Biology:Transcranial direct-current stimulation
| Transcranial direct-current stimulation | |
|---|---|
 Anodal tDCS administration. Anodal (b) and cathodal (c) electrodes with 35 cm2 size are put on F3 and right supraorbital region, respectively. A head strap is used (d) for convenience and reproducibility, and a rubber band (e) for reducing resistance. | |
| MeSH | D065908 |
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. This type of neurotherapy was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation.[1]
Research shows increasing evidence for tDCS as a treatment for depression.[2][3][4] There is emerging supportive evidence for tDCS in the management of schizophrenia – especially for negative symptoms.[5][6] There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease,[7] non-neuropathic pain,[8] nor for improving arm or leg functioning and muscle strength in people recovering from a stroke.[9]
Efficacy
Depression
There is some evidence tDCS might be of moderate benefit as treatment for mild and moderate depression,[10][11] major depressive disorder[12] and treatment-resistant depression.[13]
Other medical use
Recent research on tDCS has shown promising results in treating other mental health conditions such as anxiety[10] and PTSD.[14] More research is required on the topic. There is also evidence that tDCS is useful in treating neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury.[15] There is evidence of very low to moderate quality that tDCS can improve activities of daily living assessment in the short-term after stroke.[16][9]
Transcranial direct-current stimulaiton is also used to augment speech therapy in patients with acquired language disorders like aphasia, or to help maintain language abilities in the case of primary progressive aphasia, a neurodegenerative condition.[17]
Safety
According to the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), the evidence on tDCS for depression raises no major safety concerns.[18]
As of 2017, at stimulation up to 60 min and up to 4 mA over two weeks, adverse effects include skin irritation, a phosphene at the start of stimulation, nausea, headache, dizziness, and itching under the electrode. Typical treatment sessions lasting for about 20–30 min repeated daily for several weeks in the treatment of depression.[19] Adverse effects of long term treatment were not known as of 2017.[20] Nausea most commonly occurs when the electrodes are placed above the mastoid for stimulation of the vestibular system. A phosphene is a brief flash of light that can occur if an electrode is placed near the eye.[21][22]
People susceptible to seizures, such as people with epilepsy should not receive tDCS.[21] Studies have been completed to determine the current density at which overt brain damage occurs in rats. It was found that in cathodal stimulation, a current density of 142.9 A/m2 delivering a charge density of 52400 C/m2 or higher caused a brain lesion in the rat. This is over two orders of magnitude higher than protocols that were in use as of 2009.[23][24][25]
Mechanism of action
tDCS stimulates and activates brain cells by delivering electrical signals. The lasting modulation of cortical excitability produced by tDCS makes it an effective solution to facilitate rehabilitation and treat a range of neuropsychiatric disorders.[26] The way that the stimulation changes brain function is either by causing the neuron's resting membrane potential to depolarize or hyperpolarize. When positive stimulation (anodal tDCS) is delivered, the current causes a depolarization of the resting membrane potential, which increases neuronal excitability and allows for more spontaneous cell firing. When negative stimulation (cathodal tDCS) is delivered, the current causes a hyperpolarization of the resting membrane potential. This decreases neuron excitability due to the decreased spontaneous cell firing.[21][27]
In case of treating depression, tDCS currents specifically target the left side of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) located in the frontal lobe. Left DLPFC has been shown to be associated with lower activity in the depressed population.[28][12]
tDCS is able to achieve cortical changes even after the stimulation is ended. The duration of this change depends on the length of stimulation as well as the intensity of stimulation. The effects of stimulation increase as the duration of stimulation increases or the strength of the current increases.[29] tDCS has been proposed to promote both long term potentiation and long term depression,[21][27] and further research is needed for validation.
