Chemistry:Mercury(II) stearate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Mercuric stearate, mercury distearate, mercury dioctadecanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
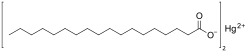
| C36H70HgO4 | |
| Molar mass | 767.529 |
| Appearance | yellow wax |
| Melting point | 112.2 °C (234.0 °F; 385.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K) |
| insoluble[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in fatty oils[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 162.4 °C (324.3 °F; 435.5 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Mercury(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of mercury and stearic acid with the chemical formula C36H70HgO4.[2] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.[1]
Synthesis
An exchange reaction of sodium stearate and mercury dichloride:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathsf{ HgCl_2 + 2C_{17}H_{35}COONa \ \xrightarrow{}\ Hg(C_{17}H_{35}COO)_2\downarrow + 2 NaCl } }[/math]
Also, heating mercurious oxide with stearic acid.[3]
Physical properties
The compound forms yellow waxy substance.[4]
Uses
It is used as a germicide[1] and as a plasticizer in the production of ceramics.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lewis, Robert A. (1 April 2016) (in en). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary. John Wiley & Sons. p. 878. ISBN 978-1-119-26784-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=KPrfCwAAQBAJ&dq=mercuric+stearate&pg=PA878. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ "CAS 645-99-8 Mercury stearate - Alfa Chemistry". alfa-chemistry.com. https://www.alfa-chemistry.com/cas_645-99-8.htm.
- ↑ (in en) Works of the Cavendish Society: Gmelin, Leopold. Hand-book of chemistry. 18 v. & index. 1848-72. 1866. p. 112. https://books.google.com/books?id=z-AJAAAAIAAJ&dq=mercuric+stearate&pg=PA112. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ Morris, Christopher G.; Press, Academic; Morris, Christopher W. (27 August 1992) (in en). Academic Press Dictionary of Science and Technology. Gulf Professional Publishing. p. 1350. ISBN 978-0-12-200400-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=nauWlPTBcjIC&dq=mercuric+stearate&pg=PA1350. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
 |

