Astronomy:SN Refsdal
| File:250px SN Refsdal (inset picture) and galaxy cluster MACS J1149.6+2223 | |
| Event type | Supernova |
|---|---|
| Date | c. 9.34 billion years ago (discovered 11 November 2014 by the Hubble Space Telescope) |
| Constellation | Leo |
| Right ascension | 11h 49m 35.45s[1] |
| Declination | 22° 23′ 44.84″[1] |
| Epoch | J2000 |
| Distance | c. 14.4 billion ly |
| Redshift | z=1.49[1] |
| Host | SP 1149 |
| Notable features | First multiply-lensed supernova |
SN Refsdal is the first detected multiply-lensed supernova, visible within the field of the galaxy cluster MACS J1149+2223. It was named after Norwegian astrophysicist Sjur Refsdal, who, in 1964, first proposed using time-delayed images from a lensed supernova to study the expansion of the universe.[1][2][3] The observations were made using the Hubble Space Telescope.[4]
Einstein cross
The host galaxy of SN Refsdal is at a redshift of 1.49, corresponding to a comoving distance of 14.4 billion light-years and a lookback time of 9.34 billion years.[5] The multiple images are arranged around the elliptical galaxy at z = 0.54 in a cross-shaped pattern, also known as an "Einstein cross".[1]
Reappearance
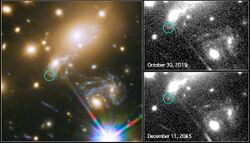
After the discovery of the supernova, astronomers predicted that they would be able to see it again in about one year, after the four images had faded away. This is because the initially observed four-image pattern was only one component of the lensing display. The supernova may also have appeared as a single image some 40–50 years ago elsewhere in the cluster field.[1]
The supernova reappeared at the predicted position between 14 November and 11 December 2015[6] (with the exact date being uncertain by approximately one month which is the interval between two consecutive Hubble observations),[7] in excellent agreement with the blind model predictions made before the reappearance was observed.[8][9][10] The time delay between the original quadruplet observed in 2014 and the latest appearance of the supernova in 2015 was used to infer the value of the Hubble constant. This is the first time this technique, originally suggested by Refsdal, has been applied to supernovae.[11]
Using measurements from SN Refsdal and galaxy cluster lens models, astronomers found that the Hubble constant has value H0 = 66.6+4.1
−3.3 km s−1 Mpc−1.[12]
Other multiply-lensed supernova
Other reported multiply-lensed supernova are iPTF16geu,[13][14][15] SN Requiem (AT2016jka),[16][17][18][15] Supernova Zwicky (SN 2022qmx),[19][20][15] Chen et al SN,[21][15] SN H0pe[22][15] and SN 2022riv.[23]
Besides SN Refsdal, SN H0pe has also been used to measure the value of the Hubble constant using the relative delay in the arrival between images.[24][25][26]
See also
- Einstein Cross, the gravitationally lensed quasar that gave rise to the term "Einstein cross"
- How One Supernova Measured The Universe
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Kelly, P. L.; Rodney, S. A.; Treu, T.; Foley, R. J.; Brammer, G.; Schmidt, K. B.; Zitrin, A.; Sonnenfeld, A. et al. (2015). "Multiple images of a highly magnified supernova formed by an early-type cluster galaxy lens". Science 347 (6226): 1123–1126. doi:10.1126/science.aaa3350. PMID 25745167. Bibcode: 2015Sci...347.1123K.
- ↑ Overbye, Dennis (March 5, 2015). "Astronomers Observe Supernova and Find They're Watching Reruns". New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2015/03/06/science/astronomers-observe-supernova-and-find-theyre-watching-reruns.html.
- ↑ Amina Khan (5 March 2015). "Don't believe the light: Supernova in 'Einstein Cross' is a cosmic trick". Los Angeles Times. http://www.latimes.com/science/sciencenow/la-sci-sn-supernova-four-way-einstein-cross-gravitational-lens-galaxy-cluster-20150305-story.html.
