ Mason, Brian D; Wycoff, Gary L; Hartkopf, William I; Douglass, Geoffrey G; Worley, Charles E (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M.
 |