Operation
Transcranial direct current stimulation works by sending constant, low direct current through the electrodes. When these electrodes are placed in the region of interest, the current induces intracerebral current flow. This current flow then either increases or decreases the neuronal excitability in the specific area being stimulated based on which type of stimulation is being used. This change of neuronal excitability leads to alteration of brain function, which can be used in various therapies as well as to provide more information about the functioning of the human brain.[21]
Parts
Transcranial direct current stimulation is a relatively simple technique requiring only a few parts. These include two electrodes and a battery-powered device that delivers constant current. Control software can also be used in experiments that require multiple sessions with differing stimulation types so that neither the person receiving the stimulation nor the experimenter knows which type is being administered. Each device has an anodal, positively charged electrode and a cathodal, negative electrode. Current is "conventionally" described as flowing from the positive anode, through the intervening conducting tissue, to the cathode, creating a circuit. Note that in traditional electric circuits constructed from metal wires, charge drift is created by the motion of negatively charged electrons, which actually flow from cathode to anode. However, in biological systems, such as the head, current is usually created by the flow of ions, which may be positively or negatively charged – positive ions will flow towards the cathode; negative ions will flow toward the anode. The device may control the current as well as the duration of stimulation.[30]
Setup
To set up the tDCS device, the electrodes and the skin need to be prepared. This ensures a low resistance connection between the skin and the electrode. The careful placement of the electrodes is crucial to successful tDCS technique. The electrode pads come in various sizes with benefits to each size. A smaller sized electrode achieves a more focused stimulation of a site while a larger electrode ensures that the entirety of the region of interest is being stimulated.[31] If the electrode is placed incorrectly, a different site or more sites than intended may be stimulated resulting in faulty results.[21] One of the electrodes is placed over the region of interest and the other electrode, the reference electrode, is placed in another location in order to complete the circuit. This reference electrode is usually placed on the neck or shoulder of the opposite side of the body than the region of interest. Since the region of interest may be small, it is often useful to locate this region before placing the electrode by using a brain imaging technique such as fMRI or PET.[21] Once the electrodes are placed correctly, the stimulation can be started. Many devices have a built-in capability that allows the current to be "ramped up" or increased gradually until the necessary current is reached. This decreases the amount of stimulation effects felt by the person receiving the tDCS.[32] After the stimulation has been started, the current will continue for the amount of time set on the device and then will automatically be shut off. Recently a new approach has been introduced where instead of using two large pads, multiple (more than two) smaller sized gel electrodes are used to target specific cortical structures. This new approach is called High Definition tDCS (HD-tDCS).[31][33] In a pilot study, HD-tDCS was found to have greater and longer lasting motor cortex excitability changes than sponge tDCS.[34]
Types of stimulation
There are three different types of stimulation: anodal, cathodal, and sham. The anodal stimulation is positive (V+) stimulation that increases the neuronal excitability of the area being stimulated. Cathodal (V−) stimulation decreases the neuronal excitability of the area being stimulated. Cathodal stimulation can treat psychiatric disorders that are caused by the hyper-activity of an area of the brain.[35] Sham stimulation is used as a control in experiments. Sham stimulation emits a brief current but then remains off for the remainder of the stimulation time. With sham stimulation, the person receiving the tDCS does not know that they are not receiving prolonged stimulation. By comparing the results in subjects exposed to sham stimulation with the results of subjects exposed to anodal or cathodal stimulation, researchers can see how much of an effect is caused by the current stimulation, rather than by the placebo effect.
At-home administration
Recently, tDCS devices are being researched and created intended for at-home use – ranging from treating medical conditions such as depression to enhancing general cognitive well-being.[36][37] Clinical trials are needed to establish the efficacy, feasibility and acceptability of home-based tDCS treatment.[38]
History
The basic design of tDCS, using direct current (DC) to stimulate the area of interest, has existed for over 100 years. There were a number of rudimentary experiments completed before the 19th century using this technique that tested animal and human electricity. Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta were two such researchers that utilized the technology of tDCS in their explorations of the source of animal cell electricity [citation needed]. It was due to these initial studies that tDCS was first brought into the clinical scene. In 1801, Giovanni Aldini (Galvani's nephew) started a study in which he successfully used the technique of direct current stimulation to improve the mood of melancholy patients.[39]
There was a brief rise of interest in transcranial direct current stimulation in the 1960s when studies by researcher D. J. Albert proved that the stimulation could affect brain function by changing the cortical excitability.[40] He also discovered that positive and negative stimulation had different effects on the cortical excitability.[41]
Research continued, further fueled by knowledge gained from other techniques like TMS and fMRI.[29][21]
Comparison to other devices
In transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), an electric coil is held above the region of interest on the scalp that uses rapidly changing magnetic fields to induce small electrical currents in the brain. There are two types of TMS: repetitive TMS and single pulse TMS. Both are used in research therapy but effects lasting longer than the stimulation period are only observed in repetitive TMS. Similar to tDCS, an increase or decrease in neuronal activity can be achieved using this technique, but the method of how this is induced is very different. Transcranial direct current stimulation has the two different directions of current that cause the different effects. Increased neuronal activity is induced in repetitive TMS by using a higher frequency and decreased neuronal activity is induced by using a lower frequency.[30]