- ↑ Sharon, K.; Johnson, T. L. (2015). "Revised Lens Model for the Multiply Imaged Lensed Supernova, "Sn Refsdal" in Macs J1149+2223". The Astrophysical Journal 800 (2): L26. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/800/2/L26. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...800L..26S.
- ↑ "Cosmological redshift z=1.49". Wolfram Alpha. http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=redshift+z%3D1.49&a=FSelect_**LookbackTimeFromRedshift--.
- ↑ "Caught in the act - Hubble captures first-ever predicted exploding star" (in en-GB). http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1525/.
- ↑ "Detection of a SN near the center of the galaxy cluster field MACS1149 consistent with predictions of a new image of Supernova Refsdal". Patrick Kelly. The Astronomer's Telegram. 13 Dec 2015. http://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=8402.
- ↑ Oguri, Masamune (2015). "Predicted Properties of Multiple Images of the Strongly Lensed Supernova SN Refsdal". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 449 (1): L86–L89. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slv025. Bibcode: 2015MNRAS.449L..86O.
- ↑ Diego, J.M; Broadhurst, T.; Chen, C.; Lim, J.; Zitrin, A.; Chan, B.; Coe7, D.; Ford, H. C. et al. (2016). "A Free-Form Prediction for the Reappearance of Supernova Refsdal in the Hubble Frontier Fields Cluster MACSJ1149.5+2223". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 456 (1): 356–365. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2638. Bibcode: 2016MNRAS.456..356D.
- ↑ Treu, T (2016). "Refsdal meets Popper: comparing predictions of the re-appearance of the multiply imaged supernova behind MACS1149.5+2223". The Astrophysical Journal 817 (1): 60. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/817/1/60. Bibcode: 2016ApJ...817...60T.
- ↑ Vega-Ferrero, J.; Diego, J.M; Miranda, V.; Bernstein, G. (2018). "The Hubble Constant from SN Refsdal". Astrophysical Journal Letters 853 (1): 31–36. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa95f. Bibcode: 2018ApJ...853...31O.
- ↑ Kelly, P. L. (2023). "Constraints on the Hubble constant from Supernova Refsdal's reappearance". Science 380 (6649). doi:10.1126/science.abh1322. PMID 37167351. Bibcode: 2023Sci...380.1322K.
- ↑ Goobar, A.; Amanullah, R.; Kulkarni, S. R.; Nugent, P. E.; Johansson, J.; Steidel, C.; Law, D.; Mörtsell, E. et al. (2017-04-21). "iPTF16geu: A multiply imaged, gravitationally lensed type Ia supernova" (in en). Science 356 (6335): 291–295. doi:10.1126/science.aal2729. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 28428419. Bibcode: 2017Sci...356..291G. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aal2729.
- ↑ "Rare Supernova Discovery Ushers in New Era for Cosmology" (in en). https://cs.lbl.gov/news-media/news/2017/rare-supernova-discovery-ushers-in-new-era-for-cosmology/.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 Suyu, Sherry H.; Goobar, Ariel; Collett, Thomas; More, Anupreeta; Vernardos, Giorgos (February 2024). "Strong Gravitational Lensing and Microlensing of Supernovae" (in en). Space Science Reviews 220 (1): 13. doi:10.1007/s11214-024-01044-7. ISSN 0038-6308. PMID 39099881. Bibcode: 2024SSRv..220...13S.
- ↑ Rodney, Steven A.; Brammer, Gabriel B.; Pierel, Justin D. R.; Richard, Johan; Toft, Sune; O'Connor, Kyle F.; Akhshik, Mohammad; Whitaker, Katherine E. (November 2021). "A gravitationally lensed supernova with an observable two-decade time delay" (in en). Nature Astronomy 5 (11): 1118–1125. doi:10.1038/s41550-021-01450-9. ISSN 2397-3366. Bibcode: 2021NatAs...5.1118R. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-021-01450-9.
