Biology:Mixotricha paradoxa
| Mixotricha paradoxa | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota
|
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | Metamonada
|
| Class: | Parabasalia
|
| Order: | Trichomonadida
|
| Family: | Devescovinidae
|
| Genus: | Mixotricha
|
| Species: | M. paradoxa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mixotricha paradoxa Sutherland, 1933
| |
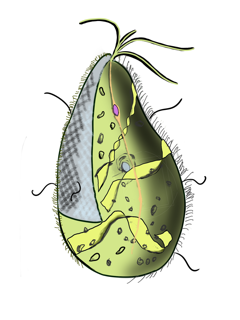
Mixotricha paradoxa is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species Mastotermes darwiniensis.
It is composed of five different organisms: three bacterial ectosymbionts live on its surface for locomotion and at least one endosymbiont lives inside to help digest cellulose in wood to produce acetate for its host(s).
Mixotricha mitochondria degenerated in hydrogenosomes and mitosomes and lost the ability to produce energy aerobically by oxidative phosphorylation.[1][2] The mitochondria-derived nuclear genes were however conserved.[2]
Discovery
The name was given by the Australian biologist J.L. Sutherland, who first described Mixotricha in 1933.[3][4] The name means "the paradoxical being with mixed-up hairs" because this protist has both cilia and flagella, which was not supposed to be the case with protists where they were supposed to have one or the other but not both.[5][2]
Behavior
Mixotricha is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species Mastotermes darwiniensis and has multiple bacterial symbionts.[6][7]
Mixotricha is a large protozoan .5 millimetres (0.020 in) long and contains hundreds of thousands of bacteria.[5] It is an endosymbiont and digests cellulose for the termite.[5]
Trichomonads like Mixotricha reproduce by a special form of longitudinal fission, leading to large numbers of trophozoites in a relatively short time. Cysts never form, so transmission from one host to another is always based on direct contact between the sites they occupy.[8]
Anatomy
Species of the order Trichomonadida typically have four to six flagella at the cell's apical pole, one of which is recurrent - that is, it runs along a surface wave, giving the aspect of an undulating membrane. Mixotricha paradoxa have four weak flagella that serve as rudders.[9] It has four large flagella at the front end, three pointing forwards and one backward.[5]
The basal bodies are also bacteria, not spirochaetes but oval, pill-shaped bacteria. There is a one-to-one relationship between a bracket, a spirochaete, and a basal bacterium. Each bracket has one spirochaete running through it and one pill bacterium at its base as the basal body.[5] It has not been shown definitely, but the basal bodies could also be making cellulases that digest wood.[5]
Endosymbionts for biochemical processes
At least one endosymbiont lives inside the protist to help digest cellulose and lignin, a major component of the wood the termites eat. The cellulose gets converted to glucose then to acetate, and the lignin is digested directly to acetate.[2] The acetate probably crosses the termite gut membrane to be digested later.[2]
Mixotricha forms a mutualistic relationship with bacteria living inside the termite. There are a total of four species of bacterial symbionts. It has spherical bacteria inside the cell, which function as mitochondria, which Mixotricha lacks. Mixotricha mitochondria degenerated and lost the ability to produce energy aerobically by oxidative phosphorylation.[1][2] Mitochondrial relics include hydrogenosomes which produce hydrogen and small structures called mitosomes.[2]
Ectosymbionts for movement
Three surface colonising bacteria are anchored on the surface.[10]
The flagella and cilia are actually two different single celled organisms. The ciliate belongs to an archaic group that used to be called archezoa but this term is no longer in fashion.[11] It has four weak flagella, which serve as a rudder.[12][11]
While Mixotricha has four anterior flagella, it does not use them for locomotion, but more for steering.[5] For locomotion, about 250,000 hairlike Treponema spirochaetes, a species of helical bacteria, are attached to the cell surface and provide the cell with cilia-like movements.[2]
The wavelength of the cilia is about .1 millimetres (0.0039 in) and suggests that the spirochaetes are somehow in touch with each other.[5]
Mixotricha also has rod-shaped bacteria arranged in an ordered pattern on the surface of the cell.[13]
Each spirochaete has its own little emplacement, called a 'bracket'.[14] Spirochetes move continuously forwards or backwards but when they are attached they move in one direction.[2]
Sperm tails might have their origin in spirochaetes.[2] The evidence that cilia (undulipodia) are symbiotic bacteria is found unpersuasive.[5]
Genome
Mixotricha have five genomes, as they form very close symbiotic relationships with four types of bacteria.[15] It is a good example organism for symbiogenesis and nestedness.[2]
There are two spirochete and one-rod bacteria on its surface, one endosymbiotic bacteria inside to digest cellulose and the host nucleus.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cepicka, Ivan; Dolan, Michael F.; Gile, Gillian (2017-09-01). "Parabasalia". Handbook of the Protists: Second Edition: 1175–1218. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-28149-0_9. ISBN 978-3-319-28147-6. https://asu.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/parabasalia.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Thompson, William Irwin (1991). Gaia 2: Emergence : The New Science of Becoming. pp. 51–58. ISBN 9780940262409.
