Engineering:Kosmos 1074
From HandWiki
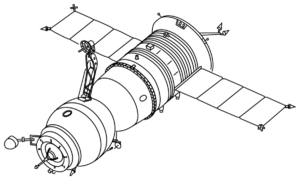 Soyuz T | |
| Mission type | Orbital test flight |
|---|---|
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| COSPAR ID | 1979-008A |
| SATCAT no. | 11259 |
| Mission duration | 60 days, 1 hour and 9 minutes |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Soyuz-T s/n 5L |
| Spacecraft type | Soyuz 7K-ST (11F732)[1] |
| Manufacturer | NPO Energia |
| Launch mass | 6,450 kg (14,220 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 31, 1979, 09:00:00 GMT[2] |
| Rocket | Soyuz-U |
| Launch site | Baikonur 31/6 |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Deorbited |
| Landing date | April 1, 1979, 10:09:00 GMT |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric[2] |
| Perigee altitude | 195 km (121 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 238 km (148 mi) |
| Inclination | 51.6° |
| Period | 88.8 min |
Kosmos (satellites) | |
Kosmos 1074 (Russian: Космос 1074 meaning Cosmos 1074) was a Soviet unmanned long-duration test flight of the Soyuz-T spacecraft launched on January 31, 1979 and de-orbited on April 1, 1979.[3] It is the last Soyuz spacecraft that has received a Kosmos designation, and its mission is officially intended to investigate the upper atmosphere and outer space[2]
Mission parameters
- Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-ST
- Mass: 6450 kg
- Crew: None
- Launched: January 31, 1979
- Landed: April 1, 1979
References
- ↑ "Soyuz-T 1 - 15 (7K-ST, 11F732)". https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/soyuz-t.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Soyuz T". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/s/soyuzt.html.
- ↑ David S. F. Portree (1995). Mir Hardware Heritage. NASA. pp. 90-102. NASA-SP-4225. https://www.hq.nasa.gov/pao/History/SP-4225/documentation/mhh/mirheritage.pdf.
 |

