Social:Botlikh language
| Botlikh | |
|---|---|
| Botlix | |
| буйхалъи мицIцIи/Template:Tlit | |
| Pronunciation | cau |
| Native to | North Caucasus |
| Region | Southwestern Dagestan[1] |
| Ethnicity | 3,788 Botlikh people (2020) |
Native speakers | 5,073 (2020 census)[2] c. 8,000 (2012)[3] |
Northeast Caucasian
| |
| Dialects |
|
| unwritten (transcribed using Cyrillic script) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bph |
| Glottolog | botl1242[4] |
 Botlikh | |
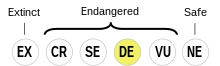 Botlikh is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |
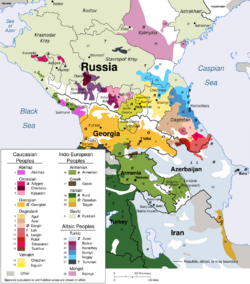
Botlikh (also spelled Botlix) is an Andic language of the Northeast Caucasian language family spoken by the Botlikhs in the villages of Botlikh (Buikhe), Miarso and Ashino, as well as in Chontaul, Ankho and in Batlakhatli,[5] in southwestern Dagestan, Russia by approximately 5,000 people, according to the 2020 census.[2]
Dialects
Botlikh has two dialects, being Botlikh proper and Miarso. Differences in phonology and morphology are small, and the two are mutually intelligible.[5]
Phonology
Vowels
Botlikh has five basic vowels. Vowels can also be long or nasalized.[6]
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u |
| Mid | e | o |
| Open | a |
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| central | lateral | |||||||||||||||
| lenis | fortis | lenis | fortis | lenis | fortis | lenis | fortis | lenis | fortis | lenis | fortis | |||||
| Plosive | voiced | b ⟨б⟩ | d ⟨д⟩ | ɡ ⟨г⟩ | ||||||||||||
| voiceless | p ⟨п⟩ | t ⟨т⟩ | k ⟨к⟩ | |||||||||||||
| ejective | tʼ ⟨тӀ⟩ | kʼ ⟨кӀ⟩ | q͡χʼː ⟨къ⟩ | ʔ ⟨ъ⟩ | ||||||||||||
| Affricate | voiceless | t͡s ⟨ц⟩ | t͡sː ⟨цц⟩ | t͡ʃ ⟨ч⟩ | t͡ʃː ⟨чч⟩ | t͡ɬː ⟨лӀ⟩ | k͡xː ⟨кк⟩ | q͡χː ⟨хъ⟩ | ||||||||
| ejective | t͡sʼ ⟨цӀ⟩ | t͡sʼː ⟨цӀцӀ⟩ | t͡ʃʼ ⟨чӀ⟩ | t͡ʃʼː ⟨чӀчӀ⟩ | t͡ɬʼː ⟨кь⟩ | k͡xʼː ⟨кӀкӀ⟩ | ||||||||||
| voiced | d͜ʒ ⟨дж⟩ | |||||||||||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | v ⟨в⟩ | s ⟨с⟩ | sː ⟨сс⟩ | ʃ ⟨ш⟩ | ʃː ⟨щ⟩ | ɬ ⟨лъ⟩ | ɬː ⟨лълъ⟩ | çː ⟨хь⟩ | ɣ ⟨гь⟩ | xː ⟨хх⟩ | χ ⟨х⟩ | ʜ ⟨хӀ⟩ | h ⟨гь⟩ | ||
| voiced | z ⟨з⟩ | ʒ ⟨ж⟩ | j ⟨й⟩ | x ⟨х⟩ | ʁ ⟨гъ⟩ | ʕ ⟨гӀ⟩ | ||||||||||
| Approximant | m ⟨м⟩ | n ⟨н⟩ | r ⟨р⟩ | l ⟨л⟩ | ||||||||||||
Orthography
Botlikh is unwritten, and Botlikhs have mostly used Avar as their medium of written communication. When Botlikhs need to write their language, they use the Avar alphabet.[5] The following orthography is used in a Botlikh–Russian dictionary.[7]
| А а | Аᴴ аᴴ | Б б | В в | Г г | Гъ гъ | Гь гь | ГӀ гӀ | Д д | Дж дж | (Е е) | Ж ж | З з | И и |
| Иᴴ иᴴ | Й й | К к | Кк кк | Къ къ | Кь кь | КӀ кӀ | КӀкӀ кӀкӀ | Л л | Лъ лъ | Лълъ лълъ | ЛӀ лӀ | М м | Н н |
| О о | П п | ПӀ пӀ | Р р | С с | Сс сс | Т т | ТӀ тӀ | У у | Уᴴ уᴴ | Х х | Хх хх | Хъ хъ | Хь хь |
| ХӀ хӀ | Ц ц | Цц цц | ЦӀ цӀ | ЦӀцӀ цӀцӀ | Ч ч | Чч чч | ЧӀ чӀ | ЧӀчӀ чӀчӀ | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Э э | Эᴴ эᴴ |
References
- ↑ Ethnologue language map of European Russia, with Botlikh shown in the inset with reference number 9
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 7. НАСЕЛЕНИЕ НАИБОЛЕЕ МНОГОЧИСЛЕННЫХ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОСТЕЙ ПО РОДНОМУ ЯЗЫКУ
- ↑ "Ботлихский язык" (in ru). 2022-05-21. https://bigenc.ru/c/botlikhskii-iazyk-d00034.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Botlikh". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/botl1242.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Ботлихский язык | Малые языки России". https://minlang.iling-ran.ru/lang/botlikhskiy-yazyk.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Грамматика ботлихского языка | Малые языки России". https://minlang.iling-ran.ru/grammar/grammatika-botlikhskogo-yazyka.
- ↑ Alekseev, Michail Egorovič; Azaev, Chalil Gadžimagomedovič (2019). Botlichsko-russkij slovarʹ: = Botlikh-Russian dictionary. Issledovanija i materialy po jazykam Kavkaza. Moskva: Academia. ISBN 978-5-87444-416-7. https://www.rfbr.ru/rffi/ru/books/o_2121002.
Further reading
- Alekseev, M.; Azaev, X. (2019). Botlixsko-russkij slovar'. Moscow: Academia.
- Dirr, Adolf (1928). Einführung in das Studium der Kaukasischen Sprachen mit einer sprachenkarte. Leipzig: Verlag der Asia Major. https://books.google.com/books?id=WiE5YAAACAAJ.
- Gamzatova, G. G. (2000). Jazyki Dagestana. Jazyki Narodov Rossii. Machackala: Rossijskaja Akademija Nauk.
- Gudava, Togo E. (1962). ბოთლიხური ენა: გრამატიკული ანალიზი, ტექსტები, ლექსიკონი. Tbilisi: Sak'art'velos SSR mec'nierebat'a akademiis gamomc'emloba.
- Gudava, Togo E. (1976). "Iberijsko-kavkazskie jazyki". Jazyki narodov SSSR. IV. Moskva: Nauka. pp. 293–306.
- Moroz, George; Naccarato, Chiara; Verhees, Samira (October 14-16, 2019). "Variation in two dictionaries of Botlikh". Документирование языков и диалектов коренных малочисленных народов России. St. Petersburg. https://iling.spb.ru/events/language_documentation2019/moroz_etal.pdf.
- Saidova, P. A.; Abusov, M. G. (2012). Botlixsko-russkij slovar'. Makhachkala: IJaLI.
External links
| Botlikh language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
 |