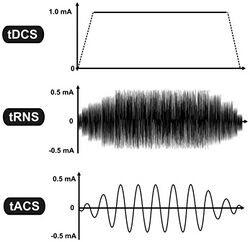
Variants related to tDCS include tACS, tPCS and transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS), a group of technologies commonly referred to as transcranial electrical stimulation, or TES.[42]
Research
Depression
Determining the safety and effectiveness of tDCS treatment for people with depression is being investigated:
- A systematic review of placebo-controlled trials investigating tDCS treatment for major depressive disorder was published 2020.[12] The meta-analysis collated results across nine eligible studies (572 participants) up until December 2018 to estimate odds ratio (OR) and number needed to treat (NNT) of response and remission, and depression improvement. The results showed statistically superior efficacy of active tDCS compared to sham for nine eligible studies (572 participants), presenting moderate/high certainty of evidence, were included. Active tDCS was significantly superior to sham for response (30.9% vs. 18.9% respectively; OR = 1.96, 95%CI [1.30–2.95], NNT = 9), remission (19.9% vs. 11.7%, OR = 1.94 [1.19–3.16], NNT = 13) and depression improvement (effect size of β = 0.31, [0.15–0.47]).[12]
- A 2016 meta-analysis showed that 34% of people treated with tDCS showed at least 50% symptom reduction (compared to 19% placebo).[43]
- A 2017 study conducted by Brunoni showed 6-weeks of tDCS treatment resulted in reduction of at least half of depression symptoms in 41% of depressed people (vs. 22% placebo and 47% antidepressants).[44]
- In 2015, the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) found tDCS to be safe and to appear effective for depression treatment. Up until 2014, there have been several small randomized clinical trials (RCT) in major depressive disorder (MDD); most found alleviation of depressive symptoms. There have been only two RCTs in treatment-resistant MDD; both were small, and one found an effect and the other did not.[45] One meta-analysis of the data focused on reduction in symptoms and found an effect compared to sham treatment, but another that was focused on relapse found no effect compared to sham.[45]
Other disorders
Cognition
There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. Several reviews have found evidence of small yet significant cognitive improvements.[46][47][48][49] Other reviews found no evidence at all,[50][51] although one of them[51] has been criticized for overlooking within-subject effects[52] and evidence from multiple-session tDCS trials. However, the original authors addressed these raised concerns in a further analysis and continued to find no evidence of impact [53]
A 2015 review of results from hundreds of tDCS experiments found that there was no statistically conclusive evidence to support any net cognitive effect, positive or negative, of single session tDCS in healthy populations – there is no evidence that tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement.[51] A second study by the same authors found there was little-to-no statistically reliable impact of tDCS on any neurophysiologic outcome.[50]
Parkinson's, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia
There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease,[7] schizophrenia,[54] non-neuropathic pain.[8] A few clinical trials have been conducted on the use of tDCS to ameliorate memory deficits in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease and healthy subjects, with mixed results.[7] Research conducted as of 2013 in schizophrenia, has found that while large effect sizes were initially found for symptom improvement, later and larger studies have found smaller effect sizes (see also section on use of tDCS in psychiatric disorders below).[54] Studies have mostly concentrated on positive symptoms like auditory hallucinations; research on negative symptoms is lacking.[54]
Stroke
There is no strong evidence that tDCS can help improve upper limb function after stroke.[55][56] In stroke, research conducted as of 2014, has found that tDCS is not effective for improving upper limb function after stroke.[55][56] While some reviews have suggested an effect of tDCS for improving post-stroke aphasia, a 2015 Cochrane review could find no improvement from combining tDCS with conventional treatment.[57][56][58] Research conducted as of 2013 suggests that tDCS may be effective for improve vision deficits following stroke.[56]
Motor Learning and Memory Function
There is evidence that certain tDCS montages can increase learning rates for particular tasks in healthy individuals, namely motor tasks and memory function.[59] However, reproducibility remains to be fully tested across studies and standardization for these kinds of studies has not been implemented fully, though an attempt at formalizing standards was released in 2017.[59]
Other
Research conducted as of 2012 on the use of tDCS to treat pain, found that the research has been of low quality and cannot be used as a basis to recommend use of tDCS to treat pain.[8] In chronic pain following spinal cord injury, research is of high quality and has found tDCS to be ineffective.[60] tDCS has also been studied in addiction.[61][62] There is some moderate (level B) evidence to indicate that, in addition to treating major depressive disorder, tDCS may also be appropriate to treat fibromyalgia, and craving disorders.[63]
tDCS has been used in neuroscience research, particularly to try to link specific brain regions to specific cognitive tasks[64] or psychological phenomena.[65] The cerebellum has been a focus of research, due to its high concentration of neurons, its location immediately below the skull, and its multiple reciprocal anatomical connections to motor and associative parts of the brain.[66] Most such studies focus on the impact of cerebellar tDCS on motor, cognitive, and affective functions in healthy and patient populations, but some also employ tDCS over the cerebellum to study the functional connectivity of the cerebellum to other areas of the brain.[67]
Limitations
While growing literature shows the efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for treating nervous diseases such as acute depressive episodes, the lack of knowledge about the nature of this treatment at the cell level[1] raises concerns regarding possible adverse effects that would appear long after the treatment has ended.
