Chemistry:Carbarsone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
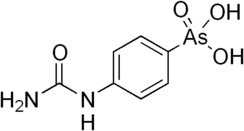
| Preferred IUPAC name
[4-(Carbamoylamino)phenyl]arsonic acid | |
| Other names
(4-Ureidophenyl)arsonic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Carbarson |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H9AsN2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 260.081 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Carbarsone is an organoarsenic compound used as an antiprotozoal drug for treatment of amebiasis and other infections.[1][2][3] It was available for amebiasis in the United States as late as 1991. Thereafter, it remained available as a turkey feed additive for increasing weight gain and controlling histomoniasis (blackhead disease).[4][5]
Carbarsone is one of four arsenical animal drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in poultry and/or swine, along with nitarsone, arsanilic acid, and roxarsone.[6] In September 2013, the FDA announced that Zoetis and Fleming Laboratories would voluntarily withdraw current roxarsone, arsanilic acid, and carbarsone approvals, leaving only nitarsone approvals in place.[7] In 2015 FDA withdrew the approval of using nitarsone in animal feeds. The ban came into effect at the end of 2015.[8]
References
- ↑ "Asymptomatic amebiasis; treatment with atabrine in combination with carbarsone or chiniofon". United States Armed Forces Medical Journal 7 (3): 363–8. 1956. PMID 13299463.
- ↑ RADKE RA (1955). "Ameboma of the intestine: an analysis of the disease as presented in 78 collected and 41 previously unreported cases". Ann. Intern. Med. 43 (5): 1048–66. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-43-5-1048. PMID 13268997.
- ↑ HOEKENGA MT (1 July 1951). "A comparison of aureomycin and carbarsone in the treatment of intestinal amebiasis". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 31 (4): 423–5. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.423. PMID 14857246. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/abstract/s1-31/4/423.
- ↑ McDougald LR (1979). "Efficacy and compatibility of amprolium and carbarsone against Coccidiosis and blackhead in turkeys". Poult. Sci. 58 (1): 76–80. doi:10.3382/ps.0580076. PMID 572970.
- ↑ "The effect of Carbarsone (33.6 per cent w-v p-ureidobenzene arsonic acid) on bodyweight gain, food conversion and tissue arsenic levels of turkey poults". J. Sci. Food Agric. 24 (1): 35–41. 1973. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740240107. PMID 4696593.
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (June 8, 2011). "Questions and Answers Regarding 3-Nitro (Roxarsone)". https://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth/ProductSafetyInformation/ucm258313.htm.
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (September 20, 2011). "FDA Response to Citizen Petition on Arsenic-based Animal Drugs". https://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth/ProductSafetyInformation/ucm370568.htm.
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (April 1, 2015). "FDA Announces Pending Withdrawal of Approval of Nitarsone". https://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/NewsEvents/CVMUpdates/ucm440668.htm.
 |
