Astronomy:111 Tauri
| Observation data {{#ifeq:J2000|J2000.0 (ICRS)|Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS)| Epoch J2000 [[Astronomy:Equinox (celestial coordinates)|Equinox J2000}} | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| A | |
| Right ascension | 05h 24m 25.46328s[1] |
| Declination | +17° 23′ 00.7264″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.0[2] |
| B | |
| Right ascension | 05h 23m 38.37950s[3] |
| Declination | +17° 19′ 26.8209″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.9[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| A | |
| Evolutionary stage | main sequence[1] |
| Spectral type | F8 V[5] |
| U−B color index | −0.05[6] |
| B−V color index | 0.544[7] |
| Variable type | BY Dra[6] |
| B | |
| Evolutionary stage | main sequence[3] |
| Spectral type | K5 V[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| A | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +37.8[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +250.585[1] mas/yr Dec.: −7.156[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 68.5908 ± 0.1040[1] mas |
| Distance | 47.55 ± 0.07 ly (14.58 ± 0.02 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 3.49±0.06[2] |
| B | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 38.03±0.12[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +250.984[3] mas/yr Dec.: −5.707[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 68.7662 ± 0.0246[3] mas |
| Distance | 47.43 ± 0.02 ly (14.542 ± 0.005 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +7.2[9] |
| Details | |
| 111 Tau A | |
| Mass | 1.08[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.67±0.06[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.845[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.24[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,015[11] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.14[11] dex |
| Rotation | 3.503±0.006 d[12] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 16.0[13] km/s |
| Age | 20–50[14] Myr |
| 111 Tau B | |
| Mass | 0.72[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.70[15] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.20[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.43[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,757[9] K |
| Rotation | 9.6 days[16] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 4.3[17] km/s |
| Age | 445[17] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| 111 Tau A: Gl 202, HR 1780, BD+17°920, HD 35296, SAO 94526, HIP 25278, V1119 Tau | |
| 111 Tau B: Gl 201, BD+17°917, HD 35171, SAO 94513, HIP 25220 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | A |
| B | |
111 Tauri is a wide binary star[5] system in the constellation Taurus. It is located at a distance of 48 light years from the Sun. Primary component A is a main sequence star with a stellar classification of F8V. The secondary component B (Gliese 201) is a K-type main sequence star.[5] The primary is larger and more luminous than the Sun, with about 130% of the Sun's radius and 185% of the Sun's luminosity. The apparent magnitude of 5.0 indicates it is a faint star that can be viewed by the naked eye under good, dark-sky conditions.
The metallicity of the primary star, which measures the proportion of elements other than hydrogen and helium, is similar to the Sun. Estimates of [Fe/H], which is the logarithm of the ratio of iron to hydrogen as compared to the Sun, range from a low of −0.14 to a high of 0.05.[11][19] This star shows an unusually high content of lithium, which remains unexplained.[19] Age estimates for this star range from 3.6 to 3.76 billion years.[8][20] however the most recent age determination indicates a very young star with an age of 20 to 50 million years.[14] It is a prominent X-ray source.[19]
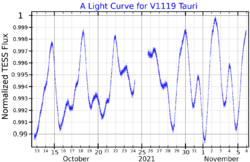
This star is rotating relatively rapidly, completing a rotation along the equator every 3.5 days[12] as compared to 25 days for the Sun. It is also undergoing differential rotation in which the rotation velocity varies by latitude.[21] In 1996, Kazimierz Stępień and Edward H. Geyer announced that 111 Tauri is a variable star.[22] It is a BY Draconis variable, and was given the variable star designation V1119 Tauri, in 1997.[23][24]
This star was examined for an excess of infrared emission that could indicate it has a circumstellar debris disk of dust, but no significant excess was observed.[20] The space velocity components of this star are [U, V, W] = [−36.94, −14.63, 7.63] km/s.[25] It is a member of the Hyades stellar kinematic group of co-moving stars.[19]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Fuhrmann, Klaus (February 2008). "Nearby stars of the Galactic disc and halo - IV". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 384 (1): 173–224. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12671.x. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.384..173F.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Koen, C.; Kilkenny, D.; Van Wyk, F.; Marang, F. (2010). "UBV(RI)C JHK observations of Hipparcos-selected nearby stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 403 (4): 1949. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16182.x. Bibcode: 2010MNRAS.403.1949K.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "V* V1119 Tau -- Variable of BY Dra". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=111+Tauri. Retrieved 2011-07-03.
