Astronomy:HL Tau 76
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox (celestial coordinates) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 18m 56.638s[2] |
| Declination | +27° 17′ 48.31″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 14.1–15.28[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | DA4.3[4] |
| B−V color index | 0.2[5] |
| Variable type | DAV (ZZ Ceti)[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 62.600[2] mas/yr Dec.: −72.819[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 20.7244 ± 0.0338[2] mas |
| Distance | 157.4 ± 0.3 ly (48.25 ± 0.08 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 11.69[4] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.575±0.005[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.0162[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.00389[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 7.8[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 11,375±30[6] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
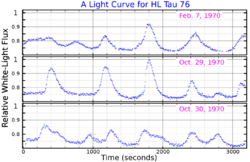
HL Tau 76 is a variable white dwarf star of the DAV (or ZZ Ceti) type. It was observed by G. Haro and W. J. Luyten in 1961,[8][9] and was the first variable white dwarf discovered when, in 1968, Arlo U. Landolt found that it varied in brightness with a period of approximately 749.5 seconds, or 12.5 minutes.[9] Like other DAV white dwarfs, its variability arises from non-radial gravity wave pulsations within itself.[10], § 7. Later observation and analysis has found HL Tau 76 to pulsate in over 40 independent vibrational modes, with periods between 380 seconds and 1390 seconds.[11]
The designation HL Tau 76 derives from the discovery of this star as a white dwarf, when it was described as Taurus no.76 in a publication authored by Guillermo Haro and Willem Jacob Luyten.[8] The exact designation HL Tau 76 was then used in subsequent papers, including one giving the star its designation EGGR 265 where it was noted to be variable.[12] It was then included in the 57th name-list of variable stars and given the variable star designation V441 Tauri.[13] The unusual designation HL Tau 76 continues to be used by most authors.[14]
Notes and references
- ↑ Warner, Brian; Nather, R. Edward (January 1972). "Observations of rapid blue variables-III. HL Tau-76". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 156: 1–5. doi:10.1093/mnras/156.1.1. Bibcode: 1972MNRAS.156....1W.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Combined General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS), v. 4.2. CDS ID II/250.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gianninas, A.; Bergeron, P.; Ruiz, M. T. (2011). "A Spectroscopic Survey and Analysis of Bright, Hydrogen-rich White Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal 743 (2): 138. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/743/2/138. Bibcode: 2011ApJ...743..138G.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "HL Tau 76". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=HL+Tau+76.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Pech, D.; Vauclair, G.; Dolez, N. (2006). "Asteroseismological constraints on the structure of the ZZ Ceti star HL Tau 76". Astronomy and Astrophysics 446 (1): 223. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053150. Bibcode: 2006A&A...446..223P.
- ↑ Gentile Fusillo, N. P.; Tremblay, P. -E.; Cukanovaite, E.; Vorontseva, A.; Lallement, R.; Hollands, M.; Gänsicke, B. T.; Burdge, K. B. et al. (2021). "A catalogue of white dwarfs in Gaia EDR3". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 508 (3): 3877. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab2672. Bibcode: 2021MNRAS.508.3877G.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Haro, G.; Luyten, W. J. (1961). "Nueva estrella enana blanca en las nubes obscuras del Toro". Boletín de los Observatorios de Tonantzintla y Tacubaya 3: 35. Bibcode: 1961BOTT....3...35H.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Landolt, Arlo U. (1968). "A New Short-Period Blue Variable". The Astrophysical Journal 153: 151. doi:10.1086/149645. Bibcode: 1968ApJ...153..151L.
- ↑ Koester, D.; Chanmugam, G. (1990). "Physics of white dwarf stars". Reports on Progress in Physics 53 (7): 837. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/53/7/001. Bibcode: 1990RPPh...53..837K.
- ↑ Dolez, N. et al. (2006). "Whole Earth telescope observations of the ZZ Ceti star HL Tau 76". Astronomy and Astrophysics 446 (1): 237. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053149. Bibcode: 2006A&A...446..237D. https://ruj.uj.edu.pl/xmlui/bitstream/handle/item/173277/zola_krzesinski_et-al_whole_earth_telescope_observations_of_the_zz_ceti_star_hl_tau_76_2006.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y.
- ↑ Greenstein, Jesse L. (October 1969). "The Lowell Suspect White Dwarfs". Astrophysical Journal 158: 281. doi:10.1086/150191. Bibcode: 1969ApJ...158..281G.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V. et al. (October 1970). "57th Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 480 (1): 1. Bibcode: 1970IBVS..480....1K.
- ↑ Chen, Y. H.; Shu, H. (January 2021). "Asteroseismology of the DAV star R808". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 500 (4): 4703–4709. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3572. Bibcode: 2021MNRAS.500.4703C.
 |