Chemistry:Arabitol
From HandWiki
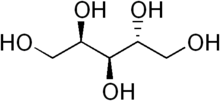
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
D-Arabinitol[2]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,4R)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | |
| Other names
(2R,4R)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol (not recommended)
Arabitol Lyxitol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 152.146 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Prismatic crystals |
| Melting point | 103 °C (217 °F; 376 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Arabitol, or arabinitol, is a sugar alcohol. It can be formed by the reduction of either arabinose or lyxose. Some organic acid tests check for the presence of D-arabitol, which may indicate overgrowth of intestinal microbes such as Candida albicans or other yeast/fungus species.[3]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 789
- ↑ "2-Carb-19". https://iupac.qmul.ac.uk/2carb/19.html.
- ↑ "Candida and Yeast Overgrowth". http://www.greatplainslaboratory.com/home/eng/candida.asp.
Further reading
- Herman, Anna; Herman, Andrzej Przemysław (15 January 2022). "Could Candida Overgrowth Be Involved in the Pathophysiology of Autism?". Journal of Clinical Medicine 11 (2): 442. doi:10.3390/jcm11020442. PMID 35054136.
External links
 |