- ↑ van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Holmberg, J.; Nordstrom, B.; Andersen, J. (July 2009). "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the solar neighbourhood. III. Improved distances, ages, and kinematics". Astronomy and Astrophysics 501 (3): 941–947. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811191. Bibcode: 2009A&A...501..941H.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Takeda, Yoichi; Honda, Satoshi (2020). "Spectroscopic Determination of Stellar Parameters and Oxygen Abundances for Hyades/Field G-K Dwarfs". The Astronomical Journal 159 (4): 174. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab799f. Bibcode: 2020AJ....159..174T.
- ↑ Takeda, Yoichi (April 2007). "Fundamental Parameters and Elemental Abundances of 160 F-G-K Stars Based on OAO Spectrum Database". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 59 (2): 335–356. doi:10.1093/pasj/59.2.335. Bibcode: 2007PASJ...59..335T.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Chen, Y. Q.; Nissen, P. E.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H. W.; Benoni, T. (February 2000). "Chemical composition of 90 F and G disk dwarfs". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 141 (3): 491–506. doi:10.1051/aas:2000124. Bibcode: 2000A&AS..141..491C.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Hempelmann, A. et al. (2016). "Measuring rotation periods of solar-like stars using TIGRE. A study of periodic CaII H+K S-index variability". Astronomy and Astrophysics 586: A14. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201526972. Bibcode: 2016A&A...586A..14H. https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2016/02/aa26972-15/aa26972-15.html.
- ↑ Schröder, C.; Reiners, Ansgar; Schmitt, Jürgen H. M. M. (January 2009). "Ca II HK emission in rapidly rotating stars. Evidence for an onset of the solar-type dynamo". Astronomy and Astrophysics 493 (3): 1099–1107. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810377. Bibcode: 2009A&A...493.1099S.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Waite, I. A. et al. (2015). "Magnetic fields on young, moderately rotating Sun-like stars – I. HD 35296 and HD 29615". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 449 (1): 8–24. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv006. Bibcode: 2015MNRAS.449....8W.
- ↑ Hardegree-Ullman, Kevin K.; Apai, Dániel; Bergsten, Galen J.; Pascucci, Ilaria; López-Morales, Mercedes (2023). "Bioverse: A Comprehensive Assessment of the Capabilities of Extremely Large Telescopes to Probe Earth-like O2 Levels in Nearby Transiting Habitable-zone Exoplanets". The Astronomical Journal 165 (6): 267. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/acd1ec. Bibcode: 2023AJ....165..267H.
- ↑ Fuhrmeister, B.; Czesla, S.; Robrade, J.; González-Pérez, J. N.; Schneider, C.; Mittag, M.; Schmitt, J. H. M. M. (2022). "The corona - chromosphere connection studied with simultaneous eROSITA and TIGRE observations". Astronomy and Astrophysics 661: A24. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141020. Bibcode: 2022A&A...661A..24F.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Grandjean, A.; Lagrange, A. -M.; Meunier, N.; Rubini, P.; Desidera, S.; Galland, F.; Borgniet, S.; Zicher, N. et al. (2021). "A SOPHIE RV search for giant planets around young nearby stars (YNS). A combination with the HARPS YNS survey". Astronomy and Astrophysics 650. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039672. Bibcode: 2021A&A...650A..39G.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 Makarov, V. V.; Zacharias, N.; Hennessy, G. S. (November 2008). "Common Proper Motion Companions to Nearby Stars: Ages and Evolution". The Astrophysical Journal 687 (1): 566–578. doi:10.1086/591638. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...687..566M.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Trilling, D. E. (February 2008). "Debris Disks around Sun-like Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 674 (2): 1086–1105. doi:10.1086/525514. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...674.1086T.
- ↑ Reiners, Ansgar (January 2006). "Rotation- and temperature-dependence of stellar latitudinal differential rotation". Astronomy and Astrophysics 446 (1): 267–277. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053911. Bibcode: 2006A&A...446..267R.
- ↑ Stepien, K.; Geyer, E. (May 1996). "Rotation of solar-like main sequence stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 117: 83–91. doi:10.1051/aas:1996141. Bibcode: 1996A&AS..117...83S. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1996A%26AS..117...83S. Retrieved 1 September 2025.
- ↑ Kazarovets, E. V.; Samus, N. N. (April 1997). "The 73rd Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4471: 1–45. Bibcode: 1997IBVS.4471....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/4401/4471.pdf. Retrieved 1 September 2025.
- ↑ "V1119 Tau". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=36136.
- ↑ Montes, D. et al. (November 2001). "Late-type members of young stellar kinematic groups - I. Single stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 328 (1): 45–63. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04781.x. Bibcode: 2001MNRAS.328...45M.
 |