Astronomy:KELT-6b
From HandWiki
Short description: Exoplanet orbiting KELT-6
Coordinates: ![]() 13h 03m 55.65s, +30° 38′ 24.28″
13h 03m 55.65s, +30° 38′ 24.28″
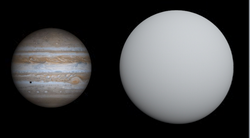 KELT-6b (white) compared to Jupiter | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Collins et al. |
| Discovery site | KELTNorth |
| Discovery date | 2014 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.0804±0.0014 astronomical unit|AU[2] | |
| Eccentricity | 0.22±0.11[3] |
| Orbital period | 7.8457±0.0002 d[3] |
| Inclination | 88.81°±0.85°[3] |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2,456,269.2+1.7 −2.5 JD[1] |
| 308°+30° −272°[4] | |
| Semi-amplitude | 42.8±4.3 km/s[3] |
| Star | KELT-6 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 1.30±0.09 RJ[3] |
| Mass | 0.442±0.019 Jupiter mass[4] |
| Mean density | 0.333+0.120 −0.079 g/cm3[2](0.012+0.004 −0.002 lb/cu in) |
| Physics | 1313+59 −38 K[1] |
KELT-6b is an exoplanet orbiting the F-type subgiant KELT-6 approximately 791 light years away in the northern constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered in 2013 using the transit method, and was announced in 2014.
Discovery
In 2014, the planet's parameters were observed. The paper states that KELT-6 has just entered the subgiant phase, and is no longer on the main sequence. In 2015, an additional planet, c, was discovered using the radial velocity method.[4]
Properties
KELT-6b is a hot Saturn with 44.2% Jupiter's mass, but has been bloated to 1.3 times Jupiter's radius. It's density is half of Saturn's, and it has an equilibrium temperature of 1,313 K, but a hotter dayside temperature of 1,531 K.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Collins, Karen A.; Eastman, Jason D.; Beatty, Thomas G.; Siverd, Robert J.; Gaudi, B. Scott; Pepper, Joshua; Kielkopf, John F.; Johnson, John Asher et al. (1 February 2014). "KELT-6b: A P ~ 7.9 Day Hot Saturn Transiting a Metal-poor Star with a Long-period Companion". The Astronomical Journal 147 (2): 39. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/147/2/39. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2014AJ....147...39C. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014AJ....147...39C/abstract.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bonomo, A. S.; Desidera, S.; Benatti, S.; Borsa, F.; Crespi, S.; Damasso, M.; Lanza, A. F.; Sozzetti, A. et al. (June 2017). "The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG . XIV. Investigating giant planet migration history via improved eccentricity and mass determination for 231 transiting planets" (in en). Astronomy and Astrophysics 602: A107. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629882. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2017A&A...602A.107B. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017A&A...602A.107B.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Stassun, Keivan G.; Collins, Karen A.; Gaudi, B. Scott (March 2017). "Accurate Empirical Radii and Masses of Planets and Their Host Stars with Gaia Parallaxes" (in en). The Astronomical Journal 153 (3): 136. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa5df3. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2017AJ....153..136S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Damasso, M.; Esposito, M.; Nascimbeni, V.; Desidera, S.; Bonomo, A. S.; Bieryla, A.; Malavolta, L.; Biazzo, K. et al. (1 September 2015). "The GAPS programme with HARPS-N at TNG. IX. The multi-planet system KELT-6: Detection of the planet KELT-6 c and measurement of the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect for KELT-6 b". Astronomy and Astrophysics 581: L6. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201526995. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2015A&A...581L...6D. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2015A%26A...581L...6D/abstract.
- ↑ "KELT-6 b". http://www.exoplanetkyoto.org/exohtml/KELT-6_b.html.
 |