Astronomy:2013 ET
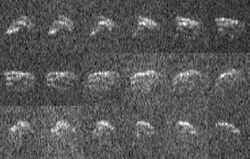 Radar imaging of 2013 ET | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Catalina Sky Survey |
| Discovery site | Mount Lemmon Obs. (first observed only) |
| Discovery date | March 3, 2013 |
| Designations | |
| 2013 ET | |
| 2001 SY169 | |
| Minor planet category | NEO · Apollo |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 2020-May-31 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 11 years |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 1.6688 astronomical unit|AU (249.65 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.74228 AU (111.044 Gm) |
| 1.2055 AU (180.34 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.38428 |
| Orbital period | 1.32 yr (483.49 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 121.70° |
| Mean motion | 0° 44m 39.048s /day[1] |
| Inclination | 4.8515° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 171.30° |
| 81.937° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0041 AU (610,000 km)[2] |
| Mercury MOID | 0.287 AU (42,900,000 km)[1] |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 100 m (330 ft)[3] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 22.7[2] |
2013 ET is a near-Earth asteroid that was first observed on March 3, 2013,[4] six days before its closest approach to Earth. It is estimated to be around 100 meters (330 feet) wide.[3][5] The orbit of 2001 SY169 has been connected to 2013 ET extending the observation arc to 11 years.
Its closest approach to Earth was 0.0065207 astronomical unit|AU (975,480 km; 606,140 mi) on March 9, 2013 at 12:09 UT.[2][6] The asteroid also makes close approaches to Mars and Venus.[2] The asteroid was imaged by Goldstone radar on March 10, 2013.[7]
2013 ET was one of four asteroids that passed in the vicinity of Earth during one week in early March 2013.[8] The other asteroids in this group besides 2013 ET, included 2013 EC, 2013 EC20, and 2013 EN20.[8]
See also
- List of asteroid close approaches to Earth in 2013
- 2013 EC
- 2013 PJ10
- List of asteroid close approaches to Earth
- List of Near-Earth asteroids by distance from Sun
- Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "2013 ET". Minor Planet Center. http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?utf8=✓&object_id=2013+ET. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "(2013 ET)". JPL Small-Body Database. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=3629117.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wall, Mike (March 5, 2013). "Big Asteroid to Zoom By Earth This Weekend". Space.com. http://www.space.com/20085-asteroid-buzzes-earth-this-weekend.html.
- ↑ "MPEC 2013-E14 : 2013 ET". IAU Minor Planet Center. 2012-03-04. http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K13/K13E14.html. Retrieved 2012-03-09. (K13E00T)
- ↑ Dr. Lance A. M. Benner (2013-03-07). "2013 ET Goldstone Radar Observations Planning". NASA/JPL Asteroid Radar Research. http://echo.jpl.nasa.gov/asteroids/2013ET/2013ET_planning.html. Retrieved 2013-03-09.
- ↑ Gray, Melissa (March 7, 2013). "Asteroid to fly past Earth this weekend". Light Years. CNN. http://lightyears.blogs.cnn.com/2013/03/07/asteroid-to-fly-past-earth-this-weekend/?hpt=hp_t3.
- ↑ DC Agle (2013-03-18). "Goldstone Radar Snags Images of Asteroid 2013 ET". NASA/JPL. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2013-101. Retrieved 2013-03-19.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Four Asteroids Buzz Earth in Single Week". Space.com. https://www.space.com/20149-asteroids-buzz-earth-week.html.
External links
- 2013 ET at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |



