Astronomy:HD 88366
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Carina |
| Right ascension | 10h 09m 21.894s[2] |
| Declination | −61° 32′ 56.43″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.5 - 10.0[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[4] |
| Spectral type | K5e - M6e[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.93 to +1.93[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.43 to +2.60[5] |
| Variable type | Mira[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 289.30[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −94.237[2] mas/yr Dec.: 76.811[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.0110 ± 0.0855[2] mas |
| Distance | 1,620 ± 70 ly (500 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.71 to −3.41[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.6[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 120[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,200[5] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.9 - 1.0[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,050 - 3,590[9] K |
| Other designations | |
HR 3999, HD 88366, CP−60°1701, HIP 49751, SAO 250840, GC 13971 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
S Carinae (HD 88366) is a variable star in the constellation Carina.
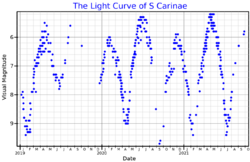
S Carinae is an M-type red giant with a mean apparent magnitude of +6.94. It is approximately 1,620 light years from Earth. It is classified as a Mira type variable star and its brightness varies between magnitude +4.5 and +10.0 with a period of 149.49 days.[3] It has one of the earliest spectral types, and hence the hottest temperatures, of any Mira variable, and has a relatively short period for the class.[10] The temperature of this pulsing star is highest at visual brightness maximum and lowest at visual brightness minimum.[9]
S Carinae has exhausted its core hydrogen and expanded to become a red giant. It has also exhausted its core helium and evolved to the asymptotic giant branch, where it fuses hydrogen and helium in separate shells outside the core.[10][4]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/gcvs. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Eggen, Olin J. (1992). "Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars Near the Sun". The Astronomical Journal 104: 275. doi:10.1086/116239. Bibcode: 1992AJ....104..275E.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Eggen, O. J. (1972). "Narrow-and broad-band photometry of red stars. VII. Luminosities and temperatures for halo-population red stars of high luminosity". The Astrophysical Journal 172: 639. doi:10.1086/151383. Bibcode: 1972ApJ...172..639E.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Celis, L. (1995). "Luminosity Attenuation and Distances of Red Giant Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 98: 701. doi:10.1086/192175. Bibcode: 1995ApJS...98..701C.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Willson, L. A.; Wallerstein, G.; Pilachowski, C. A. (1982). "Atmospheric kinematics of high velocity long period variables". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 198 (2): 483–516. doi:10.1093/mnras/198.2.483. Bibcode: 1982MNRAS.198..483W.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Shinkawa, Donna (1973). "The Mira Variable S Carinae". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 25: 253. doi:10.1086/190269. Bibcode: 1973ApJS...25..253S.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Schultheis, M.; Glass, I. S. (2001). "Asymptotic giant branch variables in Baade's Windows". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 327 (4): 1193–1200. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04825.x. Bibcode: 2001MNRAS.327.1193S.