- ↑ Tomaswick, Andy (2021-06-21). "Astronomers saw the Same Supernova Three Times Thanks to Gravitational Lensing. And in Twenty Years They Think They'll see it one More Time" (in en-US). https://www.universetoday.com/151581/astronomers-saw-the-same-supernova-three-times-thanks-to-gravitational-lensing-and-in-twenty-years-they-think-theyll-see-it-one-more-time/.
- ↑ "SN Requiem" (in en-US). https://requiem-galaxies.com/requiemsn.
- ↑ Goobar, Ariel; Johansson, Joel; Schulze, Steve; Arendse, Nikki; Carracedo, Ana Sagués; Dhawan, Suhail; Mörtsell, Edvard; Fremling, Christoffer et al. (September 2023). "Uncovering a population of gravitational lens galaxies with magnified standard candle SN Zwicky" (in en). Nature Astronomy 7 (9): 1098–1107. doi:10.1038/s41550-023-01981-3. ISSN 2397-3366. PMID 37736027. Bibcode: 2023NatAs...7.1098G.
- ↑ "Rare Gravitational Lensing Warps Light Of Distant Supernova Into Four Images – W. M. Keck Observatory" (in en-US). 2023-06-12. https://www.keckobservatory.org/sn-zwicky/.
- ↑ Chen, Wenlei; Kelly, Patrick L.; Oguri, Masamune; Broadhurst, Thomas J.; Diego, Jose M.; Emami, Najmeh; Filippenko, Alexei V.; Treu, Tommaso L. et al. (November 2022). "Shock cooling of a red-supergiant supernova at redshift 3 in lensed images" (in en). Nature 611 (7935): 256–259. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05252-5. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 36352131. Bibcode: 2022Natur.611..256C. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05252-5.
- ↑ Polletta, M.; Nonino, M.; Frye, B.; Gargiulo, A.; Bisogni, S.; Garuda, N.; Thompson, D.; Lehnert, M. et al. (July 2023). "Spectroscopy of the supernova H0pe host galaxy at redshift 1.78". Astronomy & Astrophysics 675: L4. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346964. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2023A&A...675L...4P. https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202346964.
- ↑ Roberts-Pierel, Justin; The LensWatch Collaboration (January 2023). "First Results of the LensWatch Collaboration: Hubble Observations and Constraints for Two New Gravitationally Lensed Supernovae". Bulletin of the AAS 241: 432.07. Bibcode: 2023AAS...24143207R. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2023AAS...24143207R/abstract.
- ↑ Pascale, Massimo; Frye, Brenda L.; Pierel, Justin D. R.; Chen, Wenlei; Kelly, Patrick L.; Cohen, Seth H.; Windhorst, Rogier A.; Riess, Adam G. et al. (2025-01-14). "SN H0pe: The First Measurement of H0 from a Multiply Imaged Type Ia Supernova, Discovered by JWST". The Astrophysical Journal 979 (1): 13. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad9928. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2025ApJ...979...13P.
- ↑ "Webb Researchers Discover Lensed Supernova, Confirm Hubble Tension – James Webb Space Telescope" (in en-US). 2024-10-01. https://blogs.nasa.gov/webb/2024/10/01/webb-researchers-discover-lensed-supernova-confirm-hubble-tension/.
- ↑ Grayson, Skylar (April 2024). "A New H0pe for the Hubble Constant?". https://astrobites.org/2024/04/16/sn_h0pe/.
External links
- Images of first SN Refsdal in March and reappeared in December 2015 at hubblesite.org
- NASA's Hubble Discovers Four Images of Same Supernova Split by Cosmic Lens - by NASA
- Predicted Reappearance of SN Refsdal (March 2015)
- The image taken by Hubble around November 2015 shows new supernovae 'SX' in multiply image system at astro.berkeley.edu.
- Hubble Hangout December 17 2015 discussing SN Refsdal
- View of Exploding Star Appears, Right on Cue National Geographic Society 17 December 2015
 |


