Astronomy:T Leporis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Lepus |
| Right ascension | 05h 04m 50.85s[1] |
| Declination | −21° 54′ 16.5″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.4 - 14.3[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M6e-M9e[2] |
| Variable type | Mira[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −4[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +13.59[4] mas/yr Dec.: −34.55[4] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.06 ± 0.04[4] mas |
| Distance | 1,066±13 ly (327±4 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.7[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 204[4] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.5[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 2,800[5] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
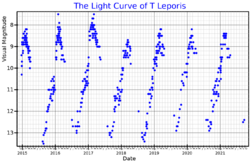
T Leporis (T Lep / HD 32803 / HIP 23636) is a variable star in the constellation of Lepus, the Hare. It is located half a degree from ε Leporis in the sky; its distance is approximately 1,100 light years from the Solar System. It has the spectral type M6ev, and is a Mira variable — as is R Leporis, in the same constellation — whose apparent magnitude varies between +7.40 and +14.30 with a period of 368.13 days.[2]
The annual parallax of T Leporis was measured by the Hipparcos mission, but the results were hopelessly imprecise.[6] The parallax from Gaia Data Release 2 is more accurate and yields a distance of 340±20 pc.[1] The distance has also been measured using very-long-baseline interferometry and found to be 327±4 pc.[4]
Mira variables are some of the major sources of molecules and dust in the Universe. With each pulsation, T Leporis expels matter into space, each year losing an amount equivalent to the mass of Earth. Images of T Leporis obtained with the Very Large Telescope interferometer of the European Southern Observatory (ESO) have revealed a shell of gas and dust surrounding the star, whose diameter is some 100 times larger than that of the Sun.[8] Given the great distance at which this class of stars lie, its apparent angular diameter — despite its enormous size — is no more than a millionth of the solar apparent angular diameter.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/GCVS. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Nakagawa, Akiharu; Omodaka, Toshihiro; Handa, Toshihiro; Honma, Mareki; Kawaguchi, Noriyuki; Kobayashi, Hideyuki; Oyama, Tomoaki; Sato, Katsuhisa et al. (2014). "VLBI astrometry of AGB variables with VERA: A Mira-type variable T Lepus". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 66 (6): 101. doi:10.1093/pasj/psu103. Bibcode: 2014PASJ...66..101N.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Pérez-Mesa, V.; Zamora, O.; García-Hernández, D. A.; Plez, B.; Manchado, A.; Karakas, A. I.; Lugaro, M. (2017). "Rubidium and zirconium abundances in massive Galactic asymptotic giant branch stars revisited". Astronomy and Astrophysics 606: A20. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201731245. Bibcode: 2017A&A...606A..20P.
- ↑ Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ "Unique Details Of Double Star In Orion Nebula And Star T Leporis Captured By 'Virtual' Telescope". 19 February 2009. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/02/090218103517.htm.
 |