First, tDCS therapy involves exposure of the brain to an intense electric field, which is several times and even orders of magnitude higher than natural ones in the brain.[68][69] While the therapeutic effect is observed in a short period of months, the impact of the electric fields on the brain, specifically on the treated neuronal structures, is a question of further long-term research.
Second, tDCS brain tissue stimulation targets a large area of poorly characterized tissue.[68][70] Therefore, it is unclear whether electrical fields reach only the neural structures of the brain that need treatment. The radiation can destroy healthy cells which don't need treatment during tDCS therapy.[70]
Regulatory approvals
tDCS is a CE approved treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD) in the UK, EU, Australia, and Mexico. As of 2015, tDCS has not been approved for any use by the US FDA.[58] An FDA briefing document prepared in 2012 stated that "there is no regulation for therapeutic tDCS".[71]
See also
- Cranial electrotherapy stimulation
- Neurotechnology
- Transcranial alternating current stimulation
- Transcranial random noise stimulation
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation
- Brainwave entrainment
- Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Somatic treatments for mood disorders". Neuropsychopharmacology 37 (1): 102–116. January 2012. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.225. PMID 21976043.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation for acute major depressive episodes: meta-analysis of individual patient data". The British Journal of Psychiatry 208 (6): 522–531. June 2016. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.115.164715. PMID 27056623. "Our findings indicates two potential applications for tDCS in the therapeutic arsenal for depression: in primary care settings and as a non-pharmacological, neuromodulatory therapy for depression.".
- ↑ "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of non-surgical brain stimulation for the acute treatment of major depressive episodes in adults: systematic review and network meta-analysis". BMJ 364. March 2019. doi:10.1136/bmj.l1079. PMID 30917990. "we found tDCS to be efficacious across outcomes in both pairwise and network meta-analyses.".
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for depression". The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). UK. August 2015. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg530/chapter/1-Recommendations.
- ↑ "Effects of transcranial electrical stimulation on working memory in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Psychiatry Research 296. February 2021. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113656. PMID 33360429.
- ↑ "Efficacy and Safety of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Treating Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Psychiatry 77 (2): 121–129. February 2020. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3199. PMID 31617873.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Transcranial direct current stimulation for memory enhancement: from clinical research to animal models". Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience 8: 159. Sep 2014. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2014.00159. PMID 25237299.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Transcranial direct current stimulation for the reduction of clinical and experimentally induced pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Clinical Journal of Pain 28 (5): 452–461. June 2012. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31823853e3. PMID 22569218.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving activities of daily living, and physical and cognitive functioning, in people after stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020 (11). November 2020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009645.pub4. PMID 33175411.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Cheng, Ying-Chih; Kuo, Po-Hsiu; Su, Min-I; Huang, Wei-Lieh (2022-04-01). "The efficacy of non-invasive, non-convulsive electrical neuromodulation on depression, anxiety and sleep disturbance: a systematic review and meta-analysis" (in en). Psychological Medicine 52 (5): 801–812. doi:10.1017/S0033291721005560. ISSN 0033-2917. PMID 35105413.
