Astronomy:Teegarden's Star
Coordinates: ![]() 02h 53m 00.89133s, +16° 52′ 52.6421″
02h 53m 00.89133s, +16° 52′ 52.6421″
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 02h 53m 00.89179s[1] |
| Declination | +16° 52′ 52.6322″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 15.13[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M7.0 V[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | ~17.21[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | ~15.40[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (R) | ~14.1[5] |
| Apparent magnitude (I) | ~10.4[5] |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 8.394 ± 0.027[6] |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 7.883 ± 0.040[6] |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 7.585 ± 0.046[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 68.3[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +3,429.083[1] mas/yr Dec.: −3,805.541[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 260.9884 ± 0.0934[1] mas |
| Distance | 12.497 ± 0.004 ly (3.832 ± 0.001 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 17.22[8] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.093±0.003[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.107±0.004[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.00073±0.00001[9] L☉ |
| Temperature | 2,904±51[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.19±0.16[9] dex |
| Rotation | 99.6±1.4 days[10] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | <2[11] km/s |
| Age | >8[11] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Data sources: | |
| Hipparcos Catalogue, CCDM (2002), Bright Star Catalogue (5th rev. ed.) | |
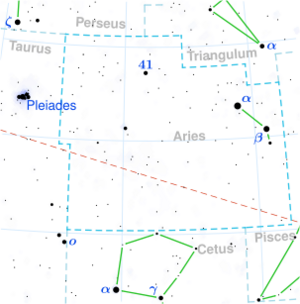
Location of Teegarden's Star in the constellation Aries | |
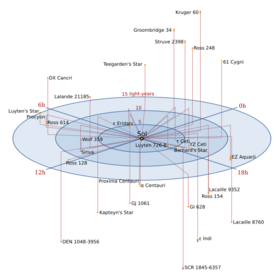
Teegarden's Star /ˈtiːɡɑːrdənz/ (SO J025300.5+165258, 2MASS J02530084+1652532, LSPM J0253+1652) is an M-type red dwarf[3] in the constellation Aries, 12.5 light-years (3.8 parsecs) from the Solar System. Although it is near Earth it is a dim magnitude 15 and can only be seen through large telescopes. This star was found to have a very large proper motion of about 5 arcseconds per year. Only seven stars with such large proper motions are currently known.[4]
Discovery

Teegarden's Star was discovered in 2003 using asteroid-tracking data that had been collected years earlier. This data set is a digital archive created from optical images taken over a five-year period by the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) program using two 1 m telescopes on Maui, Hawaii. The star is named after the discovery team leader, Bonnard J. Teegarden, an astrophysicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.[13]
Astronomers have long thought it was quite likely that many undiscovered dwarf stars exist within 20 light-years of Earth, because stellar-population surveys show the count of known nearby dwarf stars to be lower than otherwise expected and these stars are dim and easily overlooked. Teegarden's team thought that these dim stars might be found by data mining some of the huge optical sky survey data sets taken by various programs for other purposes in previous years. So they reexamined the NEAT asteroid tracking data set and found this star. The star was then precovered on photographic plates from the Palomar Sky Survey taken in 1951. This discovery is significant as the team did not have direct access to any telescopes and did not include professional astronomers at the time of the discovery.[13]
Properties
Teegarden's Star is classified as a red dwarf as its approximate calculated mass of just over 0.09 times that of the Sun is narrowly above the limit of brown dwarfs.[9] The inherently low temperature of such objects explains why it was not discovered earlier,[14] since it has an apparent magnitude of only 15.1[2] (and an absolute magnitude of 17.22[8]). Like most red and brown dwarfs it emits most of its energy in the infrared spectrum.[15]
The parallax was initially measured as 0.43 ± 0.13 arcseconds. This would have placed its distance at only 7.50 light-years, making Teegarden's Star only the third star system in order of distance from the Sun, ranking between Barnard's Star and Wolf 359.[13] However, even at that time the anomalously low luminosity (the absolute magnitude would have been 18.5) and high uncertainty in the parallax suggested that it was in fact somewhat farther away, still one of the Sun's nearest neighbors but not nearly as high in the ranking in order of distance. A more accurate parallax measurement of 0.2593 arcseconds was made by George Gatewood in 2009, yielding a distance of 12.578 light-years,[16] very close to the value now accepted.[11]
Planetary system
Observations by the ROPS survey in 2010, published in 2012, showed variation in Teegarden's star's radial velocity, though there was insufficient data to make claims of planet detection at that time.[17]
In June 2019, scientists conducting the CARMENES survey at the Calar Alto Observatory announced evidence of two Earth-mass exoplanets orbiting the star within its habitable zone;[11][18] Teegarden's Star b orbits inside the optimistic habitable zone—the equivalent in the Solar System would be in between Earth and Venus—whereas Teegarden's Star c orbits on the outer edge of the conservative habitable zone, similarly to Mars.[11]
According to one group of researchers, who were specifically studying this star, both planets could have maintained a dense atmosphere and so therefore there would be a high likelihood that at least one may harbour liquid water.[19] However, another group of scientists, looking at Earth-sized planets in general in the habitable zones of stars, specifically in a likely tidal locked scenario, give Teegarden's b a 3% chance, and Teegarden's c only a 2% chance, of having even retained an atmosphere.[20]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥1.05+0.13 −0.12 M⊕ |
0.0252+0.0008 −0.0009 |
4.91±0.0014 | 0+0.16 −0 |
— | — |
| c | ≥1.11+0.16 −0.15 M⊕ |
