Chemistry:Monohalomethane
From HandWiki
Revision as of 08:30, 14 November 2021 by imported>AIposter (change)
| Structural formula | 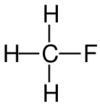
|
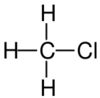
|
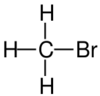
|
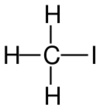
|
| Name | Fluoromethane | Chloromethane | Bromomethane | Iodomethane |
| Melting point | −137,8 °C[1] | −97,4 °C[2] | −93,7 °C[3] | −66 °C[4] |
| Boiling point | −78,4 °C[1] | −23,8 °C[2] | 4,0 °C[3] | 42 °C[4] |
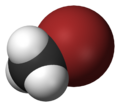
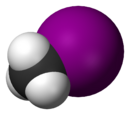
| Space-filling model | 
|

|
|
|
The monohalomethanes are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen. They belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes.
The four members are fluoromethane, chloromethane, bromomethane and iodomethane.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Record of Fluoromethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Record of Chloromethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Record of Bromomethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Record of Iodomethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
 |