- ↑ Zheng, Esther Zhiwei; Wong, Nichol M. L.; Yang, Angela S. Y.; Lee, Tatia M. C. (2024-07-18). "Evaluating the effects of tDCS on depressive and anxiety symptoms from a transdiagnostic perspective: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials" (in en). Translational Psychiatry 14 (1): 295. doi:10.1038/s41398-024-03003-w. ISSN 2158-3188. PMID 39025832.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 "Efficacy and acceptability of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for major depressive disorder: An individual patient data meta-analysis". Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 99. April 2020. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109836. PMID 31837388. https://unsworks.unsw.edu.au/bitstreams/967e9af1-ae7e-4a90-98f0-7f943f35d83b/download.
- ↑ Li, John; Kung, Simon; Croarkin, Paul; Lapid, Maria (2024-04-01). "Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) for Treatment Resistant Depression (TRD): A Systematic Review" (in en). The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 32 (4): S99. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2024.01.181. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1064748124001921.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): A randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial". Brain Research Bulletin 153: 273–278. November 2019. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.09.011. PMID 31560945.
- ↑ "Effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation and visual illusion on neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury". Brain 133 (9): 2565–2577. September 2010. doi:10.1093/brain/awq184. PMID 20685806.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving capacity in activities and arm function after stroke: a network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation 14 (1): 95. September 2017. doi:10.1186/s12984-017-0301-7. PMID 28903772.
- ↑ Galletta, Elizabeth E.; Conner, Peggy; Vogel-Eyny, Amy; Marangolo, Paola (2016). "Use of TDCS in Aphasia Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review of the Behavioral Interventions Implemented with Noninvasive Brain Stimulation for Language Recovery". American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 25 (4S): S854–S867. doi:10.1044/2016_AJSLP-15-0133. PMID 27997958. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/abs/10.1044/2016_AJSLP-15-0133.
- ↑ "1 Recommendations | Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for depression | Guidance". The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). UK. 26 August 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg530/chapter/1-Recommendations.
- ↑ "3 The procedure | Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for depression | Guidance | NICE". The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). UK. 26 August 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg530/chapter/3-The-procedure.
- ↑ "Safety aspects of transcranial direct current stimulation concerning healthy subjects and patients". Brain Research Bulletin 72 (4–6): 208–214. May 2007. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.01.004. PMID 17452283.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 21.5 21.6 21.7 "Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art 2008". Brain Stimulation 1 (3): 206–223. July 2008. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2008.06.004. PMID 20633386. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/handle/20.500.14299/132349.
- ↑ "Low intensity transcranial electric stimulation: Safety, ethical, legal regulatory and application guidelines". Clinical Neurophysiology 128 (9): 1774–1809. September 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.001. PMID 28709880.
- ↑ "Safety criteria for transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in humans". Clinical Neurophysiology 114 (11): 2220–2222; author reply 2222–2223. November 2003. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00235-9. PMID 14580622.
- ↑ "Safety limits of cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation in rats". Clinical Neurophysiology 120 (6): 1161–1167. June 2009. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2009.01.022. PMID 19403329.
- ↑ "Establishing safety limits for transcranial direct current stimulation". Clinical Neurophysiology 120 (6): 1033–1034. June 2009. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2009.03.018. PMID 19394269.
- ↑ "Physiological and modeling evidence for focal transcranial electrical brain stimulation in humans: a basis for high-definition tDCS". NeuroImage 74: 266–75. July 2013. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.042. PMID 23370061.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation". The Journal of Physiology 527 (Pt 3): 633–639. September 2000. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00633.x. PMID 10990547.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation in the treatment of depression". Medicographia. Servier Laboratories. 2011-10-24. https://www.medicographia.com/2011/10/transcranial-direct-current-stimulation-in-the-treatment-of-depression/.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Electrified minds: transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and galvanic vestibular stimulation (GVS) as methods of non-invasive brain stimulation in neuropsychology--a review of current data and future implications". Neuropsychologia 48 (10): 2789–2810. August 2010. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.06.002. PMID 20542047.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Noninvasive brain stimulation with transcranial magnetic or direct current stimulation (TMS/tDCS)-From insights into human memory to therapy of its dysfunction". Methods 44 (4): 329–337. April 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.02.001. PMID 18374276.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "Gyri-precise head model of transcranial direct current stimulation: improved spatial focality using a ring electrode versus conventional rectangular pad". Brain Stimulation 2 (4): 201–7, 207.e1. October 2009. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2009.03.005. PMID 20648973.