0.0443+0.0014 −0.0015 |
11.409±0.009 | 0+0.16 −0 |
— | — |
See also
- Astronomy:List of brown dwarfs
- Astronomy:List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs – Stars and brown dwarfs within 20 light years of the Solar System
- Astronomy:Stars named after people
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lépine, Sébastien; Hilton, Eric J.; Mann, Andrew W.; Wilde, Matthew; Rojas-Ayala, Bárbara; Cruz, Kelle L.; Gaidos, Eric (2013). "A Spectroscopic Catalog of the Brightest (J < 9) M Dwarfs in the Northern Sky". The Astronomical Journal 145 (4): 102. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/4/102. Bibcode: 2013AJ....145..102L.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Davison, Cassy L.; White, R. J.; Henry, T. J.; Riedel, A. R.; Jao, W.-C.; Bailey, J. I.; Quinn, S. N.; Cantrell, J. R. et al. (2015). "A 3D Search for Companions to 12 Nearby M Dwarfs". The Astronomical Journal 149 (3): 106. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/149/3/106. Bibcode: 2015AJ....149..106D.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "2MASS J02530084+1652532 -- Brown Dwarf (M<0.08solMass)". SIMBAD – Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=NAME+Teegarden%27s+star.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Monet, David G. et al. (February 2003), "The USNO-B Catalog", The Astronomical Journal 125 (2): 984–993, doi:10.1086/345888, Bibcode: 2003AJ....125..984M
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Cutri, R. M. et al. (June 2003), "2MASS All Sky Catalog of point sources", The IRSA 2MASS All-Sky Point Source Catalog (NASA/IPAC), Bibcode: 2003tmc..book.....C
- ↑ Tanner, Angelle et al. (November 2012), "Keck NIRSPEC Radial Velocity Observations of Late-M Dwarfs", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement 203 (1): 7, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/203/1/10, Bibcode: 2012ApJS..203...10T.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Henry, Todd J. et al. (December 2006), "The Solar Neighborhood. XVII. Parallax Results from the CTIOPI 0.9 m Program: 20 New Members of the RECONS 10 Parsec Sample", The Astronomical Journal 132 (6): 2360–2371, doi:10.1086/508233, Bibcode: 2006AJ....132.2360H.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Schweitzer, A. et al. (May 2019). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. Different roads to radii and masses of the target stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 625: 16. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834965. A68. Bibcode: 2019A&A...625A..68S.
- ↑ Terrien, Ryan C.; Keen, Allison; Oda, Katy; Parts, Winter; Stefánsson (3 March 2022). "Rotational Modulation of Spectroscopic Zeeman Signatures in Low-mass Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 927 (1): 11. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac4fc8. Bibcode: 2022ApJ...927L..11T.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 Caballero, J. A. et al. (12 June 2019). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. Two temperate Earth-mass planet candidates around Teegarden's Star" (in en). Astronomy & Astrophysics 627: A49. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935460. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2019A&A...627A..49Z.
- ↑ Golovin, Alex; Reffert, Sabine; Just, Andreas; Jordan, Stefan; Vani, Akash; Jahreiß, Hartmut (November 2022). "The Fifth Catalogue of Nearby Stars (CNS5)". Astronomy & Astrophysics 670: A19. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202244250. Bibcode: 2023A&A...670A..19G. Catalogue can be accessed here.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Teegarden, B. J. (May 20, 2003). "Discovery of a New Nearby Star". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 589 (1): L51–L53. doi:10.1086/375803. Bibcode: 2003ApJ...589L..51T.
- ↑ Reid, Neill I.; Hawley, Suzanne L. (2013), New Light on Dark Stars: Red Dwarfs, Low-Mass Stars, Brown Dwarfs, Springer Praxis Books, p. 342, ISBN 978-1-4471-3663-7, https://books.google.com/books?id=04_aBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA342.
- ↑ Kaler, James B. (2011), Stars and Their Spectra: An Introduction to the Spectral Sequence, Cambridge University Press, pp. 126, 132, ISBN 978-0-521-89954-3, https://books.google.com/books?id=ZEKO2pzuRHoC&pg=PA126.
- ↑ "Allegheny Observatory Parallaxes for Late M Dwarfs and White Dwarfs". The Astronomical Journal 137 (1): 402–405. January 2009. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/137/1/402. Bibcode: 2009AJ....137..402G.
- ↑ Barnes J.R. (July 2012). "ROPS: A New Search for Habitable Earths in the Southern Sky". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 424 (1): 591–604. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21236.x. Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.424..591B.
- ↑ University of Göttingen (18 June 2019). "View of the Earth in front of the Sun – International research team discovers two new Earth-like planets near Teegarden's star". EurekAlert!. https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2019-06/uog-vot061819.php.
- ↑ Wandel, Amri; Tal-Or, Lev (2019). "On the Habitability of Teegarden's Star Planets". The Astrophysical Journal 880 (2): L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab2df7. ISSN 2041-8213. Bibcode: 2019ApJ...880L..21W.
- ↑ Rodriguez-Mozos, J. M.; Moya, A. (October 2019). "Erosion of an exoplanetary atmosphere caused by stellar winds" (in en). Astronomy & Astrophysics 630: Table A.4. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935543. Bibcode: 2019A&A...630A..52R.
External links
- Barnes, J. R.; Jenkins, J. S.; Jones, H. R. A.; Rojo, P.; Arriagada, P.; Jordán, A.; Minniti, D.; Tuomi, M. et al. (April 27, 2012), "ROPS: A New Search for Habitable Earths in the Southern Sky", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 424 (1): 591–604, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21236.x, Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.424..591B
- SolStation.com
- David's Astronomy Pages – Nearby Stars
- Image Teegarden's Star
 |