- ↑ Jean L. Sutherland: Protozoa from Australian Termites. Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science, Band s2-76, S. 145-173. (Abstract)
- ↑ L. R. Cleveland, A. V. Grimstone: The Fine Structure of the Flagellate Mixotricha paradoxa and Its Associated Micro-Organisms. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, Band 159, 1964, S. 668-686. doi:10.1098/rspb.1964.0025
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 Dawkins, Richard; Wong, Yan (2016). The Ancestor's Tale. ISBN 978-0544859937.
- ↑ Radek R, Nitsch G (November 2007). "Ectobiotic spirochetes of flagellates from the termite Mastotermes darwiniensis: attachment and cyst formation". Eur. J. Protistol. 43 (4): 281–94. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2007.06.004. PMID 17764914.
- ↑ Brugerolle G (October 2004). "Devescovinid features, a remarkable surface cytoskeleton, and epibiotic bacteria revisited in Mixotricha paradoxa, a parabasalid flagellate". Protoplasma 224 (1–2): 49–59. doi:10.1007/s00709-004-0052-8. PMID 15726809.
- ↑ Kamaruddin, Mudyawati; Tokoro, Masaharu; Rahman, Md. Moshiur; Arayama, Shunsuke; Hidayati, Anggi P.N.; Syafruddin, Din; Asih, Puji B.S.; Yoshikawa, Hisao et al. (2014). "Molecular Characterization of Various Trichomonad Species Isolated from Humans and Related Mammals in Indonesia". The Korean Journal of Parasitology 52 (5): 471–478. doi:10.3347/kjp.2014.52.5.471. PMID 25352694.
- ↑ Overmann, Jörg (10 January 2006). Molecular Basis of Symbiosis. pp. 76–95. ISBN 9783540282105. https://archive.org/details/molecularbasissy00over_347.
- ↑ "Movement symbiosis2". http://www.pmbio.icbm.de/mikrobiologischer-garten/eng/enmix04.htm.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 König, Helmut (2006). Intestinal Microorganisms of Termites and Other Invertebrates. pp. 261–263. ISBN 9783540281801. https://archive.org/details/intestinalmicroo00knig.
- ↑ "Movement symbiosis". http://www.pmbio.icbm.de/mikrobiologischer-garten/eng/enmix03.htm.
- ↑ Rosenberg, Eugene; Gophna, Uri (30 August 2011). Beneficial Microorganisms in Multicellular Life Forms. p. 9. ISBN 9783642216800. https://archive.org/details/beneficialmicroo00rose.
- ↑ Hongoh, Y.; Sato, T.; Dolan, M. F.; Noda, S.; Ui, S.; Kudo, T.; Ohkuma, M. (2007). "The Motility Symbiont of the Termite Gut Flagellate Caduceia versatilis Is a Member of the "Synergistes" Group". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73 (19): 6270–6276. doi:10.1128/AEM.00750-07. PMID 17675420. Bibcode: 2007ApEnM..73.6270H.
- ↑ Margulis, Lynn; Sagan, Dorion (June 2001). "The Beast with Five Genomes". Natural History. http://www.naturalhistorymag.com/0601/0601_feature.html. Retrieved 3 May 2007.
Wikidata ☰ Q311708 entry
 |

