Chemistry:Carbon tetraiodide
| |||
 Carbon tetraiodide crystals (left)
Solution in Et2O (right) | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Tetraiodomethane[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1733108 | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CI4 | |||
| Molar mass | 519.629 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Dark violet crystals | ||
| Density | 4.32 g mL−1 | ||
| -136·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| Tetragonal | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
0.500 J K−1 g−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
384.0–400.4 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−794.4–−778.4 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | toxic | ||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P305+351+338 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Carbon tetrafluoride Carbon tetrachloride Carbon tetrabromide | ||
Other cations
|
Silicon tetraiodide Germanium tetraiodide Tin(IV) iodide | ||
Related alkanes
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Carbon tetraiodide is a tetrahalomethane with the molecular formula CI4. Being bright red, it is a relatively rare example of a highly colored methane derivative. It is only 2.3% by weight carbon, although other methane derivatives are known with still less carbon.
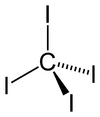
Structure
The tetrahedral molecule features C-I distances of 2.12 ± 0.02 Å.[2] The molecule is slightly crowded with short contacts between iodine atoms of 3.459 ± 0.03 Å, and possibly for this reason, it is thermally and photochemically unstable.
Carbon tetraiodide crystallizes in tetragonal crystal structure (a 6.409, c 9.558 (.10−1 nm)).[3]
It has zero dipole moment due to its symmetrically substituted tetrahedral geometry.
Properties, synthesis, uses
Carbon tetraiodide is slightly reactive towards water, giving iodoform and I2. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It decomposes thermally and photochemically to tetraiodoethylene, C2I4. Its synthesis entails AlCl3-catalyzed halide exchange, which is conducted at room temperature:[4]
The product crystallizes from the reaction solution.
Carbon tetraiodide is used as an iodination reagent, often upon reaction with bases.[5] Ketones are converted to 1,1-diiodoalkenes upon treatment with triphenylphosphine (PPh3) and carbon tetraiodide. Alcohols are converted in and to iodide, by a mechanism similar to the Appel reaction. In an Appel reaction, carbon tetrachloride is used to generate alkyl chlorides from alcohols.
Safety considerations
Manufacturers recommend that carbon tetraiodide be stored near 0 °C (32 °F). As a ready source of iodine, it is an irritant. Its LD50 on rats is 18 mg/kg. In general, perhalogenated organic compounds should be considered toxic, with the narrow exception of small perfluoroalkanes (essentially inert due to the strength of the C-F bond).
References
- ↑ "Tetraiodomethane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=10487. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ↑ Finbak, Chr.; Hassel, O. (1937). "Kristallstruktur und Molekülbau von CI4 und CBr4". Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie B36: 301–308. doi:10.1515/zpch-1937-3621.
- ↑ Pohl, S. (1982). "Die Kristallstruktur von CI4". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 159 (1–4): 211–216. doi:10.1524/zkri.1982.159.14.211.
- ↑ McArthur, R. E.; Simons, J. H. (1950). "Carbon Tetraiodide". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. III. pp. 37–39. doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch8. ISBN 9780470132340.
- ↑ P. R. Schreiner, A. A. Fokin (2005). "Carbon Tetraiodide". in L. Paquette. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Further reading
- Sorros H., Hinkam J. B. (1945). "The Redistribution Reaction. XI. Application to the Preparation of Carbon Tetraiodide and Related Halides". Journal of the American Chemical Society 67 (10): 1643. doi:10.1021/ja01226a004.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |