Biology:URM1
| Urm1 (Ubiquitin related modifier) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
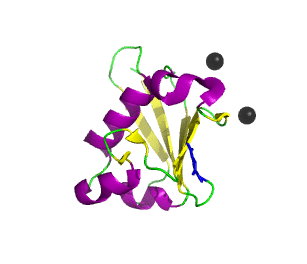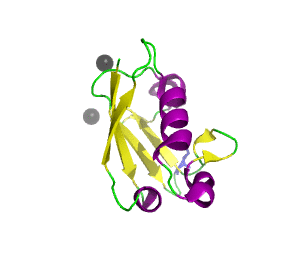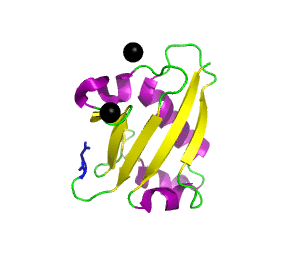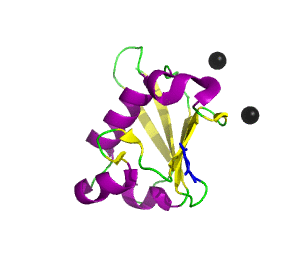 Ubiquitin related modifier-1 (2qjl). In the center of protein β-grasp fold is located. Additionally, carboxy terminal glycine within a di-glycine motif is marked blue, and Mg ions are represented by black spheres. | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | URM1 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF09138 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015221 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | d.15.3.3 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Ubiquitin-related modifier-1 (URM1) is a ubiquitin-like protein that modifies proteins in the yeast ubiquitin-like urmylation pathway.[1] Structural comparisons and phylogenetic analysis of the ubiquitin superfamily has indicated that Urm1 has the most conserved structural and sequence features of the common ancestor of the entire superfamily.[2][3]
Urm1 is characterized by a core β-grasp fold and an essential carboxy terminal glycine within a di-glycine motif. Urm1 is known to be conjugated to the peroxiredoxin Ahp1, ATPBD3, and CTU2 and human MOCS3, through a mechanism involving the E1-like protein Uba4 via lysine residues.[4] Similar to ubiquitination, urmylation requires a thioester intermediate and forms isopeptide bonds between Urm1 and its substrates. Moreover, the urmylation process can be significantly enhanced by oxidative stress.[5] Functions as a protein tag with roles in nutrient sensing and oxidative stress response.
Recently it has been demonstrated that Urm1 can acts as a sulfur carrier in the thiolation of eukaryotic tRNA via a mechanism that requires the formation of a thiocarboxylated Urm1.[6] URM1 is involved in thiolation of cytoplasmic tRNAs; receives sulfur from the E1-like enzyme Uba4 and transfers it to tRNA. Sequence and structural homology studies suggest that Urm1 can be more closely linked to the prokaryotic sulphur transfer proteins, ThiS and MoaD, that can be considered as prokaryotic counterparts of the eukaryotic UBls.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ "Urmylation: a ubiquitin-like pathway that functions during invasive growth and budding in yeast". Molecular Biology of the Cell 14 (11): 4329–41. November 2003. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-02-0079. PMID 14551258.
- ↑ "Solution structure of Urm1 and its implications for the origin of protein modifiers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103 (31): 11625–30. August 2006. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604876103. PMID 16864801. Bibcode: 2006PNAS..10311625X.
- ↑ "Urmylation: a ubiquitin-like pathway that functions during invasive growth and budding in yeast". Molecular Biology of the Cell 14 (11): 4329–41. November 2003. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-02-0079. PMID 14551258.
- ↑ "Role of the ubiquitin-like protein Urm1 as a noncanonical lysine-directed protein modifier". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (5): 1763–70. February 2011. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014402108. PMID 21209336.
- ↑ "The dual role of ubiquitin-like protein Urm1 as a protein modifier and sulfur carrier". Protein & Cell 2 (8): 612–9. August 2011. doi:10.1007/s13238-011-1074-6. PMID 21904977.
- ↑ "Urm1 couples sulfur transfer to ubiquitin-like protein function in oxidative stress". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (5): 1749–50. February 2011. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019043108. PMID 21245332. Bibcode: 2011PNAS..108.1749P.
- ↑ "Urm1 at the crossroad of modifications. 'Protein Modifications: Beyond the Usual Suspects' Review Series". EMBO Reports 9 (12): 1196–202. December 2008. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.209. PMID 19047990.
 |
