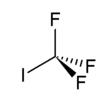
Chemistry:Trifluoroiodomethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Trifluoro(iodo)methane | |||
| Other names
Trifluoroiodomethane
Iodotrifluoromethane Monoiodotrifluoromethane Trifluoromethyl iodide Perfluoromethyl iodide Freon 13T1 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CF3I | |||
| Molar mass | 195.91 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless odorless gas | ||
| Density | 2.5485 g/cm3 at -78.5 °C 2.3608 g/cm3 at -32.5 °C | ||
| Melting point | −110 °C (−166 °F; 163 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −22.5 °C (−8.5 °F; 250.7 K) | ||
| Slightly | |||
| Vapor pressure | 541 kPa | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H341 | |||
| P201, P202, P281, P308+313, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Trifluoroiodomethane, also referred to as trifluoromethyl iodide is a halomethane with the formula CF3I. It is an experimental alternative to Halon 1301 (CBrF3) in unoccupied areas.[1] It would be used as a gaseous fire suppression flooding agent for in-flight aircraft and electronic equipment fires.
Chemistry
It is used in the rhodium-catalyzed α-trifluoromethylation of α,β-unsaturated ketones.[2]
It can be used as a new generation fire extinguishing agent to replace Halon in fire protection systems.[3] The mechanism of extinguishing fires for CF3I is active and primarily based on interruption of the chain reaction in the combustion area of the flame by so-called "negative" catalytic action.[4] It is also used as an eco-friendly insulation gas to replace SF6 in electrical power industry.[5]
In the presence of sunlight or at temperatures above 100 °C it can react with water, forming hazardous by-products such as hydrogen fluoride (HF), hydrogen iodide (HI) and carbonyl fluoride (COF2).[citation needed]
Environmental effects
Trifluoroiodomethane contains carbon, fluorine, and iodine atoms. Although iodine is several hundred times more efficient at destroying stratospheric ozone than chlorine, experiments have shown that because the weak C-I bond breaks easily under the influence of water (owing to the electron-attracting fluorine atoms), trifluoroiodomethane has an ozone depleting potential less than one-thousandth that of Halon 1301 (0.008-0.01). Its atmospheric lifetime, at less than 1 month, is less than 1 percent that of Halon 1301, and less even than hydrogen chloride formed from volcanoes.
There is, however, still the problem of the C-F bonds absorbing in the atmospheric window.[6] However, the IPCC has calculated the 100-year global warming potential of trifluoroiodomethane to be 0.4 (i.e., 40% of that of CO2).[7]
References
- ↑ Vitali, Juan. "Halon Substitute Protects Aircrews and the Ozone Layer" (in en-US). http://www.afrlhorizons.com/Briefs/0012/ML0008.html.
- ↑ "Trifluoroiodomethane 171441". http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/171441.
- ↑ "Fire extinguishing agents trifluoroiodomethane/CF3I". http://www.beijingyuji.com/english/product/fluorine/Fire-Extinguishing-Agents/.[unreliable source?]
- ↑ "CFI rim seal fire protection for floating roof tanks". 2018-09-20. https://www.saval.nl/uploads/2017/08/CFI-rim-seal-fire-protection.pdf.
- ↑ Katagiri, H.; Kasuya, H.; Mizoguchi, H.; Yanabu, S. (October 2008). "Investigation of the Performance of CF3I Gas as a Possible Substitute for SF6". IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation 15 (5): 1424–1429. doi:10.1109/TDEI.2008.4656252.
- ↑ Shimanouchi, T. (July 1977). "Tables of molecular vibrational frequencies. Consolidated volume II". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data 6 (3): 993–1102. doi:10.1063/1.555560. Bibcode: 1977JPCRD...6..993S.
- ↑ Ramfjord, Birgit (2012-03-05). "Listing of GWP Values as per Report IPCC WG1 AR4". Swedish Defence Materiel Administration. http://www.fmv.se/Global/Dokument/Engelska%20webben/Our%20activities/Enviromental%20work/Environmental%20criteria%20documents/121023/12FMV1533%202%201%20GWP%20eng.pdf.
Further reading
- National Research Council (US) Subcommittee on Iodotrifluoromethane (2004). Iodotrifluoromethane. doi:10.17226/11090. ISBN 978-0-309-09307-1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207825/.
- Solomon, Susan; Burkholder, James B.; Ravishankara, A. R.; Garcia, Rolando R. (1994). "Ozone depletion and global warming potentials of CF3I". Journal of Geophysical Research 99 (D10): 20929. doi:10.1029/94JD01833.
- Duan, Y. Y.; Shi, L.; Sun, L. Q.; Zhu, M. S.; Han, L. Z. (1 March 2000). "Thermodynamic Properties of Trifluoroiodomethane (CF3I)". International Journal of Thermophysics 21 (2): 393–404. doi:10.1023/A:1006683529436.
- Duan, Yuan-Yuan; Shi, Lin; Zhu, Ming-Shan; Han, Li-Zhong (January 1999). "Surface tension of trifluoroiodomethane (CF3I)". Fluid Phase Equilibria 154 (1): 71–77. doi:10.1016/S0378-3812(98)00439-7.
- Duan, Y. Y.; Sun, L. Q.; Shi, L.; Zhu, M. S.; Han, L. Z. (1 September 1997). "Thermal Conductivity of Gaseous Trifluoroiodomethane (CF3I)". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 42 (5): 890–893. doi:10.1021/je9700378.
- Duan, Yuan-Yuan; Shi, Lin; Zhu, Ming-Shan; Han, Li-Zhong (1 May 1999). "Critical Parameters and Saturated Density of Trifluoroiodomethane (CF3I)". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 44 (3): 501–504. doi:10.1021/je980251b.
- Markgraf, Stewart J.; Wells, J. R.; Wiseman, Floyd L. (30 April 1996). Chamber Studies of Photolysis and Hydroxyl Radical Reactions of Trifluoroiodomethane. Template:DTIC.
External links
- National Research Council (US) Subcommittee on Iodotrifluoromethane (2004). "Physical and Chemical Properties And Efficacy". Iodotrifluoromethane. pp. 15–17. doi:10.17226/11090. ISBN 978-0-309-09307-1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207826/.
- Data sheet (in Japanese)
- Material Safety Data Sheet CF3I (in English)
- CF3I can be used as fire extinguishing agent
 |