Astronomy:V337 Carinae
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation of Carina
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Carina |
| Right ascension | 10h 17m 04.9753s[1] |
| Declination | −61° 19′ 56.288″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.36 to 3.44[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K2.5II[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.72[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.54[4] |
| R−I color index | +0.77[4] |
| Variable type | LC[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 8.2±0.9[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −23.922[1] mas/yr Dec.: 6.734[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.3046 ± 0.1345[6] mas |
| Distance | 760 ± 20 ly (232 ± 7 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 9.0[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 128[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 3,236[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.17 - 1.36[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,118[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.54[7] dex |
| Age | 45.5[8] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
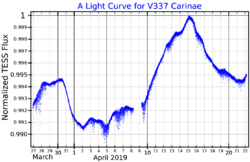
V337 Carinae (V337 Car, q Carinae) is a K-type bright giant star in the constellation of Carina. It is an irregular variable and has an apparent visual magnitude which varies between 3.36 and 3.44.
V337 has a spectral class of K2.5II, indicating a bright giant. It is considered likely to be on the red giant branch of stars fusing hydrogen around an inert helium core.[7] Its limb-darkened angular diameter has been measured using interferometry at 2.4 mas.[11]
V337 Carinae has two companions listed in multiple star catalogues. Both are 13th-magnitude stars, component B 16.9″ and component C 25.9″ away.[12] Component B is a distant background star,[13] while component C is at about the same distance as V337 Carinae.[14]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 V337 Car, database entry, The combined table of GCVS Vols I-III and NL 67-78 with improved coordinates, General Catalogue of Variable Stars , Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow, Russia. Accessed on line August 27, 2008.
- ↑ Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989). "The Perkins Catalog of Revised MK Types for the Cooler Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 71: 245. doi:10.1086/191373. Bibcode: 1989ApJS...71..245K.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 D. Hoffleit; W. H. Warren, Jr.. "The Bright Star Catalogue, Database entry for HR 4050". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS). http://webviz.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR-5?-out.add=.&-source=V/50/catalog&recno=4050.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 Kallinger, T.; Beck, P. G.; Hekker, S.; Huber, D.; Kuschnig, R.; Rockenbauer, M.; Winter, P. M.; Weiss, W. W. et al. (2019). "Stellar masses from granulation and oscillations of 23 bright red giants observed by BRITE-Constellation". Astronomy and Astrophysics 624: A35. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834514. Bibcode: 2019A&A...624A..35K.
- ↑ Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 KPC from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 410 (1): 190. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T.
- ↑ V* V337 Car -- Variable Star, database entry, SIMBAD. Accessed on line August 27, 2008.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ Richichi, A.; Percheron, I.; Davis, J. (2009). "A list of bright interferometric calibrators measured at the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope Interferometer". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 399 (1): 399. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15289.x. Bibcode: 2009MNRAS.399..399R.
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
 |