- ↑ "Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) of the visual cortex: a proof-of-concept study based on interictal electrophysiological abnormalities in migraine". The Journal of Headache and Pain 14 (1): 23. March 2013. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-14-23. PMID 23566101.
- ↑ "A pilot study of the tolerability and effects of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) on pain perception". The Journal of Pain 13 (2): 112–120. February 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2011.07.001. PMID 22104190.
- ↑ "Comparing cortical plasticity induced by conventional and high-definition 4 × 1 ring tDCS: a neurophysiological study". Brain Stimulation 6 (4): 644–648. July 2013. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2012.09.010. PMID 23149292.
- ↑ "Level of action of cathodal DC polarisation induced inhibition of the human motor cortex". Clinical Neurophysiology 114 (4): 600–604. April 2003. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00412-1. PMID 12686268.
- ↑ "At-Home Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) With Telehealth Support for Symptom Control in Chronically-Ill Patients With Multiple Symptoms". Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 12: 93. 2018-05-22. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00093. PMID 29872381.
- ↑ "Europe's first home brain-zap device for depression launched in UK" (in en-US). https://www.newscientist.com/article/2221743-europes-first-home-brain-zap-device-for-depression-launched-in-uk/.
- ↑ "Is tDCS a potential first line treatment for major depression?". International Review of Psychiatry 33 (3): 250–265. May 2021. doi:10.1080/09540261.2021.1879030. PMID 33706656. https://repository.uel.ac.uk/download/ed192b17a26c6dc14f46488abd2402249bd5f7b71c27528419001271b49f3e99/474262/Is%20tDCS%20a%20potential%20first%20line%20treatment%20in%20major%20depression.pdf.
- ↑ "Aldini's Essay on Galvanism". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 31 (4): 576–584. November 2004. doi:10.1017/S0317167100003851. PMID 15595271. http://www.biusante.parisdescartes.fr/chn/docpdf/parent_aldini.pdf. (Lanzarini pdf 5 of 9)
- (in fr) Théorique et expérimental sur le galvanisme, avec une série d'expériences faites devant des commissaires de l'Institut national de France, et en divers amphithéâtres anatomiques de Londres.. Paris: Fournier Fils. 1804.
- ↑ "The effect of spreading depression on the consolidation of learning.". Neuropsychologia 4 (1): 49–64. February 1966. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(66)90020-0.
- ↑ "The effects of polarizing currents on the consolidation of learning.". Neuropsychologia 4 (1): 65–77. February 1966. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(66)90021-2.
- ↑ "Transcranial current brain stimulation (tCS): models and technologies". IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 21 (3): 333–345. May 2013. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2012.2200046. PMID 22949089.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation for acute major depressive episodes: meta-analysis of individual patient data". The British Journal of Psychiatry 208 (6): 522–531. June 2016. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.115.164715. PMID 27056623.
- ↑ "Trial of Electrical Direct-Current Therapy versus Escitalopram for Depression" (in EN). The New England Journal of Medicine 376 (26): 2523–2533. June 2017. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1612999. PMID 28657871.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 "Can transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) alleviate symptoms and improve cognition in psychiatric disorders?". The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry 15 (4): 261–275. May 2014. doi:10.3109/15622975.2013.876514. PMID 24447054.
- ↑ "Battery powered thought: enhancement of attention, learning, and memory in healthy adults using transcranial direct current stimulation". NeuroImage 85 (Pt 3): 895–908. January 2014. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.083. PMID 23933040.
- ↑ "A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Healthy and Neuropsychiatric Samples: Influence of Stimulation Parameters". Brain Stimulation 9 (4): 501–517. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2016.04.006. PMID 27160468. https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/7206618.
- ↑ "Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Working Memory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Findings From Healthy and Neuropsychiatric Populations". Brain Stimulation 9 (2): 197–208. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2015.10.006. PMID 26597929.
