Chemistry:Mersalyl
From HandWiki
Short description: Organomercury compound once used diuretic
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
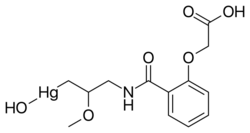
| IUPAC name
(3-{[2-(Carboxymethoxy)benzoyl]amino}-2-methoxypropyl)(hydroxy)mercury
| |
| Other names
Mersalyl acid, salyrganic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H18HgNO6 | |
| Molar mass | 484.87512 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | C03BC01 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Mersalyl (Mersal) is an organomercury compound[1] and mercurial diuretic. It is only rarely used as a drug, having been superseded by thiazides and loop diuretics that are less toxic because they do not contain mercury. It features a Hg(II) centre. Mersalyl was originally adapted from calomel (Hg2Cl2), a diuretic discovered by Paracelsus.
See also
References
- ↑ Stewart, J. H.; Edwards, K. D. (1965). "Clinical comparison of frusemide with bendrofluazide, mersalyl, and ethacrynic acid". British Medical Journal 2 (5473): 1277–1281. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5473.1277. PMID 5849145.
 |

