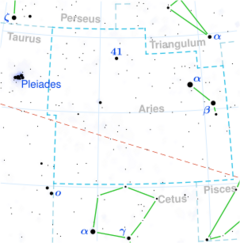
Astronomy:Zeta Arietis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 03h 14m 54.09143s[1] |
| Declination | +21° 02′ 39.9952″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +4.89[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A1 V[3] |
| U−B color index | –0.01[2] |
| B−V color index | –0.02[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +7.0[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –19.930[1] mas/yr Dec.: –72.900[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 12.7708 ± 0.3734[1] mas |
| Distance | 255 ± 7 ly (78 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.35[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.66±0.07[6] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 73[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 9,500[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 133[8] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Zeta Arietis, Latinized from ζ Arietis, is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. It is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.89.[2] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 12.77 mas,[1] the distance to this star is 255 ± 7 light-years (78 ± 2 parsecs). This is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A1 V.[3] It has a high rate of rotation with a projected rotational velocity of 133 km/s.[8] The star is shining at an effective temperature of 9,500 K,[7] giving it the characteristic white-hued glow of an A-type star.[10]
Name
This star, along with δ Ari, ε Ari, π Ari, and ρ3 Ari, were Al Bīrūnī's Al Buṭain (ألبطين), the dual of Al Baṭn, the Belly.[11] According to the catalogue of stars in the Technical Memorandum 33-507 - A Reduced Star Catalog Containing 537 Named Stars, Al Buṭain were the title for five stars : δ Ari as Botein, π Ari as Al Buṭain I, ρ3 Ari as Al Buṭain II, ε Ari as Al Buṭain III dan ζ Ari as Al Buṭain IV.[12]
In Chinese, 天陰 (Tiān Yīn), meaning Yin Force, refers to an asterism consisting of ζ Arietis, 63 Arietis, δ Arietis, τ Arietis and 65 Arietis.[13] Consequently, the Chinese name for ζ Arietis itself is 天陰二 (Lóu Su èr, English: the Second Star of Yin Force.)[14]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Johnson, H. L. et al. (1966), "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars", Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory 4 (99): 99, Bibcode: 1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cowley, A. et al. (April 1969), "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications", Astronomical Journal 74: 375–406, doi:10.1086/110819, Bibcode: 1969AJ.....74..375C.
- ↑ Wielen, R. et al. (1999), "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions", Veroeffentlichungen des Astronomischen Rechen-Instituts Heidelberg (Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg) 35 (35): 1, Bibcode: 1999VeARI..35....1W.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities", Astronomy & Astrophysics 537: A120, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691, Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Theodossiou, E.; Danezis, E. (September 1991), "The stellar temperature scale for stars of spectral types from O8 to F6 and the standard deviation of the MK spectral classification", Astrophysics and Space Science 183 (1): 91–115, doi:10.1007/BF00643019, Bibcode: 1991Ap&SS.183...91T.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Royer, F.; Zorec, J.; Gómez, A. E. (February 2007), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. III. Velocity distributions", Astronomy and Astrophysics 463 (2): 671–682, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224, Bibcode: 2007A&A...463..671R
- ↑ "zet Ari". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=zet+Ari.
- ↑ "The Colour of Stars", Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation), December 21, 2004, http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_colour.html, retrieved 2012-01-16
- ↑ Allen, R. H. (1963), Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.), New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc, p. 83, ISBN 0-486-21079-0, https://archive.org/details/starnamestheirlo00alle/page/83, retrieved 2010-12-12.
- ↑ Rhoads, Jack W. (November 15, 1971), Technical Memorandum 33-507-A Reduced Star Catalog Containing 537 Named Stars, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19720005197_1972005197.pdf.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN:978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 5 月 22 日
 |