Social:Lezgic languages
From HandWiki
Short description: Northeast Caucasian language family
| Lezgic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Template:DAG |
| Linguistic classification | Northeast Caucasian
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Lezgic language |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | lezg1248[1] |
 Lezgic | |
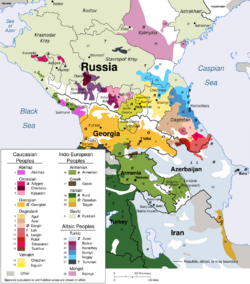
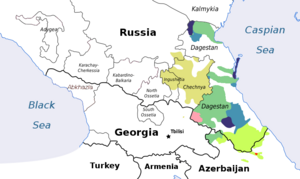
The Lezgic languages (also Lezgian or Lezghian) are one of seven branches of the Northeast Caucasian language family. Lezgin and Tabasaran are literary languages. Khinalug may either be Lezgic or an independent branch of the Northeast Caucasian family.
Classification
- Peripheral: Archi – 1,700 speakers[2]
- Samur[3] (Nuclear Lezgic)
- Eastern Samur[2]
- Southern Samur
- Kryts – 5,000 speakers
- Budukh – 200 speakers
- Jek – 1,500 speakers
- Western Samur
The voicing of ejective consonants
The Lezgic languages are relevant to the glottalic theory of Indo-European, because several have undergone the voicing of ejectives that have been postulated but widely derided as improbable in that family. The correspondences have not been well worked out (Rutul is inconsistent in the examples), but a few examples are:
- Non-Lezgic: Avar tstsʼar; Lezgic: Rutul dur, Tsakhur do 'name'
- Non-Lezgic: Archi motʃʼor, Lak tʃʼiri; Lezgic: Rutul mitʃʼri, Tabassaran midʒir, Aɡul mudʒur 'beard'
- Non-Lezgic: Avar motsʼ; Lezgic: Tabassaran vaz 'moon'
A similar change has taken place in non-initial position in the Nakh languages.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Lezgic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/lezg1248.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 7. НАСЕЛЕНИЕ НАИБОЛЕЕ МНОГОЧИСЛЕННЫХ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОСТЕЙ ПО РОДНОМУ ЯЗЫКУ
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Languages in the Caucasus, by Wolfgang Schulze (2009)
- ↑ Paul Fallon, 2002. The synchronic and diachronic phonology of ejectives, p 245.
External links
tr:Lezgice
 |