Chemistry:Iron(II) phosphate
From HandWiki
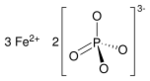
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iron(II) phosphate
| |
| Other names
Ferrous phosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Fe3(PO4)2 | |
| Appearance | brown powder |
| Density | 2.61 g/cm3 (octahydrate) |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) (octahydrate) decomposes[1] |
| insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (octahydrate) | |
| C 2/m | |
a = 10.086 (octahydrate), b = 13.441 (octahydrate), c = 4.703 (octahydrate) α = 90°, β = 104.27°, γ = 90°
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P305+351+338, P304+340, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Iron(II) phosphate, also ferrous phosphate,[3] Fe3(PO4)2, is an iron salt of phosphoric acid.
Natural occurrences
The mineral vivianite is a naturally occurring form of hydrated iron(II) phosphate.
Production
It can be formed by the reaction of ferrous hydroxide with phosphoric acid to produce hydrated iron(II) phosphate.
See also
References
- ↑ "iron(II) phosphate octahydrate". http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=4417.
- ↑ "Safety Data Sheet". https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC389955000&productDescription=IRON%28III%29+PHOSPHATE+HYDR+500GR&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en.
- ↑ "Iron(II) Phosphate". http://www.endmemo.com/chem/compound/fe3po4_2.php.
External links
 |