- ↑ "The Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Working Memory". GeNeDis 2016. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 987. 2017. pp. 283–289. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-57379-3_25. ISBN 978-3-319-57378-6.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 "Evidence that transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) generates little-to-no reliable neurophysiologic effect beyond MEP amplitude modulation in healthy human subjects: A systematic review". Neuropsychologia 66: 213–236. January 2015. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.11.021. PMID 25448853.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 "Quantitative Review Finds No Evidence of Cognitive Effects in Healthy Populations From Single-session Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)". Brain Stimulation 8 (3): 535–550. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2015.01.400. PMID 25701175.
- ↑ "Data Synthesis in Meta-Analysis may Conclude Differently on Cognitive Effect From Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation". Brain Stimulation 8 (5): 974–976. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2015.06.001. PMID 26115775.
- ↑ "New Quantitative Analyses Following Price & Hamilton's Critique do not Change Original Findings of Horvath et al.". Brain Stimulation 8 (3): 665–666. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2015.05.001. PMID 26050600.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 "Transcranial direct current stimulation in schizophrenia". Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 11 (3): 118–125. December 2013. doi:10.9758/cpn.2013.11.3.118. PMID 24465247.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 "Interventions for improving upper limb function after stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014 (11). November 2014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010820.pub2. PMID 25387001.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 56.3 "Review of transcranial direct current stimulation in poststroke recovery". Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 20 (1): 68–77. Jan 2013. doi:10.1310/tsr2001-68. PMID 23340073.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving aphasia in adults with aphasia after stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019 (5). May 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009760.pub4. PMID 31111960.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 "tDCS in post-stroke aphasia: the role of stimulation parameters, behavioral treatment and patient characteristics". Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior 63: 296–316. February 2015. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2014.08.015. PMID 25460496.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 "Effects of tDCS on motor learning and memory formation: A consensus and critical position paper". Clinical Neurophysiology 128 (4): 589–603. April 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2017.01.004. PMID 28231477. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/137645/7/137645.pdf.
- ↑ "Non-pharmacological interventions for chronic pain in people with spinal cord injury". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014 (11). November 2014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009177.pub2. PMID 25432061.
- ↑ "Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation prevents abnormal behaviors associated with abstinence from chronic nicotine consumption". Neuropsychopharmacology 39 (4): 981–988. March 2014. doi:10.1038/npp.2013.298. PMID 24154668.
- ↑ "Effects of non-invasive neurostimulation on craving: a meta-analysis". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 37 (10 Pt 2): 2472–2480. December 2013. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.07.009. PMID 23916527.
- ↑ "Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)". Clinical Neurophysiology 128 (1): 56–92. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2016.10.087. PMID 27866120. https://repository.uantwerpen.be/docman/irua/211121/142030_2018_01_01.pdf.
- ↑ "Transcranial direct current stimulation over right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex enhances error awareness in older age". The Journal of Neuroscience 34 (10): 3646–3652. March 2014. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5308-13.2014. PMID 24599463.
- ↑ "Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (ctDCS): A Novel Approach to Understanding Cerebellar Function in Health and Disease". The Neuroscientist 22 (1): 83–97. February 2016. doi:10.1177/1073858414559409. PMID 25406224.
- ↑ "tDCS of the Cerebellum: Where Do We Stand in 2016? Technical Issues and Critical Review of the Literature". Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 10: 199. 2016-01-01. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00199. PMID 27242469.
- ↑ "Targeting the Cerebellum by Noninvasive Neurostimulation: a Review". Cerebellum 16 (3): 695–741. June 2017. doi:10.1007/s12311-016-0840-7. PMID 28032321.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Grimaldi G, Argyropoulos GP, Boehringer A, Celnik P, Edwards MJ, Ferrucci R, et al. (2014). "Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation--a consensus paper" (PDF). Cerebellum. 13 (1): 121–138. doi:10.1007/s12311-013-0514-7
- ↑ Siebner HR, Hartwigsen G, Kassuba T, Rothwell JC (2009). "How does transcranial magnetic stimulation modify neuronal activity in the brain? Implications for studies of cognition". Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. 45 (9): 1035–1042. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.02.007
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Sparing R, Mottaghy FM (2008). "Noninvasive brain stimulation with transcranial magnetic or direct current stimulation (TMS/tDCS)-From insights into human memory to therapy of its dysfunction". Methods. 44 (4): 329–337. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.02.001
- ↑ "FDA Executive Summary – Petitions to Request Change in Classification for Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulators". https://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/MedicalDevices/MedicalDevicesAdvisoryCommittee/NeurologicalDevicesPanel/UCM290787.pdf.
 |
