Astronomy:Kepler-296f
From HandWiki
Short description: Goldilocks super-Earth orbiting Kepler-296
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovery site | Kepler Space Observatory |
| Discovery date | 2014 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.26300 AU (39,344,000 km) | |
| Orbital period | 63.33587900 d |
| Inclination | 89.950 |
| Star | Kepler-296 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 1.790 R⊕ |
| Physics | 194 K (−79 °C; −110 °F) |
Kepler-296f[1][2][3] (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation KOI-1422.04) is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of Kepler-296. The planet was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. NASA announced the discovery of the exoplanet on 26 February 2014.[1]
Confirmed exoplanet
Kepler 296f is a super-Earth with a radius 1.79 times that of Earth. The planet orbits Kepler-296 once every 63.3 days.
Habitability
The planet is located within the habitable zone of Kepler-296, a region where liquid water could exist on the surface of the planet.
| Notable Exoplanets – Kepler Space Telescope |
|---|
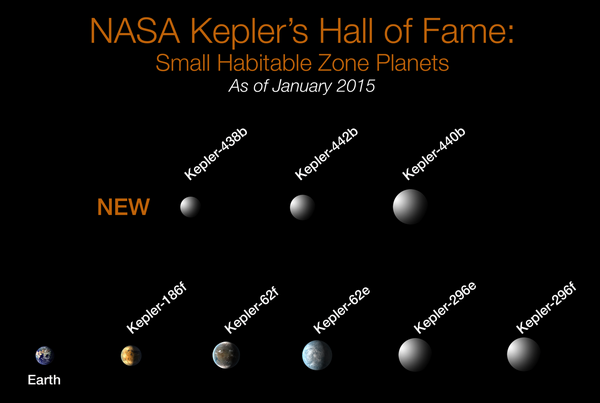
Confirmed small exoplanets in habitable zones.
(Kepler-62e, Kepler-62f, Kepler-186f, Kepler-296e, Kepler-296f, Kepler-438b, Kepler-440b, Kepler-442b) (Kepler Space Telescope; 6 January 2015).[4] |
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Staff (26 February 2014). "715 Newly Verified Planets More Than Triples the Number of Confirmed Kepler Planets". NASA. http://kepler.nasa.gov/news/nasakeplernews/index.cfm?FuseAction=ShowNews&NewsID=324.
- ↑ Lissauer, Jack J. (25 February 2014). "Validation of Kepler's Multiple Planet Candidates. II: Refined Statistical Framework and Descriptions of Systems of Special Interest". The Astrophysical Journal 784 (1): 44. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/784/1/44. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...784...44L. https://archive.org/details/arxiv-1402.6352.
- ↑ Rowe, Jason F. (2014). "Validation of Kepler's Multiple Planet Candidates. III: Light Curve Analysis & Announcement of Hundreds of New Multi-planet Systems". The Astrophysical Journal 784 (1): 45. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/784/1/45. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...784...45R.
- ↑ Clavin, Whitney; Chou, Felicia; Johnson, Michele (6 January 2015). "NASA's Kepler Marks 1,000th Exoplanet Discovery, Uncovers More Small Worlds in Habitable Zones". NASA. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2015-003.
External links
- NASA – Kepler Mission.
- NASA – Kepler Discoveries – Summary Table.
- NASA – Kepler-296f at The NASA Exoplanet Archive.
- NASA – Kepler-296f at The Exoplanet Data Explorer.
- NASA – Kepler-296f at The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia.
- Habitable Exolanets Catalog at UPR-Arecibo.
Coordinates: ![]() 19h 06m 9.60s, +49° 26′ 14.37″
19h 06m 9.60s, +49° 26′ 14.37″
 |